-
 Australia four wickets from Ashes glory as England cling on
Australia four wickets from Ashes glory as England cling on
-
Beetles block mining of Europe's biggest rare earths deposit

-
 French culture boss accused of mass drinks spiking to humiliate women
French culture boss accused of mass drinks spiking to humiliate women
-
NBA champions Thunder suffer rare loss to Timberwolves

-
 Burning effigy, bamboo crafts at once-a-decade Hong Kong festival
Burning effigy, bamboo crafts at once-a-decade Hong Kong festival
-
Joshua knocks out Paul to win Netflix boxing bout

-
 Dogged Hodge ton sees West Indies save follow-on against New Zealand
Dogged Hodge ton sees West Indies save follow-on against New Zealand
-
England dig in as they chase a record 435 to keep Ashes alive

-
 Wembanyama 26-point bench cameo takes Spurs to Hawks win
Wembanyama 26-point bench cameo takes Spurs to Hawks win
-
Hodge edges towards century as West Indies 310-4, trail by 265

-
 US Afghans in limbo after Washington soldier attack
US Afghans in limbo after Washington soldier attack
-
England lose Duckett in chase of record 435 to keep Ashes alive

-
 Australia all out for 349, set England 435 to win 3rd Ashes Test
Australia all out for 349, set England 435 to win 3rd Ashes Test
-
US strikes over 70 IS targets in Syria after attack on troops

-
 Australian lifeguards fall silent for Bondi Beach victims
Australian lifeguards fall silent for Bondi Beach victims
-
Trump's name added to Kennedy Center facade, a day after change

-
 West Indies 206-2, trail by 369, after Duffy's double strike
West Indies 206-2, trail by 369, after Duffy's double strike
-
US strikes Islamic State group in Syria after deadly attack on troops

-
 Epstein files opened: famous faces, many blacked-out pages
Epstein files opened: famous faces, many blacked-out pages
-
Ravens face 'special' Patriots clash as playoffs come into focus

-
 Newly released Epstein files: what we know
Newly released Epstein files: what we know
-
Musk wins US court appeal of $56 bn Tesla pay package

-
 US judge voids murder conviction in Jam Master Jay killing
US judge voids murder conviction in Jam Master Jay killing
-
Trump doesn't rule out war with Venezuela

-
 Haller, Aouar out of AFCON, Zambia coach drama
Haller, Aouar out of AFCON, Zambia coach drama
-
Nasdaq rallies again while yen falls despite BOJ rate hike

-
 Bologna win shoot-out with Inter to reach Italian Super Cup final
Bologna win shoot-out with Inter to reach Italian Super Cup final
-
Brandt and Beier send Dortmund second in Bundesliga

-
 Trump administration begins release of Epstein files
Trump administration begins release of Epstein files
-
UN Security Council votes to extend DR Congo mission by one year

-
 Family of Angels pitcher, club settle case over 2019 death
Family of Angels pitcher, club settle case over 2019 death
-
US university killer's mystery motive sought after suicide

-
 Rubio says won't force deal on Ukraine as Europeans join Miami talks
Rubio says won't force deal on Ukraine as Europeans join Miami talks
-
Burkinabe teen behind viral French 'coup' video has no regrets

-
 Brazil court rejects new Bolsonaro appeal against coup conviction
Brazil court rejects new Bolsonaro appeal against coup conviction
-
Three-time Grand Slam winner Wawrinka to retire in 2026

-
 Man Utd can fight for Premier League title in next few years: Amorim
Man Utd can fight for Premier League title in next few years: Amorim
-
Pandya blitz powers India to T20 series win over South Africa

-
 Misinformation complicated Brown University shooting probe: police
Misinformation complicated Brown University shooting probe: police
-
IMF approves $206 mn aid to Sri Lanka after Cyclone Ditwah

-
 US halts green card lottery after MIT professor, Brown University killings
US halts green card lottery after MIT professor, Brown University killings
-
Stocks advance as markets cheer weak inflation

-
 Emery says rising expectations driving red-hot Villa
Emery says rising expectations driving red-hot Villa
-
Three killed in Taipei metro attacks, suspect dead

-
 Seven Colombian soldiers killed in guerrilla attack: army
Seven Colombian soldiers killed in guerrilla attack: army
-
Amorim takes aim at Man Utd youth stars over 'entitlement'

-
 Mercosur meets in Brazil, EU eyes January 12 trade deal
Mercosur meets in Brazil, EU eyes January 12 trade deal
-
US Fed official says no urgency to cut rates, flags distorted data

-
 Rome to charge visitors for access to Trevi Fountain
Rome to charge visitors for access to Trevi Fountain
-
Spurs 'not a quick fix' for under-fire Frank


