-
 Blanc wins final women's race before Winter Olympics
Blanc wins final women's race before Winter Olympics
-
Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's Moscow-born Melbourne champion

-
 Ice-cool Rybakina beats Sabalenka in tense Australian Open final
Ice-cool Rybakina beats Sabalenka in tense Australian Open final
-
Pakistan attacks kill 15, dozens of militants dead: official

-
 Ten security officials, 37 militants killed in SW Pakistan attacks: official
Ten security officials, 37 militants killed in SW Pakistan attacks: official
-
Epstein survivors say abusers 'remain hidden' after latest files release

-
 'Full respect' for Djokovic but Nadal tips Alcaraz for Melbourne title
'Full respect' for Djokovic but Nadal tips Alcaraz for Melbourne title
-
Wollaston goes back-to-back in the Cadel Evans road race

-
 Women in ties return as feminism faces pushback
Women in ties return as feminism faces pushback
-
Ship ahoy! Prague's homeless find safe haven on river boat

-
 Britain's Starmer ends China trip aimed at reset despite Trump warning
Britain's Starmer ends China trip aimed at reset despite Trump warning
-
Carlos Alcaraz: rare tennis talent with shades of Federer

-
 Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
-
History beckons for Djokovic and Alcaraz in Australian Open final

-
 Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
-
Epstein offered ex-prince Andrew meeting with Russian woman: files

-
 Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
-
Montreal studio rises from dark basement office to 'Stranger Things'

-
 US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
-
Mertens and Zhang win Australian Open women's doubles title

-
 Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
-
China factory activity loses steam in January

-
 Melania Trump's atypical, divisive doc opens in theatres
Melania Trump's atypical, divisive doc opens in theatres
-
Bad Bunny set for historic one-two punch at Grammys, Super Bowl

-
 Five things to watch for on Grammys night Sunday
Five things to watch for on Grammys night Sunday
-
Venezuelan interim president proposes mass amnesty law

-
 Rose stretches lead at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes cut
Rose stretches lead at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes cut
-
Online foes Trump, Petro set for White House face-to-face

-
 Seattle Seahawks deny plans for post-Super Bowl sale
Seattle Seahawks deny plans for post-Super Bowl sale
-
US Senate passes deal expected to shorten shutdown

-
 'Misrepresent reality': AI-altered shooting image surfaces in US Senate
'Misrepresent reality': AI-altered shooting image surfaces in US Senate
-
Thousands rally in Minneapolis as immigration anger boils

-
 US judge blocks death penalty for alleged health CEO killer Mangione
US judge blocks death penalty for alleged health CEO killer Mangione
-
Lens win to reclaim top spot in Ligue 1 from PSG

-
 Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump Fed pick
Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump Fed pick
-
Ko, Woad share lead at LPGA season opener

-
 US Senate votes on funding deal - but shutdown still imminent
US Senate votes on funding deal - but shutdown still imminent
-
US charges prominent journalist after Minneapolis protest coverage

-
 Trump expects Iran to seek deal to avoid US strikes
Trump expects Iran to seek deal to avoid US strikes
-
US Justice Dept releases documents, images, videos from Epstein files

-
 Guterres warns UN risks 'imminent financial collapse'
Guterres warns UN risks 'imminent financial collapse'
-
NASA delays Moon mission over frigid weather

-
 First competitors settle into Milan's Olympic village
First competitors settle into Milan's Olympic village
-
Fela Kuti: first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award

-
 Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues oil ultimatum
Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues oil ultimatum
-
'Schitt's Creek' star Catherine O'Hara dead at 71

-
 Curran hat-trick seals 11 run DLS win for England over Sri Lanka
Curran hat-trick seals 11 run DLS win for England over Sri Lanka
-
Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues energy ultimatum

-
 France rescues over 6,000 UK-bound Channel migrants in 2025
France rescues over 6,000 UK-bound Channel migrants in 2025
-
Surprise appointment Riera named Frankfurt coach


