-
 La Rochelle suffer defeat after shock Atonio retirement
La Rochelle suffer defeat after shock Atonio retirement
-
'It wasn't working': Canada province ends drug decriminalization

-
 Kishan, Arshdeep star as India down New Zealand in T20 finale
Kishan, Arshdeep star as India down New Zealand in T20 finale
-
Moreno bags brace but Villarreal held at Osasuna

-
 Kramaric keeps in-form Hoffenheim rolling in Bundesliga
Kramaric keeps in-form Hoffenheim rolling in Bundesliga
-
'Skimo': Adrenalin-packed sprint to make Olympic debut

-
 Venezuela's 'Helicoide' prison synonymous with torture of dissenters
Venezuela's 'Helicoide' prison synonymous with torture of dissenters
-
Arsenal thrash Leeds to stretch Premier League advantage

-
 Russia's Valieva returns to ice after doping ban
Russia's Valieva returns to ice after doping ban
-
Snow storm barrels into southern US as blast of icy weather widens

-
 Ukraine sees mass power outages from 'technical malfunction'
Ukraine sees mass power outages from 'technical malfunction'
-
Gaza civil defence says Israeli strikes kill 32

-
 Kirsty Coventry set to give clues to her Olympic vision in Milan
Kirsty Coventry set to give clues to her Olympic vision in Milan
-
I'm no angel, Italy's PM says amid church fresco row

-
 Thousands join Danish war vets' silent march after Trump 'insult'
Thousands join Danish war vets' silent march after Trump 'insult'
-
Gaza civil defence says Israeli strikes kill 28

-
 Pakistan spin out Australia in second T20I to take series
Pakistan spin out Australia in second T20I to take series
-
Melbourne champion Rybakina never doubted return to Wimbledon form

-
 Luis Enrique welcomes Ligue 1 challenge from Lens
Luis Enrique welcomes Ligue 1 challenge from Lens
-
Long truck lines at Colombia-Ecuador border as tariffs loom

-
 Ex-prince Andrew dogged again by Epstein scandal
Ex-prince Andrew dogged again by Epstein scandal
-
Separatist attacks in Pakistan kill 21, dozens of militants dead

-
 'Malfunction' cuts power in Ukraine. Here's what we know
'Malfunction' cuts power in Ukraine. Here's what we know
-
Arbeloa backs five Real Madrid stars he 'always' wants playing

-
 Sabalenka 'really upset' at blowing chances in Melbourne final loss
Sabalenka 'really upset' at blowing chances in Melbourne final loss
-
Britain, Japan agree to deepen defence and security cooperation

-
 Rybakina keeps her cool to beat Sabalenka in tense Melbourne final
Rybakina keeps her cool to beat Sabalenka in tense Melbourne final
-
France tightens infant formula rules after toxin scare

-
 Blanc wins final women's race before Winter Olympics
Blanc wins final women's race before Winter Olympics
-
Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's Moscow-born Melbourne champion

-
 Ice-cool Rybakina beats Sabalenka in tense Australian Open final
Ice-cool Rybakina beats Sabalenka in tense Australian Open final
-
Pakistan attacks kill 15, dozens of militants dead: official

-
 Ten security officials, 37 militants killed in SW Pakistan attacks: official
Ten security officials, 37 militants killed in SW Pakistan attacks: official
-
Epstein survivors say abusers 'remain hidden' after latest files release

-
 'Full respect' for Djokovic but Nadal tips Alcaraz for Melbourne title
'Full respect' for Djokovic but Nadal tips Alcaraz for Melbourne title
-
Wollaston goes back-to-back in the Cadel Evans road race

-
 Women in ties return as feminism faces pushback
Women in ties return as feminism faces pushback
-
Ship ahoy! Prague's homeless find safe haven on river boat

-
 Britain's Starmer ends China trip aimed at reset despite Trump warning
Britain's Starmer ends China trip aimed at reset despite Trump warning
-
Carlos Alcaraz: rare tennis talent with shades of Federer

-
 Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
-
History beckons for Djokovic and Alcaraz in Australian Open final

-
 Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
-
Epstein offered ex-prince Andrew meeting with Russian woman: files

-
 Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
-
Montreal studio rises from dark basement office to 'Stranger Things'

-
 US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
-
Mertens and Zhang win Australian Open women's doubles title

-
 Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
-
China factory activity loses steam in January


