-
 Russian figure skating prodigy Valieva set for comeback -- but not at Olympics
Russian figure skating prodigy Valieva set for comeback -- but not at Olympics
-
Barcelona midfielder Lopez agrees contract extension

-
 Djokovic says 'keep writing me off' after beating Sinner in late-nighter
Djokovic says 'keep writing me off' after beating Sinner in late-nighter
-
US Justice Dept releasing new batch of Epstein files

-
 South Africa and Israel expel envoys in deepening feud
South Africa and Israel expel envoys in deepening feud
-
French eyewear maker in spotlight after presidential showing

-
 Olympic dream 'not over', Vonn says after crash
Olympic dream 'not over', Vonn says after crash
-
Brazil's Lula discharged after cataract surgery

-
 US Senate races to limit shutdown fallout as Trump-backed deal stalls
US Senate races to limit shutdown fallout as Trump-backed deal stalls
-
'He probably would've survived': Iran targeting hospitals in crackdown

-
 Djokovic stuns Sinner to set up Australian Open final with Alcaraz
Djokovic stuns Sinner to set up Australian Open final with Alcaraz
-
Mateta omitted from Palace squad to face Forest

-
 Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump's Fed pick
Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump's Fed pick
-
Trump attorney general orders arrest of ex-CNN anchor covering protests

-
 Djokovic 'pushed to the limit' in stunning late-night Sinner upset
Djokovic 'pushed to the limit' in stunning late-night Sinner upset
-
Tunisia's famed blue-and-white village threatened after record rains

-
 Top EU official voices 'shock' at Minneapolis violence
Top EU official voices 'shock' at Minneapolis violence
-
Kremlin says agreed to halt strikes on Kyiv until Sunday

-
 Carrick calls for calm after flying start to Man Utd reign
Carrick calls for calm after flying start to Man Utd reign
-
Djokovic to meet Alcaraz in Melbourne final after five-set marathon

-
 Italian officials to testify in trial over deadly migrant shipwreck
Italian officials to testify in trial over deadly migrant shipwreck
-
Iran says defence capabilities 'never' up for negotiation

-
 UN appeals for more support for flood-hit Mozambicans
UN appeals for more support for flood-hit Mozambicans
-
Lijnders urges Man City to pile pressure on Arsenal in title race

-
 Fulham sign Man City winger Oscar Bobb
Fulham sign Man City winger Oscar Bobb
-
Strasbourg's Argentine striker Panichelli sets sights on PSG, World Cup

-
 Jesus 'made love': Colombian president irks Christians with steamy claim
Jesus 'made love': Colombian president irks Christians with steamy claim
-
IAEA board meets over Ukraine nuclear safety concerns

-
 Eurozone growth beats 2025 forecasts despite Trump woes
Eurozone growth beats 2025 forecasts despite Trump woes
-
Israel to partially reopen Gaza's Rafah crossing on Sunday

-
 Dutch PM-elect Jetten says not yet time to talk to Putin
Dutch PM-elect Jetten says not yet time to talk to Putin
-
Social media fuels surge in UK men seeking testosterone jabs

-
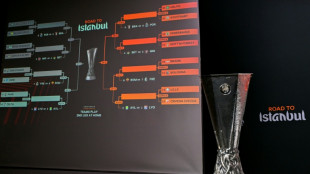 Forest face Fenerbahce, Celtic draw Stuttgart in Europa League play-offs
Forest face Fenerbahce, Celtic draw Stuttgart in Europa League play-offs
-
US speed queen Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics

-
 Trump nominates former US Fed official as next central bank chief
Trump nominates former US Fed official as next central bank chief
-
Alcaraz defends controversial timeout after beaten Zverev fumes

-
 New Dutch government pledges ongoing Ukraine support
New Dutch government pledges ongoing Ukraine support
-
Newcastle still coping with fallout from Isak exit, says Howe

