
-
 Surprise appointment Riera named Frankfurt coach
Surprise appointment Riera named Frankfurt coach
-
Maersk to take over Panama Canal port operations from HK firm

-
 US arrests prominent journalist after Minneapolis protest coverage
US arrests prominent journalist after Minneapolis protest coverage
-
Analysts say Kevin Warsh a safe choice for US Fed chair

-
 Trump predicts Iran will seek deal to avoid US strikes
Trump predicts Iran will seek deal to avoid US strikes
-
US oil giants say it's early days on potential Venezuela boom

-
 Fela Kuti to be first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award
Fela Kuti to be first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award
-
Trump says Iran wants deal, US 'armada' larger than in Venezuela raid

-
 US Justice Dept releases new batch of documents, images, videos from Epstein files
US Justice Dept releases new batch of documents, images, videos from Epstein files
-
Four memorable showdowns between Alcaraz and Djokovic

-
 Russian figure skating prodigy Valieva set for comeback -- but not at Olympics
Russian figure skating prodigy Valieva set for comeback -- but not at Olympics
-
Barcelona midfielder Lopez agrees contract extension

-
 Djokovic says 'keep writing me off' after beating Sinner in late-nighter
Djokovic says 'keep writing me off' after beating Sinner in late-nighter
-
US Justice Dept releasing new batch of Epstein files

-
 South Africa and Israel expel envoys in deepening feud
South Africa and Israel expel envoys in deepening feud
-
French eyewear maker in spotlight after presidential showing

-
 Olympic dream 'not over', Vonn says after crash
Olympic dream 'not over', Vonn says after crash
-
Brazil's Lula discharged after cataract surgery

-
 US Senate races to limit shutdown fallout as Trump-backed deal stalls
US Senate races to limit shutdown fallout as Trump-backed deal stalls
-
'He probably would've survived': Iran targeting hospitals in crackdown

-
 Djokovic stuns Sinner to set up Australian Open final with Alcaraz
Djokovic stuns Sinner to set up Australian Open final with Alcaraz
-
Mateta omitted from Palace squad to face Forest

-
 Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump's Fed pick
Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump's Fed pick
-
Trump attorney general orders arrest of ex-CNN anchor covering protests

-
 Djokovic 'pushed to the limit' in stunning late-night Sinner upset
Djokovic 'pushed to the limit' in stunning late-night Sinner upset
-
Tunisia's famed blue-and-white village threatened after record rains

-
 Top EU official voices 'shock' at Minneapolis violence
Top EU official voices 'shock' at Minneapolis violence
-
Kremlin says agreed to halt strikes on Kyiv until Sunday

-
 Carrick calls for calm after flying start to Man Utd reign
Carrick calls for calm after flying start to Man Utd reign
-
Djokovic to meet Alcaraz in Melbourne final after five-set marathon

-
 Italian officials to testify in trial over deadly migrant shipwreck
Italian officials to testify in trial over deadly migrant shipwreck
-
Iran says defence capabilities 'never' up for negotiation

-
 UN appeals for more support for flood-hit Mozambicans
UN appeals for more support for flood-hit Mozambicans
-
Lijnders urges Man City to pile pressure on Arsenal in title race

-
 Fulham sign Man City winger Oscar Bobb
Fulham sign Man City winger Oscar Bobb
-
Strasbourg's Argentine striker Panichelli sets sights on PSG, World Cup

-
 Jesus 'made love': Colombian president irks Christians with steamy claim
Jesus 'made love': Colombian president irks Christians with steamy claim
-
IAEA board meets over Ukraine nuclear safety concerns

-
 Eurozone growth beats 2025 forecasts despite Trump woes
Eurozone growth beats 2025 forecasts despite Trump woes
-
Israel to partially reopen Gaza's Rafah crossing on Sunday

-
 Dutch PM-elect Jetten says not yet time to talk to Putin
Dutch PM-elect Jetten says not yet time to talk to Putin
-
Social media fuels surge in UK men seeking testosterone jabs

-
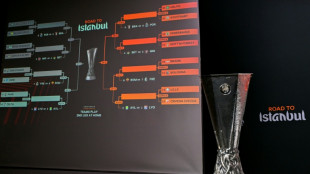 Forest face Fenerbahce, Celtic draw Stuttgart in Europa League play-offs
Forest face Fenerbahce, Celtic draw Stuttgart in Europa League play-offs
-
US speed queen Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics

-
 Trump nominates former US Fed official as next central bank chief
Trump nominates former US Fed official as next central bank chief
-
Alcaraz defends controversial timeout after beaten Zverev fumes

-
 New Dutch government pledges ongoing Ukraine support
New Dutch government pledges ongoing Ukraine support
-
Newcastle still coping with fallout from Isak exit, says Howe

