-
 Sea of colour as Malaysia's Hindus mark Thaipusam with piercings and prayer
Sea of colour as Malaysia's Hindus mark Thaipusam with piercings and prayer
-
Exiled Tibetans choose leaders for lost homeland

-
 Afghan returnees in Bamiyan struggle despite new homes
Afghan returnees in Bamiyan struggle despite new homes
-
Mired in economic trouble, Bangladesh pins hopes on election boost

-
 Chinese cash in jewellery at automated gold recyclers as prices soar
Chinese cash in jewellery at automated gold recyclers as prices soar
-
Israel to partially reopen Gaza's Rafah crossing

-
 'Quiet assassin' Rybakina targets world number one after Melbourne win
'Quiet assassin' Rybakina targets world number one after Melbourne win
-
Deportation raids drive Minneapolis immigrant family into hiding

-
 Nvidia boss insists 'huge' investment in OpenAI on track
Nvidia boss insists 'huge' investment in OpenAI on track
-
'Immortal' Indian comics keep up with changing times

-
 With Trump mum, last US-Russia nuclear pact set to end
With Trump mum, last US-Russia nuclear pact set to end
-
In Sudan's old port of Suakin, dreams of a tourism revival

-
 Narco violence dominates as Costa Rica votes for president
Narco violence dominates as Costa Rica votes for president
-
Snowstorm barrels into southern US as blast of icy weather widens

-
 LA Olympic chief 'deeply regrets' flirty Maxwell emails in Epstein files
LA Olympic chief 'deeply regrets' flirty Maxwell emails in Epstein files
-
Rose powers to commanding six-shot lead at Torrey Pines

-
 Barca wasteful but beat Elche to extend Liga lead
Barca wasteful but beat Elche to extend Liga lead
-
Konate cut short compassionate leave to ease Liverpool injury crisis

-
 Separatist attacks in Pakistan kill 33, dozens of militants dead
Separatist attacks in Pakistan kill 33, dozens of militants dead
-
Dodgers manager Roberts says Ohtani won't pitch in Classic

-
 Arsenal stretch Premier League lead as Chelsea, Liverpool stage comebacks
Arsenal stretch Premier League lead as Chelsea, Liverpool stage comebacks
-
Korda defies cold and wind to lead LPGA opener

-
 New head of US mission in Venezuela arrives as ties warm
New head of US mission in Venezuela arrives as ties warm
-
Barca triumph at Elche to extend Liga lead

-
 Ekitike, Wirtz give Liverpool sight of bright future in Newcastle win
Ekitike, Wirtz give Liverpool sight of bright future in Newcastle win
-
West Indies 'tick boxes' in shortened T20 against South Africa

-
 Chelsea have something 'special' says Rosenior
Chelsea have something 'special' says Rosenior
-
De Zerbi 'ready to go to war' to solve Marseille troubles

-
 Hornets hold off Wemby's Spurs for sixth NBA win in a row
Hornets hold off Wemby's Spurs for sixth NBA win in a row
-
Moyes blasts killjoy booking after Everton's late leveller

-
 Ex-prince Andrew again caught up in Epstein scandal
Ex-prince Andrew again caught up in Epstein scandal
-
Bayern held at Hamburg to open door for Dortmund

-
 Atletico stumble to draw at Levante, Villarreal held
Atletico stumble to draw at Levante, Villarreal held
-
Chelsea stage impressive fightback to beat West Ham

-
 Arsenal stretch Premier League lead, Chelsea fightback breaks Hammers' hearts
Arsenal stretch Premier League lead, Chelsea fightback breaks Hammers' hearts
-
Napoli edge Fiorentina as injury crisis deepens

-
 How Lego got swept up in US-Mexico trade frictions
How Lego got swept up in US-Mexico trade frictions
-
UK rights campaigner Tatchell arrested at pro-Palestinian protest

-
 Iran says progress made towards US talks despite attack jitters
Iran says progress made towards US talks despite attack jitters
-
'Empowering': Ireland's first female sumo wrestler blazes a trail

-
 US judge denies Minnesota bid to suspend immigration sweeps
US judge denies Minnesota bid to suspend immigration sweeps
-
Ukraine hit by mass power outages after 'technical malfunction'

-
 AC Milan prolong France 'keeper Maignan deal by five years
AC Milan prolong France 'keeper Maignan deal by five years
-
Arteta hails Arsenal's statement rout of Leeds

-
 Marseille buckle as Paris FC battle back for draw
Marseille buckle as Paris FC battle back for draw
-
Protesters demand 'justice' one month after Swiss bar fire

-
 Philadelphia's Paul George gets 25-game NBA drugs ban
Philadelphia's Paul George gets 25-game NBA drugs ban
-
La Rochelle suffer defeat after shock Atonio retirement

