-
 Olympic Games in northern Italy have German twist
Olympic Games in northern Italy have German twist
-
Bad Bunny: the Puerto Rican phenom on top of the music world

-
 Snapchat blocks 415,000 underage accounts in Australia
Snapchat blocks 415,000 underage accounts in Australia
-
At Grammys, 'ICE out' message loud and clear

-
 Dalai Lama's 'gratitude' at first Grammy win
Dalai Lama's 'gratitude' at first Grammy win
-
Bad Bunny makes Grammys history with Album of the Year win

-
 Stocks, oil, precious metals plunge on volatile start to the week
Stocks, oil, precious metals plunge on volatile start to the week
-
Steven Spielberg earns coveted EGOT status with Grammy win

-
 Knicks boost win streak to six by beating LeBron's Lakers
Knicks boost win streak to six by beating LeBron's Lakers
-
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga triumph at Grammys

-
 Japan says rare earth found in sediment retrieved on deep-sea mission
Japan says rare earth found in sediment retrieved on deep-sea mission
-
San Siro prepares for last dance with Winter Olympics' opening ceremony

-
 France great Benazzi relishing 'genius' Dupont's Six Nations return
France great Benazzi relishing 'genius' Dupont's Six Nations return
-
Grammy red carpet: black and white, barely there and no ICE

-
 Oil tumbles on Iran hopes, precious metals hit by stronger dollar
Oil tumbles on Iran hopes, precious metals hit by stronger dollar
-
South Korea football bosses in talks to avert Women's Asian Cup boycott

-
 Level playing field? Tech at forefront of US immigration fight
Level playing field? Tech at forefront of US immigration fight
-
British singer Olivia Dean wins Best New Artist Grammy

-
 Hatred of losing drives relentless Alcaraz to tennis history
Hatred of losing drives relentless Alcaraz to tennis history
-
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga win early at Grammys

-
 Surging euro presents new headache for ECB
Surging euro presents new headache for ECB
-
Djokovic hints at retirement as time seeps away on history bid

-
 US talking deal with 'highest people' in Cuba: Trump
US talking deal with 'highest people' in Cuba: Trump
-
UK ex-ambassador quits Labour over new reports of Epstein links

-
 Trump says closing Kennedy Center arts complex for two years
Trump says closing Kennedy Center arts complex for two years
-
Reigning world champs Tinch, Hocker among Millrose winners

-
 Venezuelan activist ends '1,675 days' of suffering in prison
Venezuelan activist ends '1,675 days' of suffering in prison
-
Real Madrid scrape win over Rayo, Athletic claim derby draw

-
 PSG beat Strasbourg after Hakimi red to retake top spot in Ligue 1
PSG beat Strasbourg after Hakimi red to retake top spot in Ligue 1
-
NFL Cardinals hire Rams' assistant LaFleur as head coach

-
 Arsenal scoop $2m prize for winning FIFA Women's Champions Cup
Arsenal scoop $2m prize for winning FIFA Women's Champions Cup
-
Atletico agree deal to sign Lookman from Atalanta

-
 Real Madrid's Bellingham set for month out with hamstring injury
Real Madrid's Bellingham set for month out with hamstring injury
-
Man City won't surrender in title race: Guardiola

-
 Korda captures weather-shortened LPGA season opener
Korda captures weather-shortened LPGA season opener
-
Czechs rally to back president locking horns with government

-
 Prominent Venezuelan activist released after over four years in jail
Prominent Venezuelan activist released after over four years in jail
-
Emery riled by 'unfair' VAR call as Villa's title hopes fade

-
 Guirassy double helps Dortmund move six points behind Bayern
Guirassy double helps Dortmund move six points behind Bayern
-
Nigeria's president pays tribute to Fela Kuti after Grammys Award

-
 Inter eight clear after win at Cremonese marred by fans' flare flinging
Inter eight clear after win at Cremonese marred by fans' flare flinging
-
England underline World Cup
credentials with series win over Sri Lanka

-
 Guirassy brace helps Dortmund move six behind Bayern
Guirassy brace helps Dortmund move six behind Bayern
-
Man City held by Solanke stunner, Sesko delivers 'best feeling' for Man Utd

-
 'Send Help' debuts atop N.America box office
'Send Help' debuts atop N.America box office
-
Ukraine war talks delayed to Wednesday, says Zelensky

-
 Iguanas fall from trees in Florida as icy weather bites southern US
Iguanas fall from trees in Florida as icy weather bites southern US
-
Carrick revels in 'best feeling' after Man Utd leave it late

-
 Olympic chiefs admit 'still work to do' on main ice hockey venue
Olympic chiefs admit 'still work to do' on main ice hockey venue
-
Pope says Winter Olympics 'rekindle hope' for world peace


