-
 Trump says Iran wants deal, US 'armada' larger than in Venezuela raid
Trump says Iran wants deal, US 'armada' larger than in Venezuela raid
-
US Justice Dept releases new batch of documents, images, videos from Epstein files

-
 Four memorable showdowns between Alcaraz and Djokovic
Four memorable showdowns between Alcaraz and Djokovic
-
Russian figure skating prodigy Valieva set for comeback -- but not at Olympics

-
 Barcelona midfielder Lopez agrees contract extension
Barcelona midfielder Lopez agrees contract extension
-
Djokovic says 'keep writing me off' after beating Sinner in late-nighter

-
 US Justice Dept releasing new batch of Epstein files
US Justice Dept releasing new batch of Epstein files
-
South Africa and Israel expel envoys in deepening feud

-
 French eyewear maker in spotlight after presidential showing
French eyewear maker in spotlight after presidential showing
-
Olympic dream 'not over', Vonn says after crash

-
 Brazil's Lula discharged after cataract surgery
Brazil's Lula discharged after cataract surgery
-
US Senate races to limit shutdown fallout as Trump-backed deal stalls

-
 'He probably would've survived': Iran targeting hospitals in crackdown
'He probably would've survived': Iran targeting hospitals in crackdown
-
Djokovic stuns Sinner to set up Australian Open final with Alcaraz

-
 Mateta omitted from Palace squad to face Forest
Mateta omitted from Palace squad to face Forest
-
Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump's Fed pick

-
 Trump attorney general orders arrest of ex-CNN anchor covering protests
Trump attorney general orders arrest of ex-CNN anchor covering protests
-
Djokovic 'pushed to the limit' in stunning late-night Sinner upset

-
 Tunisia's famed blue-and-white village threatened after record rains
Tunisia's famed blue-and-white village threatened after record rains
-
Top EU official voices 'shock' at Minneapolis violence

-
 Kremlin says agreed to halt strikes on Kyiv until Sunday
Kremlin says agreed to halt strikes on Kyiv until Sunday
-
Carrick calls for calm after flying start to Man Utd reign

-
 Djokovic to meet Alcaraz in Melbourne final after five-set marathon
Djokovic to meet Alcaraz in Melbourne final after five-set marathon
-
Italian officials to testify in trial over deadly migrant shipwreck

-
 Iran says defence capabilities 'never' up for negotiation
Iran says defence capabilities 'never' up for negotiation
-
UN appeals for more support for flood-hit Mozambicans

-
 Lijnders urges Man City to pile pressure on Arsenal in title race
Lijnders urges Man City to pile pressure on Arsenal in title race
-
Fulham sign Man City winger Oscar Bobb

-
 Strasbourg's Argentine striker Panichelli sets sights on PSG, World Cup
Strasbourg's Argentine striker Panichelli sets sights on PSG, World Cup
-
Jesus 'made love': Colombian president irks Christians with steamy claim

-
 IAEA board meets over Ukraine nuclear safety concerns
IAEA board meets over Ukraine nuclear safety concerns
-
Eurozone growth beats 2025 forecasts despite Trump woes

-
 Israel to partially reopen Gaza's Rafah crossing on Sunday
Israel to partially reopen Gaza's Rafah crossing on Sunday
-
Dutch PM-elect Jetten says not yet time to talk to Putin

-
 Social media fuels surge in UK men seeking testosterone jabs
Social media fuels surge in UK men seeking testosterone jabs
-
Forest face Fenerbahce, Celtic draw Stuttgart in Europa League play-offs
-
 US speed queen Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics
US speed queen Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics
-
Trump nominates former US Fed official as next central bank chief

-
 Alcaraz defends controversial timeout after beaten Zverev fumes
Alcaraz defends controversial timeout after beaten Zverev fumes
-
New Dutch government pledges ongoing Ukraine support

-
 Newcastle still coping with fallout from Isak exit, says Howe
Newcastle still coping with fallout from Isak exit, says Howe
-
Chad, France eye economic cooperation as they reset strained ties

