
-
 Stocks advance as markets cheer weak inflation
Stocks advance as markets cheer weak inflation
-
Emery says rising expectations driving red-hot Villa

-
 Three killed in Taipei metro attacks, suspect dead
Three killed in Taipei metro attacks, suspect dead
-
Seven Colombian soldiers killed in guerrilla attack: army

-
 Amorim takes aim at Man Utd youth stars over 'entitlement'
Amorim takes aim at Man Utd youth stars over 'entitlement'
-
Mercosur meets in Brazil, EU eyes January 12 trade deal

-
 US Fed official says no urgency to cut rates, flags distorted data
US Fed official says no urgency to cut rates, flags distorted data
-
Rome to charge visitors for access to Trevi Fountain

-
 Spurs 'not a quick fix' for under-fire Frank
Spurs 'not a quick fix' for under-fire Frank
-
Poland president accuses Ukraine of not appreciating war support

-
 Stocks advance with focus on central banks, tech
Stocks advance with focus on central banks, tech
-
Amorim unfazed by 'Free Mainoo' T-shirt ahead of Villa clash

-
 PSG penalty hero Safonov ended Intercontinental win with broken hand
PSG penalty hero Safonov ended Intercontinental win with broken hand
-
French court rejects Shein suspension
-
 'It's so much fun,' says Vonn as she milks her comeback
'It's so much fun,' says Vonn as she milks her comeback
-
Moscow intent on pressing on in Ukraine: Putin

-
 UN declares famine over in Gaza, says 'situation remains critical'
UN declares famine over in Gaza, says 'situation remains critical'
-
Guardiola 'excited' by Man City future, not pondering exit

-
 Zabystran upsets Odermatt to claim first World Cup win in Val Gardena super-G
Zabystran upsets Odermatt to claim first World Cup win in Val Gardena super-G
-
Czechs name veteran coach Koubek for World Cup play-offs

-
 PSG penalty hero Safonov out until next year with broken hand
PSG penalty hero Safonov out until next year with broken hand
-
Putin says ball in court of Russia's opponents in Ukraine talks

-
 Czech Zabystran upsets Odermatt to claim Val Gardena super-G
Czech Zabystran upsets Odermatt to claim Val Gardena super-G
-
NGOs fear 'catastrophic impact' of new Israel registration rules

-
 US suspends green card lottery after MIT professor, Brown University killings
US suspends green card lottery after MIT professor, Brown University killings
-
Stocks mixed with focus on central banks, tech

-
 Arsenal in the 'right place' as Arteta marks six years at club
Arsenal in the 'right place' as Arteta marks six years at club
-
Sudan's El-Fasher under the RSF, destroyed and 'full of bodies'

-
 From farms to court, climate-hit communities take on big polluters
From farms to court, climate-hit communities take on big polluters
-
Liverpool have 'moved on' from Salah furore, says upbeat Slot

-
 Norway crown princess likely to undergo lung transplant
Norway crown princess likely to undergo lung transplant
-
Iraq negotiates new coalition under US pressure

-
 France's budget hits snag in setback for embattled PM
France's budget hits snag in setback for embattled PM
-
Putin hails Ukraine gains, threatens more, in annual press conference

-
 US suspends green card lottery after Brown, MIT professor shootings
US suspends green card lottery after Brown, MIT professor shootings
-
Chelsea's Maresca says Man City link '100 percent' speculation

-
 Dominant Head moves into Bradman territory with fourth Adelaide ton
Dominant Head moves into Bradman territory with fourth Adelaide ton
-
Arsenal battle to stay top of Christmas charts

-
 Mexican low-cost airlines Volaris and Viva agree to merger
Mexican low-cost airlines Volaris and Viva agree to merger
-
Border casinos caught in Thailand-Cambodia crossfire

-
 Australia's Head slams unbeaten 142 to crush England's Ashes hopes
Australia's Head slams unbeaten 142 to crush England's Ashes hopes
-
Epstein files due as US confronts long-delayed reckoning

-
 'Not our enemy': Rush to rearm sparks backlash in east Germany
'Not our enemy': Rush to rearm sparks backlash in east Germany
-
West Indies 110-0, trail by 465, after Conway's epic 227 for New Zealand

-
 Arsonists target Bangladesh newspapers after student leader's death
Arsonists target Bangladesh newspapers after student leader's death
-
Volatile Oracle shares a proxy for Wall Street's AI jitters

-
 Tears at tribute to firefighter killed in Hong Kong blaze
Tears at tribute to firefighter killed in Hong Kong blaze
-
Seahawks edge Rams in overtime thriller to seize NFC lead

