
-
 Signing up to DR Congo peace is one thing, delivery another
Signing up to DR Congo peace is one thing, delivery another
-
'Amazing' figurines find in Egyptian tomb solves mystery

-
 Palestinians say Israeli army killed man in occupied West Bank
Palestinians say Israeli army killed man in occupied West Bank
-
McLaren will make 'practical' call on team orders in Abu Dhabi, says boss Brown

-
 Stocks rise as investors look to more Fed rate cuts
Stocks rise as investors look to more Fed rate cuts
-
Norris completes Abu Dhabi practice 'double top' to boost title bid

-
 Chiba leads Liu at skating's Grand Prix Final
Chiba leads Liu at skating's Grand Prix Final
-
Meta partners with news outlets to expand AI content

-
 Mainoo 'being ruined' at Man Utd: Scholes
Mainoo 'being ruined' at Man Utd: Scholes
-
Guardiola says broadcasters owe him wine after nine-goal thriller

-
 Netflix to buy Warner Bros. Discovery in deal of the decade
Netflix to buy Warner Bros. Discovery in deal of the decade
-
French stars Moefana and Atonio return for Champions Cup

-
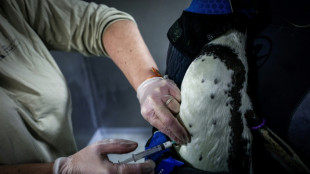 Penguins queue in Paris zoo for their bird flu jabs
Penguins queue in Paris zoo for their bird flu jabs
-
Netflix to buy Warner Bros. Discovery for nearly $83 billion

-
 Sri Lanka issues fresh landslide warnings as toll nears 500
Sri Lanka issues fresh landslide warnings as toll nears 500
-
Root says England still 'well and truly' in second Ashes Test

-
 Chelsea's Maresca says rotation unavoidable
Chelsea's Maresca says rotation unavoidable
-
Italian president urges Olympic truce at Milan-Cortina torch ceremony

-
 Norris edges Verstappen in opening practice for season-ending Abu Dhabi GP
Norris edges Verstappen in opening practice for season-ending Abu Dhabi GP
-
Australia race clear of England to seize control of second Ashes Test

-
 Stocks, dollar rise before key US inflation data
Stocks, dollar rise before key US inflation data
-
Trump strategy shifts from global role and vows 'resistance' in Europe

-
 Turkey orders arrest of 29 footballers in betting scandal
Turkey orders arrest of 29 footballers in betting scandal
-
EU hits X with 120-mn-euro fine, risking Trump ire

-
 Arsenal's Merino has earned striking role: Arteta
Arsenal's Merino has earned striking role: Arteta
-
Putin offers India 'uninterrupted' oil in summit talks with Modi

-
 New Trump strategy vows shift from global role to regional
New Trump strategy vows shift from global role to regional
-
World Athletics ditches long jump take-off zone reform

-
 French town offers 1,000-euro birth bonuses to save local clinic
French town offers 1,000-euro birth bonuses to save local clinic
-
After wins abroad, Syria leader must gain trust at home

-
 Slot spots 'positive' signs at struggling Liverpool
Slot spots 'positive' signs at struggling Liverpool
-
Eyes of football world on 2026 World Cup draw with Trump centre stage

-
 South Africa rugby coach Erasmus extends contract until 2031
South Africa rugby coach Erasmus extends contract until 2031
-
Ex-Manchester Utd star Lingard announces South Korea exit

-
 Australia edge ominously within 106 runs of England in second Ashes Test
Australia edge ominously within 106 runs of England in second Ashes Test
-
Markets rise ahead of US data, expected Fed rate cut

-
 McIlroy survives as Min Woo Lee surges into Australian Open hunt
McIlroy survives as Min Woo Lee surges into Australian Open hunt
-
German factory orders rise more than expected

-
 India's Modi and Russia's Putin talk defence, trade and Ukraine
India's Modi and Russia's Putin talk defence, trade and Ukraine
-
Flooding kills two as Vietnam hit by dozens of landslides

-
 Italy to open Europe's first marine sanctuary for dolphins
Italy to open Europe's first marine sanctuary for dolphins
-
Hong Kong university suspends student union after calls for fire justice

