
-
 Ukraine, US to meet for third day, agree 'real progress' depends on Russia
Ukraine, US to meet for third day, agree 'real progress' depends on Russia
-
Double wicket strike as New Zealand eye victory over West Indies

-
 Peace medal and YMCA: Trump steals the show at World Cup draw
Peace medal and YMCA: Trump steals the show at World Cup draw
-
NBA legend Jordan in court as NASCAR anti-trust case begins

-
 How coaches reacted to 2026 World Cup draw
How coaches reacted to 2026 World Cup draw
-
Glasgow down Sale as Stomers win at Bayonne in Champions Cup

-
 Trump takes aim at Europe in new security strategy
Trump takes aim at Europe in new security strategy
-
Witness in South Africa justice-system crimes probe shot dead

-
 Tuchel urges England not to get carried away plotting route to World Cup glory
Tuchel urges England not to get carried away plotting route to World Cup glory
-
Russian ambassador slams EU frozen assets plan for Ukraine

-
 2026 World Cup draw is kind to favorites as Trump takes limelight
2026 World Cup draw is kind to favorites as Trump takes limelight
-
WHO chief upbeat on missing piece of pandemic treaty
-
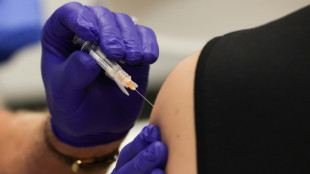
 US vaccine panel upends hepatitis B advice in latest Trump-era shift
US vaccine panel upends hepatitis B advice in latest Trump-era shift
-
Ancelotti says Brazil have 'difficult' World Cup group with Morocco

-
 Kriecmayr wins weather-disrupted Beaver Creek super-G
Kriecmayr wins weather-disrupted Beaver Creek super-G
-
Ghostwriters, polo shirts, and the fall of a landmark pesticide study

-
 Mixed day for global stocks as market digest huge Netflix deal
Mixed day for global stocks as market digest huge Netflix deal
-
Fighting erupts in DR Congo a day after peace deal signed

-
 England boss Tuchel wary of 'surprise' in World Cup draw
England boss Tuchel wary of 'surprise' in World Cup draw
-
10 university students die in Peru restaurant fire

-
 'Sinners' tops Critics Choice nominations
'Sinners' tops Critics Choice nominations
-
Netflix's Warner Bros. acquisition sparks backlash

-
 France probes mystery drone flight over nuclear sub base
France probes mystery drone flight over nuclear sub base
-
Frank Gehry: five key works

-
 US Supreme Court to weigh Trump bid to end birthright citizenship
US Supreme Court to weigh Trump bid to end birthright citizenship
-
Frank Gehry, master architect with a flair for drama, dead at 96

-
 'It doesn't make sense': Trump wants to rename American football
'It doesn't make sense': Trump wants to rename American football
-
A day after peace accord signed, shelling forces DRC locals to flee

-
 Draw for 2026 World Cup kind to favorites as Trump takes center stage
Draw for 2026 World Cup kind to favorites as Trump takes center stage
-
Netflix to buy Warner Bros. in deal of the decade

-
 US sanctions equate us with drug traffickers: ICC dep. prosecutor
US sanctions equate us with drug traffickers: ICC dep. prosecutor
-
Migration and crime fears loom over Chile's presidential runoff

-
 French officer charged after police fracture woman's skull
French officer charged after police fracture woman's skull
-
Fresh data show US consumers still strained by inflation
-
 Eurovision reels from boycotts over Israel
Eurovision reels from boycotts over Israel
-
Trump takes centre stage as 2026 World Cup draw takes place

-
 Trump all smiles as he wins FIFA's new peace prize
Trump all smiles as he wins FIFA's new peace prize
-
US panel votes to end recommending all newborns receive hepatitis B vaccine

-
 Title favourite Norris reflects on 'positive' Abu Dhabi practice
Title favourite Norris reflects on 'positive' Abu Dhabi practice
-
Stocks consolidate as US inflation worries undermine Fed rate hopes

-
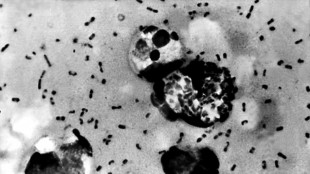 Volcanic eruptions may have brought Black Death to Europe
Volcanic eruptions may have brought Black Death to Europe
-
Arsenal the ultimate test for in-form Villa, says Emery

-
 Emotions high, hope alive after Nigerian school abduction
Emotions high, hope alive after Nigerian school abduction
-
Another original Hermes Birkin bag sells for $2.86 mn