-
 Teenager Flagg leads Mavericks to upset of Pistons
Teenager Flagg leads Mavericks to upset of Pistons
-
Australia's Head fires quickfire 68 as England's Ashes hopes fade


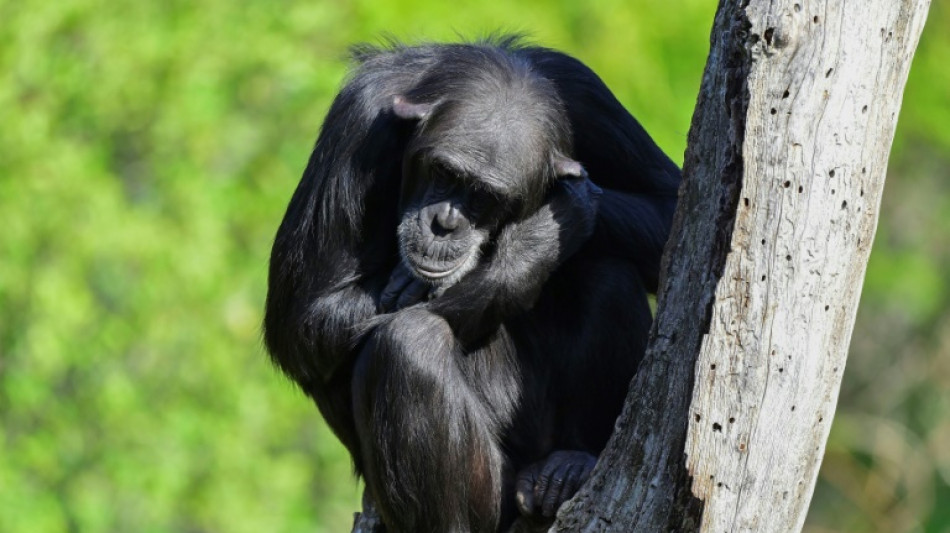
Chimps are upping their tool game, says study
"Planet of the Apes" may have been onto something.
Chimpanzees are steadily honing their tool-using skills -- a process unfolding over millennia, driven by the exchange of ideas through migrations between populations, according to a new study published Thursday in Science.
The finding in chimps -- humans' closest living relatives -- holds relevance for us too, as it supports the idea that, deep in the mists of time, our own ape ancestors leveraged social connections to improve their technologies, lead author Cassandra Gunasekaram told AFP.
Scientists have long marveled at chimps' ability to pass down intricate behaviors, like tool use, from one generation to the next.
Yet while human civilization has leapt from the Stone Age to the Space Age, chimpanzee "culture" -- defined as socially learned behaviors -- seemed to have remained static.
Gunasekaram, a doctoral student at the University of Zurich, set out to challenge this assumption.
- Connections spark innovation -
She and colleagues combined genetic data tracing ancient chimpanzee migrations across Africa with observations of 15 distinct foraging behaviors across dozens of populations and the four subspecies.
These behaviors were categorized into three levels: those requiring no tools, those with simple tools, like using chewed leaves as a sponge to absorb water from tree holes, and the most complex, which involve toolsets.
One striking example of toolset use comes from Congo, where chimps use a stout stick to bore a tunnel into the ground to reach a termite nest, then modify a plant stem by chewing its tip into a brush to "fish" for termites in the tunnel they've made.
The study found that advanced tool use strongly correlated with populations connected by genetic exchanges over the last 5,000–15,000 years, suggesting such behaviors spread when groups interacted.
Areas where three subspecies overlap exhibited the most complex tool use, highlighting how cross-group connections foster cultural knowledge.
By contrast, simpler behaviors, such as foraging without tools, seemed less tied to migration and likely evolved independently in different regions.
- Foraging efficiently -
Gunasekaram said this mirrors how trading ideas and incremental innovation have been critical to human technological progress, taking us from early abacuses to modern smartphones.
"They've become so complex that one person alone could not reinvent them from scratch," she said.
But unlike humans, chimps have far fewer opportunities to encounter new individuals and ideas -- migrations occur gradually, driven by sexually mature females moving to new communities to avoid inbreeding.
Analyzing ancient genetic flows helped the team overcome one of the biggest challenges in studying the evolution of chimpanzee culture: the limited window of observation, as the species has only been researched scientifically for about a century.
What's more, "Chimpanzee tools are made of sticks and stems, which are all perishable," Gunasekaram explained, making it nearly impossible to trace how their artifacts have evolved over time.
So, will chimps one day rival human ingenuity? Hardly. But given enough time, they could become more efficient foragers.
For example, some populations are already more advanced in cracking nuts with hammers and anvils made of stone , and one particularly innovative group has even invented a stabilizer for the anvil, said Gunasekaram.
P.Smith--AT



