
-
 Russian ambassador slams EU frozen assets plan for Ukraine
Russian ambassador slams EU frozen assets plan for Ukraine
-
2026 World Cup draw is kind to favorites as Trump takes limelight

-
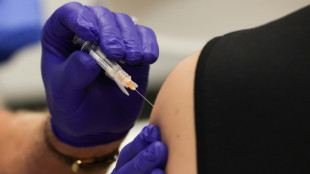 WHO chief upbeat on missing piece of pandemic treaty
WHO chief upbeat on missing piece of pandemic treaty
-
US vaccine panel upends hepatitis B advice in latest Trump-era shift

-
 Ancelotti says Brazil have 'difficult' World Cup group with Morocco
Ancelotti says Brazil have 'difficult' World Cup group with Morocco
-
Kriecmayr wins weather-disrupted Beaver Creek super-G

-
 Ghostwriters, polo shirts, and the fall of a landmark pesticide study
Ghostwriters, polo shirts, and the fall of a landmark pesticide study
-
Mixed day for global stocks as market digest huge Netflix deal

-
 Fighting erupts in DR Congo a day after peace deal signed
Fighting erupts in DR Congo a day after peace deal signed
-
England boss Tuchel wary of 'surprise' in World Cup draw

-
 10 university students die in Peru restaurant fire
10 university students die in Peru restaurant fire
-
'Sinners' tops Critics Choice nominations

-
 Netflix's Warner Bros. acquisition sparks backlash
Netflix's Warner Bros. acquisition sparks backlash
-
France probes mystery drone flight over nuclear sub base

-
 Frank Gehry: five key works
Frank Gehry: five key works
-
US Supreme Court to weigh Trump bid to end birthright citizenship

-
 Frank Gehry, master architect with a flair for drama, dead at 96
Frank Gehry, master architect with a flair for drama, dead at 96
-
'It doesn't make sense': Trump wants to rename American football

-
 A day after peace accord signed, shelling forces DRC locals to flee
A day after peace accord signed, shelling forces DRC locals to flee
-
Draw for 2026 World Cup kind to favorites as Trump takes center stage

-
 Netflix to buy Warner Bros. in deal of the decade
Netflix to buy Warner Bros. in deal of the decade
-
US sanctions equate us with drug traffickers: ICC dep. prosecutor

-
 Migration and crime fears loom over Chile's presidential runoff
Migration and crime fears loom over Chile's presidential runoff
-
French officer charged after police fracture woman's skull

-
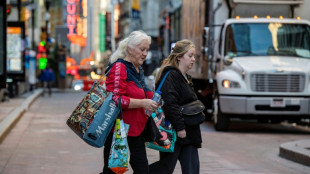 Fresh data show US consumers still strained by inflation
Fresh data show US consumers still strained by inflation
-
Eurovision reels from boycotts over Israel

-
 Trump takes centre stage as 2026 World Cup draw takes place
Trump takes centre stage as 2026 World Cup draw takes place
-
Trump all smiles as he wins FIFA's new peace prize

-
 US panel votes to end recommending all newborns receive hepatitis B vaccine
US panel votes to end recommending all newborns receive hepatitis B vaccine
-
Title favourite Norris reflects on 'positive' Abu Dhabi practice

-
 Stocks consolidate as US inflation worries undermine Fed rate hopes
Stocks consolidate as US inflation worries undermine Fed rate hopes
-
Volcanic eruptions may have brought Black Death to Europe
-
 Arsenal the ultimate test for in-form Villa, says Emery
Arsenal the ultimate test for in-form Villa, says Emery
-
Emotions high, hope alive after Nigerian school abduction

-
 Another original Hermes Birkin bag sells for $2.86 mn
Another original Hermes Birkin bag sells for $2.86 mn
-
11 million flock to Notre-Dame in year since rising from devastating fire

-
 Gymnast Nemour lifts lid on 'humiliation, tears' on way to Olympic gold
Gymnast Nemour lifts lid on 'humiliation, tears' on way to Olympic gold
-
Lebanon president says country does not want war with Israel

-
 France takes anti-drone measures after flight over nuclear sub base
France takes anti-drone measures after flight over nuclear sub base
-
Signing up to DR Congo peace is one thing, delivery another

-
 'Amazing' figurines find in Egyptian tomb solves mystery
'Amazing' figurines find in Egyptian tomb solves mystery
-
Palestinians say Israeli army killed man in occupied West Bank

-
 McLaren will make 'practical' call on team orders in Abu Dhabi, says boss Brown
McLaren will make 'practical' call on team orders in Abu Dhabi, says boss Brown
-
Stocks rise as investors look to more Fed rate cuts

-
 Norris completes Abu Dhabi practice 'double top' to boost title bid
Norris completes Abu Dhabi practice 'double top' to boost title bid
-
Chiba leads Liu at skating's Grand Prix Final