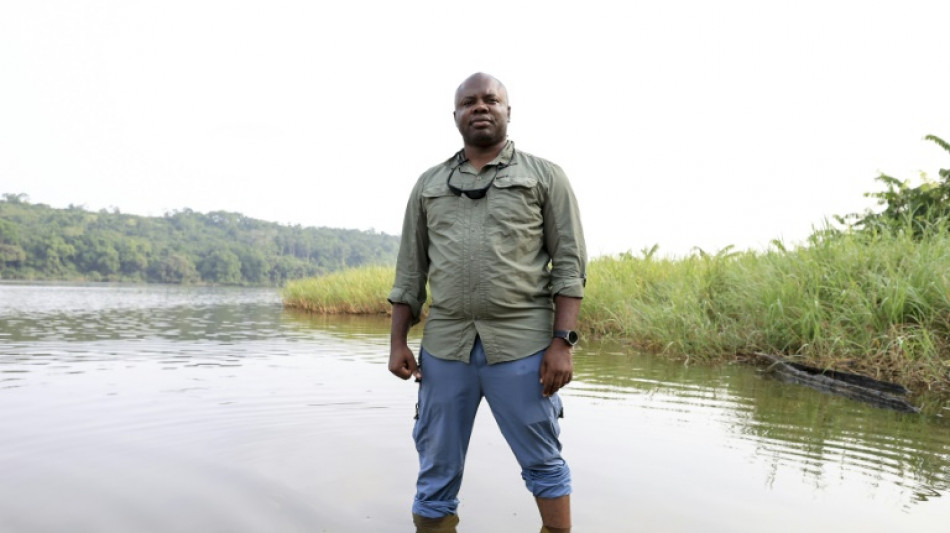
Saving the mysterious African manatee at Cameroon hotspot
Ever since his first hard-won sightings of African manatees, award-winning marine biologist Aristide Takoukam Kamla has been devoted to protecting the little known and atrisk aquatic mammals.
African manatees are found in fresh water along the coast of western Africa, such as in Cameroon's vast Lake Ossa where the researcher first saw them more than 10 years ago.
But they are shy creatures -- spotting them requires setting out before dawn when the lake is glassy and tranquil, all the better for following the trails of bubbles and, maybe just maybe, catching two big nostrils taking a quick breath.
"I was expecting to see them like on YouTube: in clear water, jumping like dolphins... a completely surreal idea" stemming from publications on manatees in Florida, the 39-year-old Cameroonian recalled, smiling.
Their African cousins, however, are very different and the then University of Dschang apprentice researcher had to row for a long time before being rewarded.
Thanks to local fishermen, Takoukam Kamla has now learnt how to spot African manatees more easily within the darkened depths of the 4,500-hectare (11,000-acre) Lake Ossa, part of a sprawling wildlife reserve in southwestern Cameroon.
They are his "favourite animal", the subject of his doctorate at the University of Florida -- and the reason he won this year's prestigious Whitley Award that recognises groundbreaking biodiversity work by grassroots conservationists.
- Endangered habitat, poaching -
American scientist Sarah Farinelli was moved to tears after seeing five African manatees, including a female with her calf, while out on the lake with Takoukam Kamla.
"Its huge! There are certain places in Africa where it's impossible to see them," said Farinelli, who is in her 30s and studies the marine mammals in Nigeria.
Much still eludes researchers about the Trichechus senegalensis -- how many are in Cameroon; how long do they live; when and where do they migrate.
African manatees are found between Mauritania and Angola but "it's a very little studied species, around which many mysteries still remain", Takoukam Kamla said.
Sometimes known as sea cows, the large marine herbivore is listed as "vulnerable" on the red list of the International Union for Conservation of Nature.
But the Cameroonian scientist thinks that is "an under-estimation of the real status of this species, which is subject to poaching" and whose habitat is "constantly in danger".
Takoukam Kamla set up the African Marine Mammal Conservation Organisation which has five laboratories including in the lakeside fishing village of Dizangue.
On Lake Ossa, the animal's sole predators are human -- only a few years ago, manatees were still being served up in the village restaurant.
Manatee hunting is now outlawed and the dish has vanished from menus. A blue statue of a manatee has even been erected in their honour.
But threats remain.
Takoukam Kamla, standing on the shores of the lake, points to a palm oil refinery whose waste is dumped into the water.
Another threat is the positioning of a net across the lake to maximise catches as it could "trap a small manatee in its mesh", he complained, getting into a heated discussion with a fisherman in his dug-out canoe.
"We're indigenous, we live off this and we have never had to suffer prohibitions at home," the old man grumbled bitterly.
"If you want to impose bans on us, you will have to pay us every month."
- Biological combat -
Relations between the scientists and the local communities whose fishing traditions have been passed down the generations are tricky.
But an environmental threat that struck three years ago brought their two worlds together.
Half of the lake's surface became covered by the invasive giant salvinia -- Salvinia molesta -- a free-floating plant that has made the lake uninhabitable for both fish and manatees.
To combat it, scientists used a microscopic insect that feeds exclusively on salvinia and called on the fishermen to help.
"They used to take the salvinia infested with weevils and put a bit everywhere in the lake," AMMCO researcher Thierry Aviti said.
Three years on, the menacing plant has all but disappeared.
"At one point, we couldn't cope anymore" but promises were kept, Dizangue fisherman Thierry Bossambo said, marked by the memories of long nights with no fish.
The bridges built with the fishermen is something Takoukam Kamla is keen to maintain to avoid "parachute science", a term referring to scientists dropping into local communities from their academic ivory towers to undertake field work.
And to counter possible poaching, he wants to develop the area's eco-tourism.
It's a "priority", agreed Gilbert Oum Ndjocka, curator of the nearby Douala-Edea National Park, who said "all stakeholders are allies for conservation".
A.O.Scott--AT