-
 11 million flock to Notre-Dame in year since rising from devastating fire
11 million flock to Notre-Dame in year since rising from devastating fire
-
Gymnast Nemour lifts lid on 'humiliation, tears' on way to Olympic gold

-
 Lebanon president says country does not want war with Israel
Lebanon president says country does not want war with Israel
-
France takes anti-drone measures after flight over nuclear sub base

-
 Signing up to DR Congo peace is one thing, delivery another
Signing up to DR Congo peace is one thing, delivery another
-
'Amazing' figurines find in Egyptian tomb solves mystery


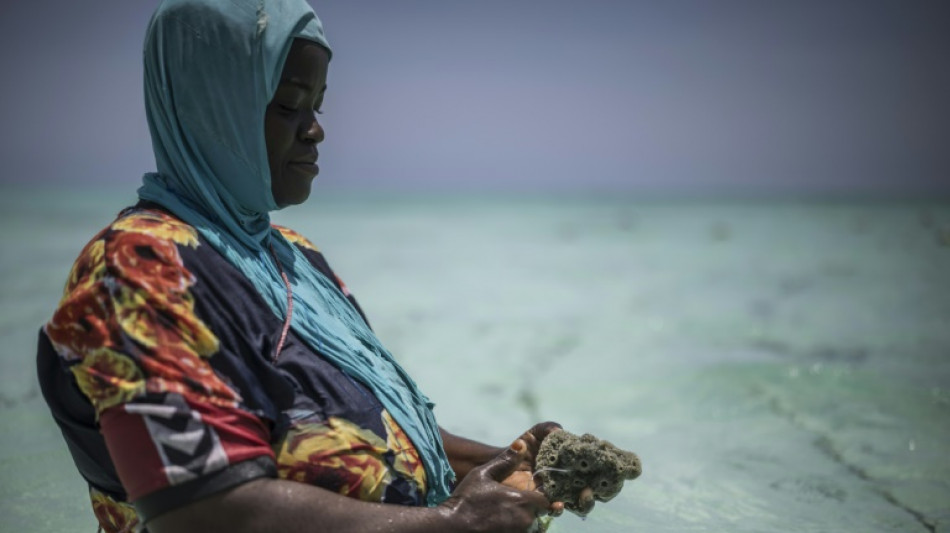
Zanzibar women turn to sponge farming as oceans heat up
Around 10 in the morning each day, women in hijabs and loose long dresses wade through Zanzibar's turquoise shallow tides to tend their sponge farms -- a new lifeline after climate change upended their former work.
Rising ocean temperatures, overfishing, and pollution have steadily degraded marine ecosystems around the island, undermining a key source of income for locals in Jambiani village who long depended on farming seaweed.
Instead, they have turned to sponge cultivation under a project set up by Swiss NGO Marine Cultures.
Hot temperatures have killed seaweed, and declining fish stocks have driven many fishermen to quit, said project manager Ali Mahmudi.
But sponges -- which provide shelter and food for sea creatures -- tend to thrive in warmer waters.
They are also lucrative as an organic personal care product, used for skin exfoliation. Depending on size, they can fetch up to $30 each and a single farm can have as many as 1,500 sponges.
From the shore, black sticks can be seen jutting out of the water, holding lines of sponges.
"I was shocked to learn that sponges exist in the ocean," Nasiri Hassan Haji, 53, told AFP, recalling when she first learned about the practice more than a decade ago.
The mother-of-four once farmed seaweed, describing the work as labour-intensive with meagre returns.
In 2009, Marine Cultures launched a pilot farm with widowed women in Jambiani to test their potential in the archipelago, where more than a quarter of the 1.9 million population live below the poverty line.
With demand for eco-friendly products on the rise, the market has grown steadily, with the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration estimating the value of the natural sponge market at $20 million in 2020.
"It has changed my life, I have been able to build my own house," said 53-year-old Shemsa Abbasi Suleiman, smiling with pride.
Many other women have now joined a cooperative to expand the project, but it was not always smooth sailing.
"At first I was afraid of getting into it because I did not know how to swim. Many discouraged me saying the water is too much and I will die," said Haji.
Thanks to an NGO programme, she learned to swim at the age of 39.
- Sponges restore coral reefs -
As well as making money for locals, sponges are beneficial to the marine environment.
Studies show that a sponge's skeletal structure aids carbon recycling within coral reef ecosystems, while its porous body naturally filters and purifies seawater.
An estimated 60 percent of the world's marine ecosystems have been degraded or are being used unsustainably, according to the United Nations, which warns that the "ocean is in deep crisis".
Sponges are also known to help restore coral reefs, which support 25 percent of marine life and are currently under threat.
"What attracted me to this is the fact that we are not destroying the environment," said Haji.
G.P.Martin--AT