-
 Chad, France eye economic cooperation as they reset strained ties
Chad, France eye economic cooperation as they reset strained ties
-
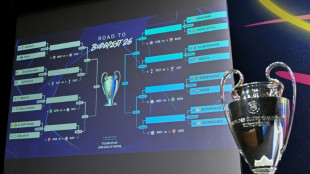
Real Madrid to play Benfica, PSG face Monaco in Champions League play-offs
-
 Everton winger Grealish set to miss rest of season in World Cup blow
Everton winger Grealish set to miss rest of season in World Cup blow
-
Trump brands Minneapolis nurse killed by federal agents an 'agitator'

-
 Arteta focuses on the positives despite Arsenal stumble
Arteta focuses on the positives despite Arsenal stumble
-
Fijian Drua sign France international back Vakatawa

-
 Kevin Warsh, a former Fed 'hawk' now in tune with Trump
Kevin Warsh, a former Fed 'hawk' now in tune with Trump
-
Zverev rails at Alcaraz timeout in 'one of the best battles ever'

-
 Turkey leads Iran diplomatic push as Trump softens strike threat
Turkey leads Iran diplomatic push as Trump softens strike threat
-
Zelensky backs energy ceasefire, Russia bombs Ukraine despite Trump intervention

-
 'Superman' Li Ka-shing, Hong Kong billionaire behind Panama ports deal
'Superman' Li Ka-shing, Hong Kong billionaire behind Panama ports deal
-
Skiing great Lindsey Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics

| SCS | 0.12% | 16.14 | $ | |
| JRI | 0.27% | 12.99 | $ | |
| RBGPF | 1.65% | 83.78 | $ | |
| BCC | -1.24% | 79.185 | $ | |
| CMSC | -0.02% | 23.69 | $ | |
| RYCEF | -2.69% | 16 | $ | |
| RELX | -1.56% | 35.61 | $ | |
| NGG | -0.65% | 84.5 | $ | |
| BCE | -0.08% | 25.465 | $ | |
| RIO | -4.67% | 90.885 | $ | |
| GSK | 1.19% | 51.265 | $ | |
| AZN | 0.55% | 93.1 | $ | |
| CMSD | 0.04% | 24.07 | $ | |
| VOD | -0.58% | 14.625 | $ | |
| BTI | -0.11% | 60.145 | $ | |
| BP | -0.67% | 37.785 | $ |

