-
 North Korea acknowledges its troops cleared mines for Russia
North Korea acknowledges its troops cleared mines for Russia
-
US unseals warrant for tanker seized off Venezuelan coast

-
 Cambodia says Thailand still bombing hours after Trump truce call
Cambodia says Thailand still bombing hours after Trump truce call
-
Machado urges pressure so Maduro understands 'he has to go'

-
 Leinster stutter before beating Leicester in Champions Cup
Leinster stutter before beating Leicester in Champions Cup
-
World stocks mostly slide, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains

-
 Crypto firm Tether bids for Juventus, is quickly rebuffed
Crypto firm Tether bids for Juventus, is quickly rebuffed
-
Union sink second-placed Leipzig to climb in Bundesliga

-
 US Treasury lifts sanctions on Brazil Supreme Court justice
US Treasury lifts sanctions on Brazil Supreme Court justice
-
UK king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026

-
 Wembanyama expected to return for Spurs in NBA Cup clash with Thunder
Wembanyama expected to return for Spurs in NBA Cup clash with Thunder
-
Five takeaways from Luigi Mangione evidence hearings

-
 UK's king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026
UK's king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026
-
Steelers' Watt undergoes surgery to repair collapsed lung

-
 Iran detains Nobel-prize winner in 'brutal' arrest
Iran detains Nobel-prize winner in 'brutal' arrest
-
NBA Cup goes from 'outside the box' idea to smash hit

-
 UK health service battles 'super flu' outbreak
UK health service battles 'super flu' outbreak
-
Can Venezuela survive US targeting its oil tankers?

-
 Democrats release new cache of Epstein photos
Democrats release new cache of Epstein photos
-
Colombia's ELN guerrillas place communities in lockdown citing Trump 'intervention' threats

-
 'Don't use them': Tanning beds triple skin cancer risk, study finds
'Don't use them': Tanning beds triple skin cancer risk, study finds
-
Nancy aims to restore Celtic faith with Scottish League Cup final win

-
 Argentina fly-half Albornoz signs for Toulon until 2030
Argentina fly-half Albornoz signs for Toulon until 2030
-
Trump says Thailand, Cambodia have agreed to stop border clashes

-
 Salah in Liverpool squad for Brighton after Slot talks - reports
Salah in Liverpool squad for Brighton after Slot talks - reports
-
Marseille coach tips Greenwood as 'potential Ballon d'Or'

-
 Draw marks 'starting gun' toward 2026 World Cup, Vancouver says
Draw marks 'starting gun' toward 2026 World Cup, Vancouver says
-
Thai PM says asked Trump to press Cambodia on border truce

-
 Salah admired from afar in his Egypt home village as club tensions swirl
Salah admired from afar in his Egypt home village as club tensions swirl
-
World stocks retrench, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains

-
 Brazil left calls protests over bid to cut Bolsonaro jail time
Brazil left calls protests over bid to cut Bolsonaro jail time
-
Trump attack on Europe migration 'disaster' masks toughening policies

-
 US plan sees Ukraine joining EU in 2027, official tells AFP
US plan sees Ukraine joining EU in 2027, official tells AFP
-
'Chilling effect': Israel reforms raise press freedom fears

-
 Iran frees child bride sentenced to death over husband's killing: activists
Iran frees child bride sentenced to death over husband's killing: activists
-
No doubting Man City boss Guardiola's passion says Toure

-
 Youthful La Rochelle name teen captain for Champions Cup match in South Africa
Youthful La Rochelle name teen captain for Champions Cup match in South Africa
-
World stocks consolidate Fed-fuelled gains

-
 British 'Aga saga' author Joanna Trollope dies aged 82
British 'Aga saga' author Joanna Trollope dies aged 82
-
Man Utd sweat on Africa Cup of Nations trio

-
 EU agrees three-euro small parcel tax to tackle China flood
EU agrees three-euro small parcel tax to tackle China flood
-
Taylor Swift breaks down in Eras documentary over Southport attack

-
 Maresca 'relaxed' about Chelsea's rough patch
Maresca 'relaxed' about Chelsea's rough patch
-
France updates net-zero plan, with fossil fuel phaseout

-
 Nowhere to pray as logs choke flood-hit Indonesian mosque
Nowhere to pray as logs choke flood-hit Indonesian mosque
-
In Pakistan, 'Eternal Love' has no place on YouTube

-
 England bowling great Anderson named as Lancashire captain
England bowling great Anderson named as Lancashire captain
-
UK's King Charles to give personal TV message about cancer 'journey'

-
 Fit-again Jesus can be Arsenal's number one striker, says Arteta
Fit-again Jesus can be Arsenal's number one striker, says Arteta
-
Spain's ruling Socialists face sex scandal fallout among women voters