-
 Asian markets rise ahead of US data, expected Fed rate cut
Asian markets rise ahead of US data, expected Fed rate cut
-
Nigerian nightlife finds a new extravagance: cabaret

-
 Tanzania tourism suffers after election killings
Tanzania tourism suffers after election killings
-
Yo-de-lay-UNESCO? Swiss hope for yodel heritage listing

-
 Weatherald fires up as Australia race to 130-1 in second Ashes Test
Weatherald fires up as Australia race to 130-1 in second Ashes Test
-
Georgia's street dogs stir affection, fear, national debate

-
 Survivors pick up pieces in flood-hit Indonesia as more rain predicted
Survivors pick up pieces in flood-hit Indonesia as more rain predicted
-
Gibbs runs for three TDs as Lions down Cowboys to boost NFL playoff bid


Milky Way's secrets revealed by massive space probe map
The Gaia space probe unveiled its latest discoveries on Monday in its quest to map the Milky Way in unprecedented detail, surveying nearly two million stars and revealing mysterious "starquakes" which sweep across the fiery giants like vast tsunamis.
The mission's third data set, which will be released to eagerly waiting astronomers around the world at 1000 GMT, "revolutionises our understanding of the galaxy," the European Space Agency (ESA) said.
"It's the Swiss Army knife of astrophysics -- there is not a single astronomer who does not use its data, directly or indirectly," said Francois Mignard, a member of the Gaia team.
Some of the map's new insights are close to home, such as a catalogue of more than 156,000 asteroids in our Solar System "whose orbits the instrument has calculated with incomparable precision," Mignard said.
But Gaia also sees beyond the Milky Way, spotting 2.9 million other galaxies as well as 1.9 million quasars -- the stunningly bright hearts of galaxies powered by supermassive black holes.
The Gaia spacecraft is nestled in a strategically positioned orbit 1.5 million kilometres (937,000 miles) from Earth, where it has been watching the skies since it was launched by the ESA in 2013.
- 'Beautiful melting pot of stars' -
"Gaia scans the sky and picks up everything it sees," said astronomer Misha Haywood of the Paris Observatory.
But it can still only detect around one percent of the stars in the Milky Way, which is about 100,000 light years across.
The probe is equipped with two telescopes as well as a billion-pixel camera, which captures images sharp enough to gauge the diameter of a human hair at a distance of 1,000 kilometres (620 miles).
It also has a range of other instruments that allow it to not just map the stars, but measure their movements, chemical compositions and ages.
"It provides a global observation of the positions of anything that moves in the sky, for the first time," Haywood said, adding that before Gaia "we had a really restricted view of the galaxy".
It also reveals the huge array of differences between stars.
"Our galaxy is a beautiful melting pot of stars," said Gaia member Alejandra Recio-Blanco.
"This diversity is extremely important, because it tells us the story of our galaxy's formation," he said.
"It also clearly shows that our Sun, and we, all belong to an ever-changing system, formed thanks to the assembly of stars and gas of different origins."
- Surprise starquakes -
The observation of "starquakes", massive vibrations that change the shape of the distant stars, was "one of the most surprising discoveries coming out of the new data", the ESA said.
Gaia was not built to observe starquakes but still detected the strange phenomenon on thousands of stars, including some that should not have any -- at least according to our current understanding of the universe.
"Gaia is opening a gold mine for 'asteroseismology' of massive stars," said Gaia member Conny Aerts.
Around 50 scientific papers were published alongside the new data, with many more expected in the coming years. Gaia's observations have fuelled thousands of studies since its first dataset was released in 2016.
The second dataset in 2018 allowed astronomers to show that the Milky Way merged with another galaxy in a violent collision around 10 billion years ago.
The torrent of raw data is combed through by a team of 450 European scientists and software engineers using six supercomputers as well as "human-driven algorithms" as part of the Data Processing and Analysis Consortium, Mignard said.
"Without this processing group, there is no mission," he added, because every day Gaia produces 700 million star positions and 150 million photometric measurements.
It took the team five years to deliver the latest data, which was observed from 2014 to 2017.
"We can't wait for the astronomy community to dive into our new data to find out even more about our galaxy and its surroundings than we could've imagined," ESA's Gaia project scientist Timo Prusti said.
The final data set will be released in 2030, after Gaia finishes its mission surveying the skies in 2025.
L.Adams--AT