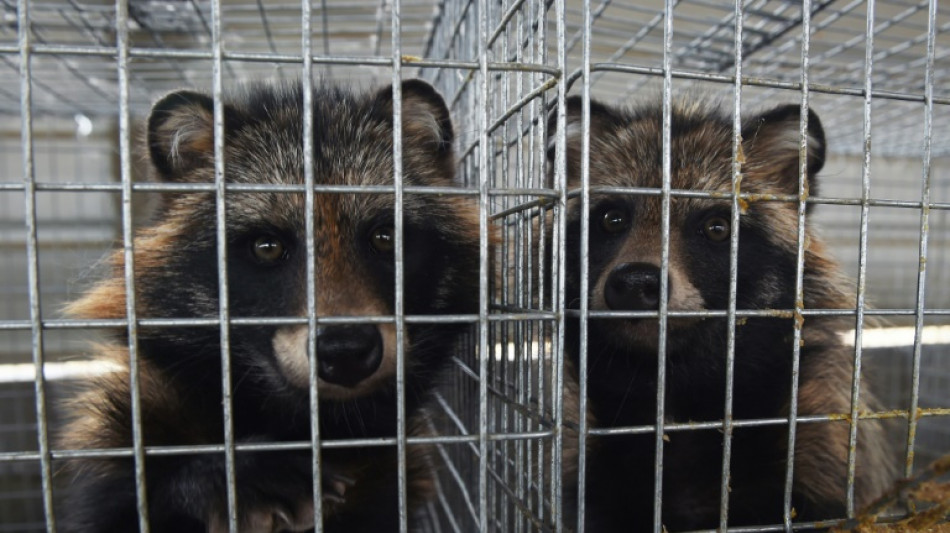
New study reinforces theory Covid emerged at Chinese market
A study on the origin of Covid-19 provided new evidence on Thursday supporting the theory that humans first caught the virus from infected animals at a Chinese market in late 2019.
Nearly five years after Covid first emerged, the international community has not been able to determine with certainty exactly where the virus came from.
The first cases were detected in the Chinese city of Wuhan in late 2019, but there have been bitter disputes between proponents of the two main theories.
One is that the virus leaked from a Wuhan lab which studied related viruses, while the other is that people caught Covid from an infected wild animal being sold at a local market.
The scientific community has favoured the latter theory, but the controversy has rumbled on.
The study published in the Cell journal is based on more than 800 samples collected at Wuhan's Huanan Seafood Market, where wild mammals were also believed to have been for sale.
The samples were collected in January 2020 after the market was shuttered, and were not taken directly from animals or people but from the surfaces of stalls selling wildlife, as well as from drains.
From this type of data, which was shared by the Chinese authorities, "we cannot say with certainty whether the animals (at the market) were infected or not," study co-author Florence Debarre told AFP.
However, "our study confirms that there were wild animals at this market at the end of 2019, notably belonging to species such as raccoon dogs and civets," said the evolutionary biologist at France's CNRS research agency.
"And these animals were in the southwest corner of the market, which also happens to be an area where a lot of SARS-CoV-2 virus, which causes Covid-19, was detected."
These small mammals can catch similar viruses to humans, which has made them suspects for serving as an intermediate host between humans and bats, in which SARS-CoV-2 is suspected to have originated.
The presence of these animals at the Huanan market had previously been disputed, despite some photographic evidence and a 2021 study.
- 'Very strong evidence' -
Numerous parts of one stall tested positive for the Covid virus, including "animal carts, a cage, a garbage cart, and a hair/feather removal machine," the study said.
"There was more DNA from mammalian wildlife species in these samples than human DNA," it added.
Mammal DNA was found in the Covid-positive samples from this stall, including from palm civets, bamboo rats and raccoon dogs.
"These data indicate either that the animals present at this stall shed the SARS-CoV-2 detected on the animal equipment or that early unreported human case(s) of Covid-19 shed virus in the exact same location as the detected animals," the study said.
The research also confirms that the "most recent common ancestor" of the Covid virus strain found in the market samples was "genetically identical" to the original pandemic strain.
"This means that the early diversity of the virus is found at the market -- as would be expected if this is the site where it emerged," Debarre explained.
James Wood, an infectious disease epidemiologist at Cambridge University not involved in the research, said the study "provides very strong evidence for wildlife stalls in the Huanan Seafood Market in Wuhan being a hotspot for the emergence of the Covid-19 pandemic."
The research was important because "little or nothing has been done to limit either the live trade in wildlife nor the biodiversity loss or land use changes that are the actual likely drivers of past and future pandemic emergence," he said.
"These aspects are also not included in the draft pandemic treaty" currently being negotiated by countries, he added.
A.Taylor--AT