-
 Knicks boost win streak to six by beating LeBron's Lakers
Knicks boost win streak to six by beating LeBron's Lakers
-
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga triumph at Grammys

-
 Japan says rare earth found in sediment retrieved on deep-sea mission
Japan says rare earth found in sediment retrieved on deep-sea mission
-
San Siro prepares for last dance with Winter Olympics' opening ceremony

-
 France great Benazzi relishing 'genius' Dupont's Six Nations return
France great Benazzi relishing 'genius' Dupont's Six Nations return
-
Grammy red carpet: black and white, barely there and no ICE

-
 Oil tumbles on Iran hopes, precious metals hit by stronger dollar
Oil tumbles on Iran hopes, precious metals hit by stronger dollar
-
South Korea football bosses in talks to avert Women's Asian Cup boycott

-
 Level playing field? Tech at forefront of US immigration fight
Level playing field? Tech at forefront of US immigration fight
-
British singer Olivia Dean wins Best New Artist Grammy

-
 Hatred of losing drives relentless Alcaraz to tennis history
Hatred of losing drives relentless Alcaraz to tennis history
-
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga win early at Grammys

-
 Surging euro presents new headache for ECB
Surging euro presents new headache for ECB
-
Djokovic hints at retirement as time seeps away on history bid

-
 US talking deal with 'highest people' in Cuba: Trump
US talking deal with 'highest people' in Cuba: Trump
-
UK ex-ambassador quits Labour over new reports of Epstein links

-
 Trump says closing Kennedy Center arts complex for two years
Trump says closing Kennedy Center arts complex for two years
-
Reigning world champs Tinch, Hocker among Millrose winners

-
 Venezuelan activist ends '1,675 days' of suffering in prison
Venezuelan activist ends '1,675 days' of suffering in prison
-
Real Madrid scrape win over Rayo, Athletic claim derby draw

-
 PSG beat Strasbourg after Hakimi red to retake top spot in Ligue 1
PSG beat Strasbourg after Hakimi red to retake top spot in Ligue 1
-
NFL Cardinals hire Rams' assistant LaFleur as head coach

-
 Arsenal scoop $2m prize for winning FIFA Women's Champions Cup
Arsenal scoop $2m prize for winning FIFA Women's Champions Cup
-
Atletico agree deal to sign Lookman from Atalanta

-
 Real Madrid's Bellingham set for month out with hamstring injury
Real Madrid's Bellingham set for month out with hamstring injury
-
Man City won't surrender in title race: Guardiola

-
 Korda captures weather-shortened LPGA season opener
Korda captures weather-shortened LPGA season opener
-
Czechs rally to back president locking horns with government

-
 Prominent Venezuelan activist released after over four years in jail
Prominent Venezuelan activist released after over four years in jail
-
Emery riled by 'unfair' VAR call as Villa's title hopes fade

-
 Guirassy double helps Dortmund move six points behind Bayern
Guirassy double helps Dortmund move six points behind Bayern
-
Nigeria's president pays tribute to Fela Kuti after Grammys Award

-
 Inter eight clear after win at Cremonese marred by fans' flare flinging
Inter eight clear after win at Cremonese marred by fans' flare flinging
-
England underline World Cup
credentials with series win over Sri Lanka

-
 Guirassy brace helps Dortmund move six behind Bayern
Guirassy brace helps Dortmund move six behind Bayern
-
Man City held by Solanke stunner, Sesko delivers 'best feeling' for Man Utd

-
 'Send Help' debuts atop N.America box office
'Send Help' debuts atop N.America box office
-
Ukraine war talks delayed to Wednesday, says Zelensky

-
 Iguanas fall from trees in Florida as icy weather bites southern US
Iguanas fall from trees in Florida as icy weather bites southern US
-
Carrick revels in 'best feeling' after Man Utd leave it late

-
 Olympic chiefs admit 'still work to do' on main ice hockey venue
Olympic chiefs admit 'still work to do' on main ice hockey venue
-
Pope says Winter Olympics 'rekindle hope' for world peace

-
 Last-gasp Demirovic strike sends Stuttgart fourth
Last-gasp Demirovic strike sends Stuttgart fourth
-
Sesko strikes to rescue Man Utd, Villa beaten by Brentford

-
 'At least 200' feared dead in DR Congo landslide: government
'At least 200' feared dead in DR Congo landslide: government
-
Coventry says 'sad' about ICE, Wasserman 'distractions' before Olympics

