-
 North Korea acknowledges its troops cleared mines for Russia
North Korea acknowledges its troops cleared mines for Russia
-
US unseals warrant for tanker seized off Venezuelan coast

-
 Cambodia says Thailand still bombing hours after Trump truce call
Cambodia says Thailand still bombing hours after Trump truce call
-
Machado urges pressure so Maduro understands 'he has to go'

-
 Leinster stutter before beating Leicester in Champions Cup
Leinster stutter before beating Leicester in Champions Cup
-
World stocks mostly slide, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains

-
 Crypto firm Tether bids for Juventus, is quickly rebuffed
Crypto firm Tether bids for Juventus, is quickly rebuffed
-
Union sink second-placed Leipzig to climb in Bundesliga

-
 US Treasury lifts sanctions on Brazil Supreme Court justice
US Treasury lifts sanctions on Brazil Supreme Court justice
-
UK king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026

-
 Wembanyama expected to return for Spurs in NBA Cup clash with Thunder
Wembanyama expected to return for Spurs in NBA Cup clash with Thunder
-
Five takeaways from Luigi Mangione evidence hearings

-
 UK's king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026
UK's king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026
-
Steelers' Watt undergoes surgery to repair collapsed lung

-
 Iran detains Nobel-prize winner in 'brutal' arrest
Iran detains Nobel-prize winner in 'brutal' arrest
-
NBA Cup goes from 'outside the box' idea to smash hit

-
 UK health service battles 'super flu' outbreak
UK health service battles 'super flu' outbreak
-
Can Venezuela survive US targeting its oil tankers?

-
 Democrats release new cache of Epstein photos
Democrats release new cache of Epstein photos
-
Colombia's ELN guerrillas place communities in lockdown citing Trump 'intervention' threats

-
 'Don't use them': Tanning beds triple skin cancer risk, study finds
'Don't use them': Tanning beds triple skin cancer risk, study finds
-
Nancy aims to restore Celtic faith with Scottish League Cup final win

-
 Argentina fly-half Albornoz signs for Toulon until 2030
Argentina fly-half Albornoz signs for Toulon until 2030
-
Trump says Thailand, Cambodia have agreed to stop border clashes

-
 Salah in Liverpool squad for Brighton after Slot talks - reports
Salah in Liverpool squad for Brighton after Slot talks - reports
-
Marseille coach tips Greenwood as 'potential Ballon d'Or'

-
 Draw marks 'starting gun' toward 2026 World Cup, Vancouver says
Draw marks 'starting gun' toward 2026 World Cup, Vancouver says
-
Thai PM says asked Trump to press Cambodia on border truce

-
 Salah admired from afar in his Egypt home village as club tensions swirl
Salah admired from afar in his Egypt home village as club tensions swirl
-
World stocks retrench, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains

-
 Brazil left calls protests over bid to cut Bolsonaro jail time
Brazil left calls protests over bid to cut Bolsonaro jail time
-
Trump attack on Europe migration 'disaster' masks toughening policies

-
 US plan sees Ukraine joining EU in 2027, official tells AFP
US plan sees Ukraine joining EU in 2027, official tells AFP
-
'Chilling effect': Israel reforms raise press freedom fears

-
 Iran frees child bride sentenced to death over husband's killing: activists
Iran frees child bride sentenced to death over husband's killing: activists
-
No doubting Man City boss Guardiola's passion says Toure

-
 Youthful La Rochelle name teen captain for Champions Cup match in South Africa
Youthful La Rochelle name teen captain for Champions Cup match in South Africa
-
World stocks consolidate Fed-fuelled gains

-
 British 'Aga saga' author Joanna Trollope dies aged 82
British 'Aga saga' author Joanna Trollope dies aged 82
-
Man Utd sweat on Africa Cup of Nations trio

-
 EU agrees three-euro small parcel tax to tackle China flood
EU agrees three-euro small parcel tax to tackle China flood
-
Taylor Swift breaks down in Eras documentary over Southport attack

-
 Maresca 'relaxed' about Chelsea's rough patch
Maresca 'relaxed' about Chelsea's rough patch
-
France updates net-zero plan, with fossil fuel phaseout

-
 Nowhere to pray as logs choke flood-hit Indonesian mosque
Nowhere to pray as logs choke flood-hit Indonesian mosque
-
In Pakistan, 'Eternal Love' has no place on YouTube

-
 England bowling great Anderson named as Lancashire captain
England bowling great Anderson named as Lancashire captain
-
UK's King Charles to give personal TV message about cancer 'journey'

