-
 North Korea acknowledges its troops cleared mines for Russia
North Korea acknowledges its troops cleared mines for Russia
-
US unseals warrant for tanker seized off Venezuelan coast

-
 Cambodia says Thailand still bombing hours after Trump truce call
Cambodia says Thailand still bombing hours after Trump truce call
-
Machado urges pressure so Maduro understands 'he has to go'

-
 Leinster stutter before beating Leicester in Champions Cup
Leinster stutter before beating Leicester in Champions Cup
-
World stocks mostly slide, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains

-
 Crypto firm Tether bids for Juventus, is quickly rebuffed
Crypto firm Tether bids for Juventus, is quickly rebuffed
-
Union sink second-placed Leipzig to climb in Bundesliga

-
 US Treasury lifts sanctions on Brazil Supreme Court justice
US Treasury lifts sanctions on Brazil Supreme Court justice
-
UK king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026

-
 Wembanyama expected to return for Spurs in NBA Cup clash with Thunder
Wembanyama expected to return for Spurs in NBA Cup clash with Thunder
-
Five takeaways from Luigi Mangione evidence hearings

-
 UK's king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026
UK's king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026
-
Steelers' Watt undergoes surgery to repair collapsed lung

-
 Iran detains Nobel-prize winner in 'brutal' arrest
Iran detains Nobel-prize winner in 'brutal' arrest
-
NBA Cup goes from 'outside the box' idea to smash hit

-
 UK health service battles 'super flu' outbreak
UK health service battles 'super flu' outbreak
-
Can Venezuela survive US targeting its oil tankers?

-
 Democrats release new cache of Epstein photos
Democrats release new cache of Epstein photos
-
Colombia's ELN guerrillas place communities in lockdown citing Trump 'intervention' threats

-
 'Don't use them': Tanning beds triple skin cancer risk, study finds
'Don't use them': Tanning beds triple skin cancer risk, study finds
-
Nancy aims to restore Celtic faith with Scottish League Cup final win

-
 Argentina fly-half Albornoz signs for Toulon until 2030
Argentina fly-half Albornoz signs for Toulon until 2030
-
Trump says Thailand, Cambodia have agreed to stop border clashes

-
 Salah in Liverpool squad for Brighton after Slot talks - reports
Salah in Liverpool squad for Brighton after Slot talks - reports
-
Marseille coach tips Greenwood as 'potential Ballon d'Or'

-
 Draw marks 'starting gun' toward 2026 World Cup, Vancouver says
Draw marks 'starting gun' toward 2026 World Cup, Vancouver says
-
Thai PM says asked Trump to press Cambodia on border truce

-
 Salah admired from afar in his Egypt home village as club tensions swirl
Salah admired from afar in his Egypt home village as club tensions swirl
-
World stocks retrench, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains

-
 Brazil left calls protests over bid to cut Bolsonaro jail time
Brazil left calls protests over bid to cut Bolsonaro jail time
-
Trump attack on Europe migration 'disaster' masks toughening policies

-
 US plan sees Ukraine joining EU in 2027, official tells AFP
US plan sees Ukraine joining EU in 2027, official tells AFP
-
'Chilling effect': Israel reforms raise press freedom fears

-
 Iran frees child bride sentenced to death over husband's killing: activists
Iran frees child bride sentenced to death over husband's killing: activists
-
No doubting Man City boss Guardiola's passion says Toure

-
 Youthful La Rochelle name teen captain for Champions Cup match in South Africa
Youthful La Rochelle name teen captain for Champions Cup match in South Africa
-
World stocks consolidate Fed-fuelled gains

-
 British 'Aga saga' author Joanna Trollope dies aged 82
British 'Aga saga' author Joanna Trollope dies aged 82
-
Man Utd sweat on Africa Cup of Nations trio

-
 EU agrees three-euro small parcel tax to tackle China flood
EU agrees three-euro small parcel tax to tackle China flood
-
Taylor Swift breaks down in Eras documentary over Southport attack

-
 Maresca 'relaxed' about Chelsea's rough patch
Maresca 'relaxed' about Chelsea's rough patch
-
France updates net-zero plan, with fossil fuel phaseout

-
 Nowhere to pray as logs choke flood-hit Indonesian mosque
Nowhere to pray as logs choke flood-hit Indonesian mosque
-
In Pakistan, 'Eternal Love' has no place on YouTube

-
 England bowling great Anderson named as Lancashire captain
England bowling great Anderson named as Lancashire captain
-
UK's King Charles to give personal TV message about cancer 'journey'

-
 Fit-again Jesus can be Arsenal's number one striker, says Arteta
Fit-again Jesus can be Arsenal's number one striker, says Arteta
-
Spain's ruling Socialists face sex scandal fallout among women voters