-
 'It wasn't working': Canada province ends drug decriminalization
'It wasn't working': Canada province ends drug decriminalization
-
Kishan, Arshdeep star as India down New Zealand in T20 finale


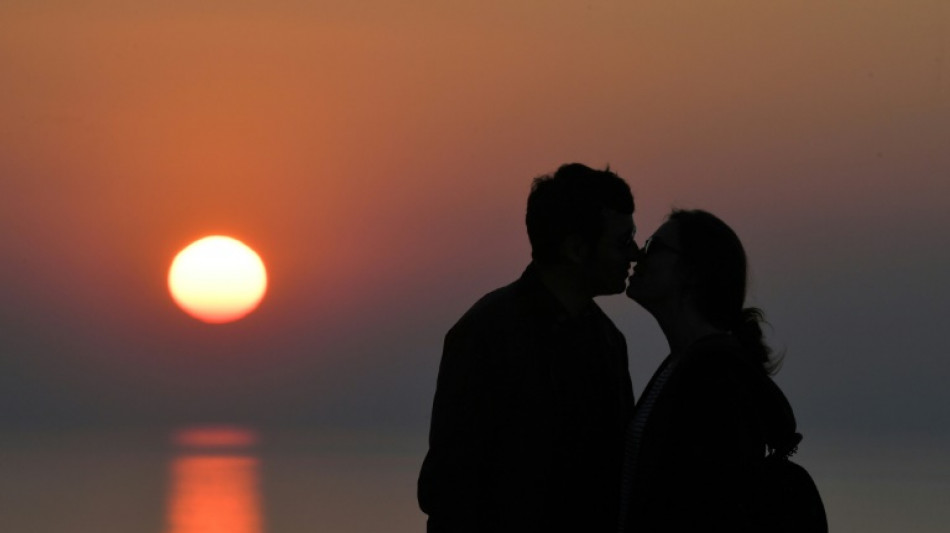
First kisses may have helped spread cold sore virus
The modern strain of the virus that causes cold sores has been traced back to around 5,000 years ago, with researchers suggesting its spread could have been propelled by the emergence of kissing.
Around 3.7 billion people -- the majority of the world's population -- have a life-long infection of the HSV-1 virus behind facial herpes, according to the World Health Organization.
But despite its ubiquity, relatively little has been known about the history of this virus, or how it spread throughout the world.
So an international team of researchers screened the DNA of teeth in hundreds of people from ancient archaeological finds.
They found four people who had the virus when they died, then sequenced their genomes for research published in the journal Science Advances on Wednesday.
"Using these reconstructed genomes, we were able to determine that the variations of modern strains all trace back to some time in the late Neolithic, early Bronze Age," said the study's co-senior author Christiana Scheib of Cambridge University.
"This was a bit surprising because it has been assumed that herpes is something that has co-evolved with humans for a very long time," she told AFP.
- Never been kissed -
She said that was still true: all primate species have a form of herpes and humans likely had a strain when they first left Africa.
But the research indicated that those earlier strains were replaced by the modern form around 5,000 years ago.
So what brought about that change? The researchers suggested two theories.
Around 5,000 years ago was a time of great migration from Eurasia into Europe, and that spread could have affected the virus.
The other theory? That was around the time when people starting romantically kissing each other.
"That is definitely one way to change the transferability of a herpes virus," Scheib said.
The virus is normally passed by a parent to their child, but kissing would have given it a whole new way to jump between hosts, she said.
"There is some textual evidence starting to show in the Bronze Age of kissing between romantic partners," Scheib said.
- 'Far grander' -
The researchers said the earliest known record of kissing was a manuscript from South Asia during the Bronze Age, suggesting the custom may have also migrated from Eurasia into Europe.
Kissing "is not a universal human trait," Scheib pointed out, emphasising that it is difficult to trace exactly when it began -- or if it is definitively linked to the spread of HSV-1.
Around 2,000 years ago, the Roman Emperor Tiberius was believed to have attempted to ban kissing at official functions to prevent the spread of herpes.
Co-senior study author Charlotte Houldcroft, also from Cambridge, said that a virus like herpes evolves on a "far grander timescale" than Covid-19, which the world has watched mutate in a matter of months.
"Facial herpes hides in its host for life and only transmits through oral contact, so mutations occur slowly over centuries and millennia," she said.
"Previously, genetic data for herpes only went back to 1925," she added, calling for more "deep time investigations" of viruses.
"Only genetic samples that are hundreds or even thousands of years old will allow us to understand how DNA viruses such as herpes and monkeypox, as well as our own immune systems, are adapting in response to each other."
R.Garcia--AT