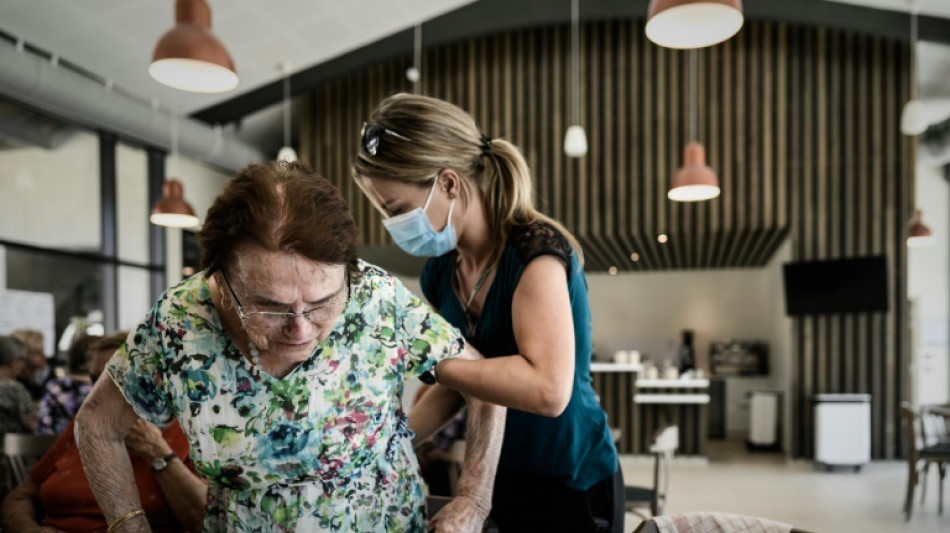
'Remarkable' Alzheimer's drug reduces cognitive decline, study shows
US pharmaceutical giant Eli Lilly on Wednesday announced its experimental Alzheimer's drug significantly slowed cognitive and functional decline, results hailed as "remarkable" by experts despite some patients experiencing serious side effects.
In an analysis of nearly 1,200 people in the early stages of the disease, donanemab slowed the progression of symptoms by 35 percent over a period of 18 months compared to placebo.
This was measured by cognition and their ability to carry out daily tasks like managing finances, driving, engaging in hobbies and conversing about current events in a standardized index called the Integrated Alzheimer's Disease Rating Scale (iADRS).
Side effects included temporary swelling in parts of the brain, which occurred in almost a quarter of the treated patients, as well as microhemorrhages that occurred in 31 percent of patients on the treatment arm and 14 percent of patients in the placebo group.
Two participants' deaths were attributed to the side effects, while a third might have also died from the treatment.
Nonetheless, the data was widely praised by independent experts, who said donanemab had the potential, if approved, to significantly improve the lives of people suffering from the most common form of dementia.
The news comes after the US approved another Alzheimer's drug in January, Biogen and Eisai's lecanemab, which slowed the rate of cognitive decline by 27 percent and was also declared a blockbuster by experts.
Biogen and Eisai had also developed aducanumab, known by the trade Aduhelm, which was given US approval in 2021, though that decision was mired in controversy and led to a damning report by Congress.
In addition to severe side effects, Aduhlem's clinical effectiveness was ambiguous, which is so far not the case for the two subsequent drugs.
Lilly said it would rapidly submit its results to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as well as other global regulators.
"We are extremely pleased that donanemab yielded positive clinical results with compelling statistical significance for people with Alzheimer's disease in this trial," said Daniel Skovronsky, Lilly's chief scientific and medical officer, in a statement.
Mark Mintun, a top Lilly executive in neuroscience R&D, added however that "like many effective treatments for debilitating and fatal diseases, there are associated risks that may be serious and life-threatening."
Eli Lilly's stock price rose 4.3 percent after Wednesday's announcement.
- Targeting amyloid -
In Alzheimer's disease, two key proteins, tau and amyloid beta, build up into tangles and plaques, known together as aggregates, which cause brain cells to die and lead to brain shrinkage.
Like lecanemab (also known by its trade name Leqembi), donanemab is an antibody therapy that targets amyloid beta.
Experts said that the results for both drugs validated the theory that removing amyloid beta does improve the course of the disease, and that future therapies targeting both proteins might have even better outcomes.
Nick Fox, of the UK Dementia Research Institute, said that although the full dataset was not yet available, the results announced by press release "confirms that we are in a new era of disease modification for Alzheimer's disease."
"This clinical trial is a real breakthrough, demonstrating a remarkable 35% slowing of cognitive decline in Alzheimer's patients with high amyloid beta but low tau burden," added Marc Busche, UK Dementia Research Institute group leader at University College London.
"These are the strongest phase 3 data for an Alzheimer's treatment to date," said Maria Carrillo, chief science officer at the US Alzheimer's Association. "This further underscores the inflection point we are at for the Alzheimer's field."
Alzheimer's disease accounts for 60-80 percent of dementia, according to the Alzheimer's Association. It progressively destroys thinking and memory, eventually robbing people of the ability to carry out the simplest of tasks.
F.Wilson--AT