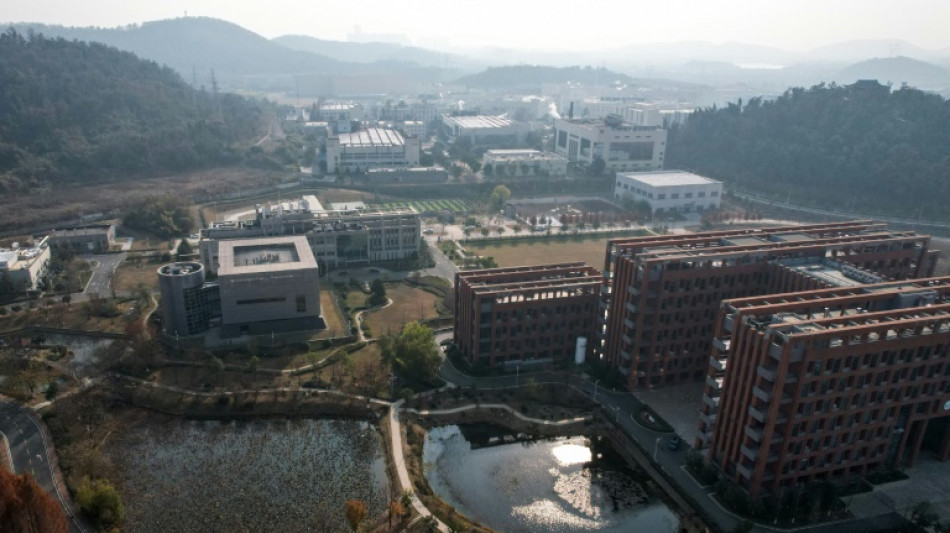
Covid's origins reviewed: Lab leak or natural spillover?
Whether Covid-19 was unleashed by a laboratory mishap or spilled over from animals remains an enduring, fiercely contested mystery.
Here are the leading arguments that fuel both sides of this debate, as AFP reflects on the virus's impact five years after it reshaped the world.
- The case for lab leak -
Proponents of the lab-leak hypothesis highlight that the earliest known Covid-19 cases emerged in Wuhan, China -- home to the Wuhan Institute of Virology (WIV), a major hub for coronavirus research -- located roughly 1,000 miles (1,600 kilometers) from the nearest bat populations carrying similar SARS-like viruses.
"Wuhan labs performed research that placed them on a trajectory to obtain SARS viruses having high pandemic potential," Richard Ebright, a microbiologist and professor at Rutgers University, told AFP.
"One year before the outbreak, Wuhan labs proposed research to obtain SARS viruses having even higher pandemic potential and features that match, in detail, the features of SARS CoV-2," he added.
This research proposal included engineering a structure called a "furin cleavage site," which increases viral growth and transmissibility but is absent in other SARS viruses.
Lab-leak advocates also cite concerns over biosafety standards at the Wuhan lab, where personnel reportedly only wore lab coats and gloves.
"There is sufficient evidence to conclude beyond reasonable doubt that SARS-CoV-2 entered humans through a research-related incident," Ebright concluded.
- The case for natural spillover -
On the other side, researchers like Angela Rasmussen, a virologist at the Vaccine and Infectious Disease Organization at the University of Saskatchewan in Canada, argue that real-world "hard evidence" consistently points to a wholesale seafood market in Wuhan.
"We've actually been looking at an evidence base that is hard evidence. It's evidence that can be measured," she told AFP, including genomic, geographic and environmental sampling data.
She contends that the case for a lab origin, by contrast, is built on "what ifs" and speculation. That would include claims that proposals for research on ways to greatly increase virus transmissibility were publicly rejected but secretly carried out.
This perspective is supported by multiple studies, including one published in the prestigious journal Science that analyzed the geographic pattern of Covid-19 cases during December 2019. The study showed cases were tightly clustered around Wuhan's Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market.
Another study, which examined genomic data from the earliest cases, concluded that the virus likely did not circulate widely in humans before November 2019.
More recently, in September 2024, a study published in Cell identified raccoon dogs, palm civets, Amur hedgehogs, and bamboo rats at the market.
Notably, raccoon dogs, which are closely related to foxes, are known to carry and transmit viruses similar to SARS-CoV-2, suggesting they could have acted as intermediaries between bats and humans.
For Rasmussen, the appeal of the lab-leak theory reflects a desire for straightforward answers. If the blame lies with wayward scientists or China, she argues, people will believe in the possibility of straightforward fixes.
- Where things stand now -
One thing is certain: the lab-leak theory, once dismissed as a conspiracy theory, has gained mainstream traction. For now, the debate remains unresolved -- scientifically and politically.
Some US agencies, like the Federal Bureau of Investigation and the Department of Energy, support the lab-leak theory, albeit with varying levels of confidence, while most elements of the intelligence community lean toward natural origins.
Lab-leak proponents, such as Alina Chan, a molecular biologist at the Broad Institute and author of "Viral: The Search for the Origin of Covid-19," continue to advocate for the full declassification of intelligence data and an independent investigation in China beyond the 2021 World Health Organization probe.
"There are many aspects of the pandemic that have damaged public trust in science and health institutions," Chan told AFP. "The origin of the pandemic is one of these."
P.Hernandez--AT