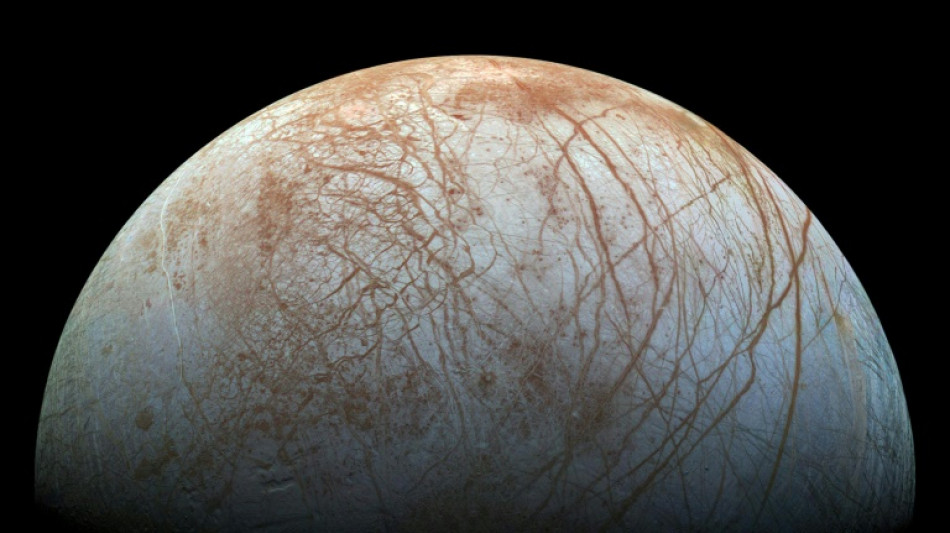
Water on Jupiter's moon closer to surface than thought: study
Ridges that criss-cross the icy surface of Jupiter's moon Europa indicate there are shallow pockets of water beneath, boosting hopes in the search for extra-terrestrial life, scientists said Tuesday.
Europa has long been a candidate for finding life in our solar system due to its vast ocean, which is widely thought to contain liquid water -- a key ingredient for life.
There is a problem: the ocean is predicted to be buried 25-30 kilometres (15-17 miles) beneath the moon's icy shell.
However water could be closer to the surface than previously thought, according to new research published in the journal Nature Communications.
The finding came partly by chance, when geophysicists studying an ice sheet in Greenland watched a presentation about Europa and spotted a feature they recognised.
"We were working on something totally different related to climate change and its impact on the surface of Greenland when we saw these tiny double ridges," said the study's senior author Dustin Schroeder, a geophysics professor at Stanford University.
They realised that the M-shaped icy crests on Greenland looked like smaller versions of double ridges on Europa, which are the most common feature on the moon.
Europa's double ridges were first photographed by NASA's Galileo spacecraft in the 1990s, but little was known about how they were formed.
The scientists used ice-penetrating radar to observe that Greenland's ridges were formed when water pockets around 30 metres (100 feet) below the ice sheet's surface refroze and fractured.
"This is particularly exciting, because scientists have been studying double ridges on Europa for more than 20 years and have not yet come to a definitive answer for how double ridges form," said lead study author Riley Culberg, an electrical engineering PhD student at Stanford.
"This was the first time that we were able to watch something similar happen on Earth and actually observe the subsurface processes that led to the formation of the ridges," he told AFP.
"If Europa's double ridges also form in this way, it suggests that shallow water pockets must have been (or maybe still are) extremely common."
- 'Life has a shot' -
Europa's water pockets could be buried five kilometres beneath the moon’s ice shell -- but that would still be much easier to access than the far deeper ocean.
"Particularly if such water pockets form because ocean water was forced up through fractures into the ice shell, then it's possible that they would preserve evidence of any life in the ocean itself," Culberg said.
Water closer to the surface would also contain "interesting chemicals" from space and other moons, increasing the "possibility that life has a shot," Schroeder said in a statement.
We may not have too long to wait to find out more.
NASA's Europa Clipper mission, scheduled to launch in 2024 and arrive in 2030, will have ice-penetrating radar equipment similar to that used by the scientists studying Greenland's double ridges.
The spacecraft is unlikely to find definitive proof of life because it will not land on Europa, instead flying by and analysing it.
But hopes remain high. The moon's ocean is predicted to have more water than all of Earth's seas combined, according to the Europa Clipper's website.
"If there is life in Europa, it almost certainly was completely independent from the origin of life on Earth... that would mean the origin of life must be pretty easy throughout the galaxy and beyond," project scientist Robert Pappalardo said on the website.
A.Taylor--AT