-
 Meta partners with news outlets to expand AI content
Meta partners with news outlets to expand AI content
-
Mainoo 'being ruined' at Man Utd: Scholes

-
 Guardiola says broadcasters owe him wine after nine-goal thriller
Guardiola says broadcasters owe him wine after nine-goal thriller
-
Netflix to buy Warner Bros. Discovery in deal of the decade


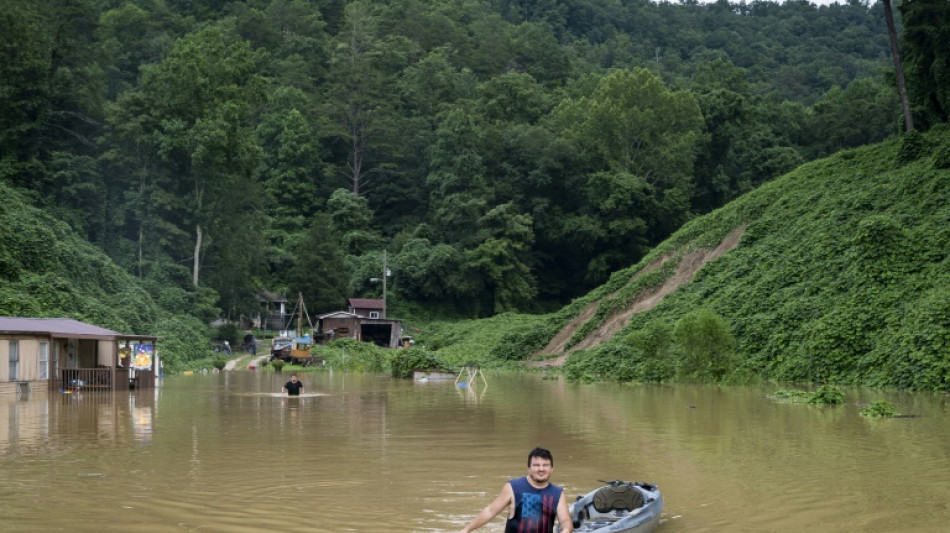
Dust to downpour: US weather whiplash shows climate change
A series of "once-in-a-millennium" rainstorms have lashed the United States in recent weeks, flooding areas baked dry by long-term droughts, as human-caused climate change brings weather whiplash.
And scientists warn that global warming means once-rare events are already much more likely, upending the models they have long used to predict possible disasters -- with worse to come.
At least 40 people have been killed in the last month by storms in Kentucky, Illinois, Texas and Missouri, inundating areas that in some cases had seen little to no rain for months.
Up to 12 inches (30 centimeters) fell in one of these storms -- the kind of downpour that statistical models say should only happen once in a thousand years.
"This is 'weather whiplash'," tweeted Peter Gleick, co-founder of the Pacific Institute, a non-governmental organization that works on water issues around the world.
It is "caused by an intensification of the global hydrological cycle & how it distributes water around the planet, influenced by human-caused climate change."
The warnings scientists have been sounding for decades about the effects of unchecked fossil fuel use are suddenly coming into focus for millions of people.
A warming planet is not a benign place in a far-off future where it is always a bit sunnier; it's a place of wild swings, where the wets are wetter and the dries are drier. And it's now.
"The commonality between these and other extreme rainfall events is you need just the right set of ingredients to come together," said David Novak, director of the Weather Prediction Center at the National Weather Service.
"You need moisture, you need instability in the atmosphere. And you need some sort of... feature to kind of ignite the storms."
While a rainstorm in Texas or Kentucky or Illinois is not unheard of at this time of year, these events were supercharged by an oversupply of atmospheric moisture -- a direct consequence of the planet being hotter.
"There's scientific consensus absolutely on the fact that warmer air can hold more moisture," Novak told AFP.
"There is more moisture available... for these fronts to tap, and so you can get these really intense rainfall events."
The science is uncontroversial -- if a little complicated for those not familiar with linear equations and difficult-to-pronounce chemistry.
The Clausius–Clapeyron equation shows that for every one degree celsius (1.8 F) the air warms, it can hold seven percent more moisture.
That's what makes hot, equatorial places noticeably more humid than cooler climes, says Novak.
And it's also what's messing with the statistics and making the one-in-1,000-year storms -- like the five that hit the US in the last month -- a lot more common.
Storms like these had a 0.1 percent chance of occurring in any given year in pre-industrial conditions, meaning that on average they would happen once every 1,000 years.
But their percentage chance of happening in a warmer environment that holds more moisture rises dramatically.
In other words, the recurrence interval -- the periods expected between these once relatively rare events -- is shrinking.
"Something that really wasn't very likely at all, just a little bit more moisture can make that quite a bit more likely," said Novak.
Y.Baker--AT