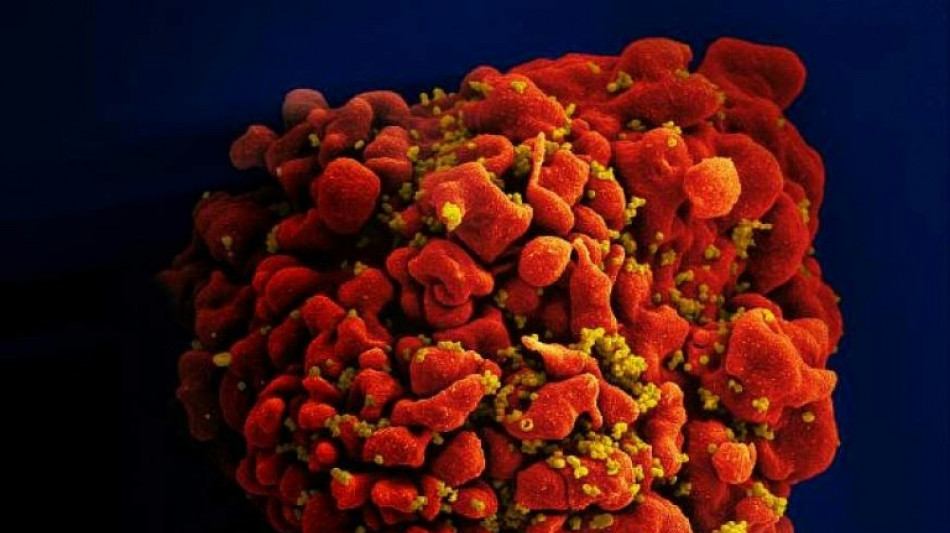
New 'highly virulent' HIV strain discovered in the Netherlands
Oxford researchers announced Thursday the discovery of a highly virulent strain of HIV that has been lurking in the Netherlands for decades, but because of the effectiveness of modern treatments, is "no cause for alarm."
Their analysis, published Thursday in the journal "Science," showed that patients infected with what they call the "VB variant" had 3.5 to 5.5 times higher levels of the virus in their blood than those infected with other variants, as well as a more rapidly fading immune system.
However, the study also found that after starting treatment, individuals with the VB variant had similar immune system recovery and survival to individuals with other HIV variants.
"There's no cause for alarm with this new viral variant," said Oxford epidemiologist Chris Wymant, the lead author on the paper, in an interview with AFP.
The variant likely arose in the late 1980s and early 1990s in the Netherlands, according to the researchers, but began to decline around 2010.
Since modern interventions still seem to work on the variant, the research team believes that widespread HIV treatment in the Netherlands did not contribute to the virus's evolution, and that early detection and treatment are paramount.
"Our findings emphasize the importance of World Health Organization guidance that individuals at risk of acquiring HIV have access to regular testing to allow early diagnosis, followed by immediate treatment," said co-author Christophe Fraser, also an Oxford researcher, in a press release announcing the findings.
The work also supports the theory that viruses can evolve to become more virulent, a widely-hypothesized idea for which few real-world examples have been found.
The Delta variant of the novel coronavirus was another recent example.
The discovery of the HIV variant should therefore "be a warning that we should never be overconfident about saying viruses will just evolve to become milder," said Wymant to AFP.
In total, the team found 109 people infected with the VB variant, with only four living outside the Netherlands, but still in western Europe.
- 500 mutations -
The HIV virus is constantly evolving, so much so that each person infected has a slightly different version.
The VB variant, however, was found to have over 500 mutations.
"Finding a new variant is normal, but finding a new variant with unusual properties is not -- especially one with increased virulence," Wyman explained.
The research team first identified the VB variant in 17 HIV positive individuals by parsing a broad data set from the BEEHIVE project, a data collection and analysis initiative in Europe and Uganda.
Because 15 of the 17 were from the Netherlands, they further studied data from 6,700 HIV-positive Dutch individuals, identifying 92 others.
The earliest appearance of the VB variant in their data was found in someone diagnosed in 1992 who had an early version of the variant, and the most recent in 2014.
Other researchers have since found other individuals with the variant diagnosed after 2014.
Doctors usually measure HIV's deterioration of the immune system by monitoring the decline of CD4 T-cells, which are targeted by the HIV virus and pivotal for protecting the body against infections.
In patients infected with the VB variant, CD4 decline occurred twice as fast compared to other variants, "placing them at risk of developing AIDS much more rapidly," the researchers said.
In addition to its increased impact on the immune system, the team also found the VB variant to be more highly transmissible.
They came to that conclusion after comparing the different versions of the VB variant drawn from infected patients.
The fact that they were so similar suggests that the virus passed rapidly to someone else before it could accumulate many mutations.
- 'Critical' to diagnose and treat early -
"Because the VB variant causes a more rapid decline in immune system strength, this makes it critical that individuals are diagnosed early and start treatment as soon as possible," the press statement noted.
"This limits the amount of time HIV can damage an individual's immune system and jeopardize their health," added Fraser.
Fraser is also the principal investigator of the BEEHIVE project, which was launched in 2014 to gather data on how mutations in the HIV virus can lead to varying degrees of severity among patients.
Those differences have previously been thought to mostly relate to the strength of individuals' own immune systems.
The researchers said they could not identify which genetic mutation in the VB variant caused its virulence, but they hope future studies will be able to.
F.Ramirez--AT