-
 In-form Lyon make it 10 wins in a row
In-form Lyon make it 10 wins in a row
-
Man Utd strike late as Carrick extends perfect start in Fulham thriller

-
 Van der Poel romps to record eighth cyclo-cross world title
Van der Poel romps to record eighth cyclo-cross world title
-
Mbappe penalty earns Real Madrid late win over nine-man Rayo


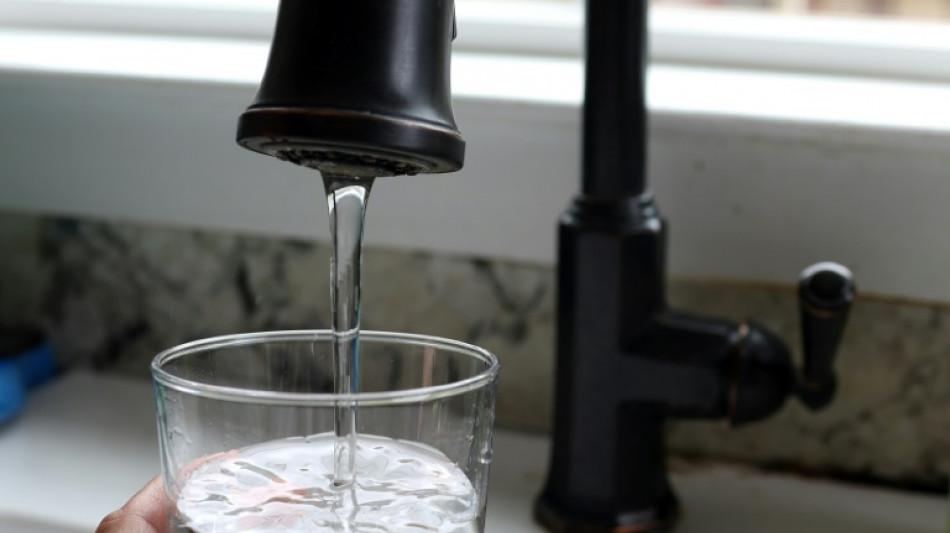
Hazardous 'forever chemicals' detected in nearly half of US tap water
At least 45 percent of the United States' tap water is contaminated with toxic "forever" chemicals, according to a study by a government agency.
Found in everyday products such as non-stick frying pans, polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) can linger in the environment for a long time and have been linked to serious health conditions including cancer and birth defects.
The chemicals can reach water supplies through industrial discharges and leaching from landfill sites.
"This USGS study was the first to compare PFAS in tap water from both private and public supplies on a broad scale throughout the country," Kelly Smalling, a USGS scientist and the study's lead author, told AFP on Friday.
The paper was published this week in the journal Environment International, and found exposure to PFAS was similar in samples collected from unregulated private wells and regulated public supply.
Overall, the study estimated the probability of PFAS being observed in the water at 75 percent in cities and 25 percent in rural areas.
- Filters recommended, not bottled water -
There are more than 12,000 types of PFAS, not all of which are detectable by current testing. For the purposes of the current research, USGS tested for only 32 types.
The team collected samples from 716 nationally representative locations.
Most exposures occurred in urban areas or places with known high concentrations of PFAS, such as industrial and waste sites.
These included the Great Plains, which runs down the middle of the country, the Great Lakes in the mid-east, as well as cities along the East and West Coasts.
Concerned residents can look up PFAS levels in the zip code via a website maintained by the nonprofit Environmental Working Group (www.ewg.org).
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) offers advice for in-home treatment options. Filters, including those that reverse osmosis technology, activated carbon, and ion exchange have been shown to be highly effective at removing them.
Bottled water may not be a good alternative. A 2022 study by USGS found bottled water was frequently contaminated with inorganic and organic compounds, with arsenic, lead, and uranium among the most common.
Last month, US industrial conglomerate 3M announced it would pay as much as $12.5 billion to settle numerous claims from US public water systems that accused the company of tainting their supplies.
The company has also agreed to large settlements in the Netherlands and Belgium, and announced in December it would stop manufacturing PFAS substances by the end of 2025.
US chemicals giant DuPont and its spinoffs Chemours and Corteva also announced in June they would pay nearly $1.2 billion to settle claims they contaminated water sources serving "the vast majority of the United States population" with PFAS.
The EPA proposed new standards on PFAS chemicals in March, requiring public water utilities to monitor for six compounds and reduce PFAS levels in the water supply.
President Joe Biden's Bipartisan Infrastructure Law passed in 2021 invests $9 billion over five years to help communities reduce PFAS contamination levels in drinking water.
M.White--AT