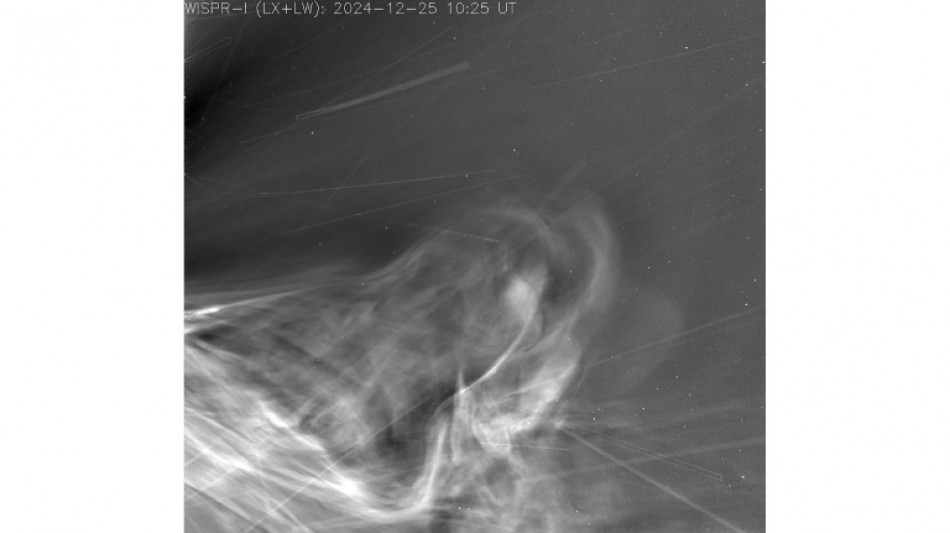
Skimming the Sun, probe sheds light on space weather threats
Eruptions of plasma piling atop one another, solar wind streaming out in exquisite detail -- the closest-ever images of our Sun are a gold mine for scientists.
Captured by the Parker Solar Probe during its closest approach to our star starting on December 24, 2024, the images were recently released by NASA and are expected to deepen our understanding of space weather and help guard against solar threats to Earth.
- A historic achievement –
"We have been waiting for this moment since the late Fifties," Nour Rawafi, project scientist for the mission at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, told AFP.
Previous spacecraft have studied the Sun, but from much farther away.
Parker was launched in 2018 and is named after the late physicist Eugene Parker, who in 1958 theorized the existence of the solar wind -- a constant stream of electrically charged particles that fan out through the solar system.
The probe recently entered its final orbit where its closest approach takes it to just 3.8 million miles from the Sun's surface -- a milestone first achieved on Christmas Eve 2024 and repeated twice since on an 88-day cycle.
To put the proximity in perspective: if the distance between Earth and the Sun measured one foot, Parker would be hovering just half an inch away.
Its heat shield was engineered to withstand up to 2,500 degrees Fahrenheit (1,370 degrees Celsius) -- but to the team's delight, it has only experienced around 2,000F (1090C) so far, revealing the limits of theoretical modeling.
Remarkably, the probe's instruments, just a yard (meter) behind the shield, remain at little more than room temperature.
- Staring at the Sun –
The spacecraft carries a single imager, the Wide-Field Imager for Solar Probe (WISPR), which captured data as Parker plunged through the Sun's corona, or outer atmosphere.
Stitched into a seconds-long video, the new images reveal coronal mass ejections (CMEs) -- massive bursts of charged particles that drive space weather -- in high resolution for the first time.
"We had multiple CMEs piling up on top of each other, which is what makes them so special," Rawafi said. "It's really amazing to see that dynamic happening there."
Such eruptions triggered the widespread auroras seen across much of the world last May, as the Sun reached the peak of its 11-year cycle.
Another striking feature is how the solar wind, flowing from the left of the image, traces a structure called the heliospheric current sheet: an invisible boundary where the Sun's magnetic field flips from north to south.
It extends through the solar system in the shape of a twirling skirt and is critical to study, as it governs how solar eruptions propagate and how strongly they can affect Earth.
- Why it matters –
Space weather can have serious consequences, such as overwhelming power grids, disrupting communications, and threatening satellites.
As thousands more satellites enter orbit in the coming years, tracking them and avoiding collisions will become increasingly difficult -- especially during solar disturbances, which can cause spacecraft to drift slightly from their intended orbits.
Rawafi is particularly excited about what lies ahead, as the Sun heads toward the minimum of its cycle, expected in five to six years.
Historically, some of the most extreme space weather events have occurred during this declining phase -- including the infamous Halloween Solar Storms of 2003, which forced astronauts aboard the International Space Station to shelter in a more shielded area.
"Capturing some of these big, huge eruptions...would be a dream," he said.
Parker still has far more fuel than engineers initially expected and could continue operating for decades -- until its solar panels degrade to the point where they can no longer generate enough power to keep the spacecraft properly oriented.
When its mission does finally end, the probe will slowly disintegrate -- becoming, in Rawafi's words, "part of the solar wind itself."
B.Torres--AT