-
 Fit-again Jesus can be Arsenal's number one striker, says Arteta
Fit-again Jesus can be Arsenal's number one striker, says Arteta
-
Spain's ruling Socialists face sex scandal fallout among women voters


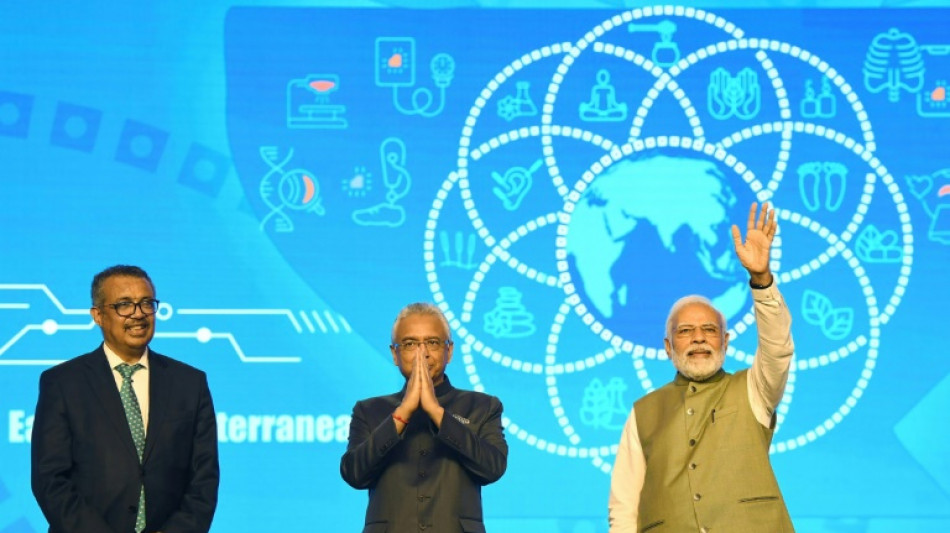
WHO launches traditional medicine hub in India
The World Health Organization launched its Global Centre for Traditional Medicine at a site in India on Tuesday, aimed at unlocking its potential by blending ancient practices with modern science.
The GCTM knowledge hub is intended to create a body of reliable evidence and data on traditional medicine practices and products to help inform standards and the cost-effective use of methods that go outside conventional medicine.
"Harnessing the potential of traditional medicine would be a game-changer for health when founded on evidence, innovation and sustainability," the WHO said, noting that traditional medicine formed part of the growing health and wellness industries.
The hub will be temporarily housed at the Institute Teaching and Research in Ayurveda in Jamnagar on India's west coast until the new 35-acre (14-hectare) site in the city is completed in 2024.
WHO chief Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus joined Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi in the Gujarati city to lay the foundation stone.
Around 80 percent of the world's population is thought to use traditional medicine, such as herbal mixtures, acupuncture, yoga, ayurvedic medicine and indigenous therapies.
- Medicine of first resort -
"For many millions of people around the world, traditional medicine is the first port of call to treat many diseases," Tedros told the ceremony.
"The WHO GCTM that we are launching will help to harness the power of science to strengthen the evidence base for traditional medicine," he said, to optimise its use for health and wellbeing around the world.
The UN health agency defines traditional medicine as the knowledge, skills and practices that indigenous and different cultures have used over time to maintain health and prevent, diagnose and treat physical and mental illness.
India has put $250 million into the project, with Modi saying traditional medicine encompasses a holistic science of life and would gain global importance in the coming 30 years.
"Our traditional medicine is a repository of hundreds of years of accumulated knowledge," he said.
"Going forward, we must use technology to create a global database, repository of traditional medicine practices," to help future generations.
"They should also make international standards so that people's trust in these traditional medicines goes up."
- Aspirin and the pill -
The hub will focus on four strategic areas: evidence and learning; data and analytics; sustainability and equity; and innovation and technology.
It is hoped that a solid evidence base will help countries regulate quality and safety.
Of the WHO's 194 member states, 170 acknowledged their use of traditional and complementary medicine since 2018, but only 124 reported having laws or regulations for the use of herbal medicines -- while only half had a national policy on such methods and medicines.
The WHO said that traditional medicine was increasingly prominent in modern science, with 40 percent of approved pharmaceutical products currently in use deriving from natural substances.
It cited aspirin drawing on formulations using willow tree bark; the contraceptive pill being developed from wild yam plant roots; child cancer treatments based on the rosy periwinkle; and the development of the anti-malaria treatment artemisinin drawing on ancient Chinese medicine texts.
The UN health agency said artificial intelligence was now used to map evidence and trends in traditional medicine and to screen natural products for pharmacokinetic properties.
rjm-burs/pvh
P.A.Mendoza--AT