-
 Chad, France eye economic cooperation as they reset strained ties
Chad, France eye economic cooperation as they reset strained ties
-
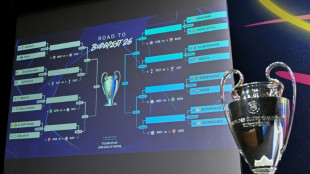
Real Madrid to play Benfica, PSG face Monaco in Champions League play-offs

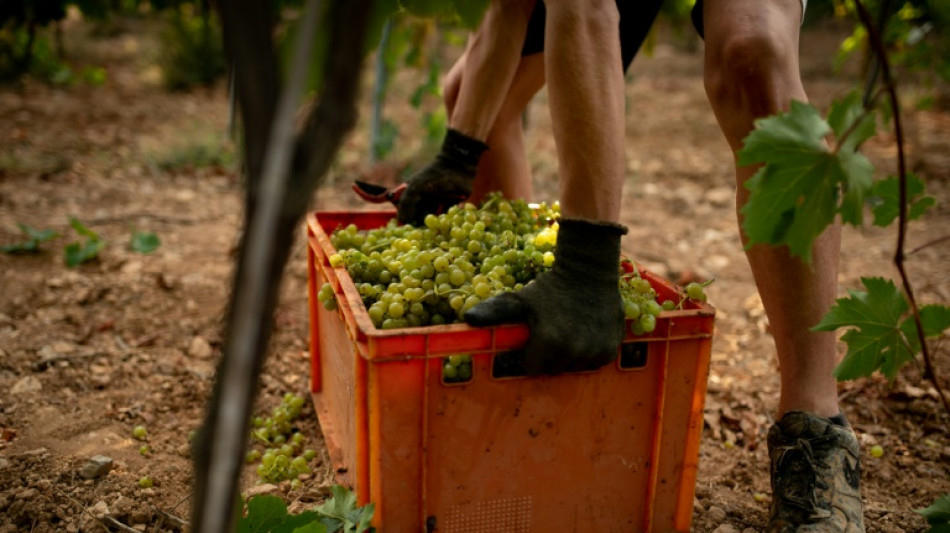
Spain, Portugal dryness 'unprecedented' in 1,200 years
Parts of Portugal and Spain are the driest they have been in a thousand years due to an atmospheric high-pressure system driven by climate change, according to research published Monday, warning of severe implications for wine and olive production.
The Azores High, an area of high pressure that rotates clockwise over parts of the North Atlantic, has a major effect on weather and long-term climate trends in western Europe.
But in a new modelling study published in the journal Nature Geoscience, researchers in the United States found this high-pressure system "has changed dramatically in the past century and that these changes in North Atlantic climate are unprecedented within the past millennium".
Using climate model simulations over the last 1,200 years, the study found that this high-pressure system started to grow to cover a greater area around 200 years ago, as human greenhouse gas pollution began to increase.
It expanded even more dramatically in the 20th century in step with global warming.
The authors then looked at evidence of rainfall levels preserved over hundreds of years in Portuguese stalagmites, and found that as the Azores High has expanded, the winters in the western Mediterranean have become drier.
The study cites projections that the level of precipitation could fall a further 10 to 20 percent by the end of this century, which the authors say would make Iberian agriculture "some of the most vulnerable in Europe".
They warn that the Azores High will continue to expand during the 21st century as greenhouse gas levels rise, leading to an increasing risk of drought on the Iberian Peninsula and threatening key crops.
"Our findings have important implications for projected changes in western Mediterranean hydroclimate throughout the twenty-first century," the authors said.
- Wither vines -
The Azores High acts as a "gatekeeper" for rainfall into Europe, according to the study, with dry air descending in the summer months to cause hot, arid conditions in much of Portugal, Spain and the western Mediterranean.
In the cool, wetter winter period, the high-pressure system swells, sending westerly winds carrying rain inland.
This winter rain is "vital" for both the ecological and economic health of the region, but it has been decreasing, particularly over the second half of the 20th century.
While previous research had not untangled the effects of natural variability on the Azores High, the authors said their findings show its expansion during the industrial era is linked to the rise of atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations.
A study cited in the latest research estimates that the area suitable for grape growing in the Iberian Peninsula could shrink by at least a quarter and potentially vanish almost completely by 2050 because of severe water shortages.
Meanwhile, researchers have predicted a 30-percent drop in production for olive regions in southern Spain by 2100.
Winemakers are already looking for ways to adapt to the changing climate, such as moving vineyards to higher altitudes and experimenting with more heat-tolerant varieties.
Last year, scientists found that a severe spring frost that ravaged grape vines in France was made more likely by climate change, with the plants budding earlier and therefore more susceptible to damage.
K.Hill--AT