-
 Real Madrid to play Benfica, PSG face Monaco in Champions League play-offs
Real Madrid to play Benfica, PSG face Monaco in Champions League play-offs
-
Everton winger Grealish set to miss rest of season in World Cup blow

-
 Trump brands Minneapolis nurse killed by federal agents an 'agitator'
Trump brands Minneapolis nurse killed by federal agents an 'agitator'
-
Arteta focuses on the positives despite Arsenal stumble

-
 Fijian Drua sign France international back Vakatawa
Fijian Drua sign France international back Vakatawa
-
Kevin Warsh, a former Fed 'hawk' now in tune with Trump

-
 Zverev rails at Alcaraz timeout in 'one of the best battles ever'
Zverev rails at Alcaraz timeout in 'one of the best battles ever'
-
Turkey leads Iran diplomatic push as Trump softens strike threat

| RBGPF | 1.65% | 83.78 | $ | |
| SCS | 0.12% | 16.14 | $ | |
| RYCEF | -2.69% | 16 | $ | |
| CMSC | 0.02% | 23.7 | $ | |
| BCC | -0.97% | 79.4 | $ | |
| BTI | -0.12% | 60.135 | $ | |
| RELX | -1.69% | 35.565 | $ | |
| NGG | -0.81% | 84.37 | $ | |
| GSK | 1.33% | 51.34 | $ | |
| RIO | -4.86% | 90.725 | $ | |
| JRI | 0.32% | 12.997 | $ | |
| CMSD | -0.12% | 24.03 | $ | |
| BCE | -0.18% | 25.44 | $ | |
| VOD | -0.58% | 14.625 | $ | |
| AZN | 0.75% | 93.285 | $ | |
| BP | -1.1% | 37.625 | $ |

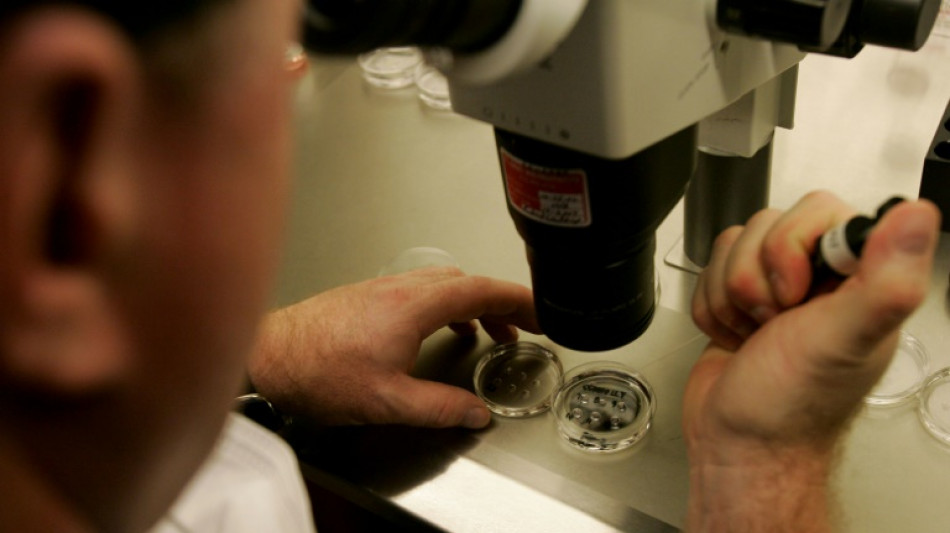
Human skin cells turned into fertilisable eggs for first time
Scientists said Wednesday they have turned human skin cells into eggs and fertilised them with sperm in the lab for the first time -- a breakthrough that is hoped to one day let infertile people have children.
The technology is still years away from potentially becoming available to aspiring parents, the US-led team of scientists warned.
But outside experts said the proof-of-concept research could eventually change the meaning of infertility, which affects one in six people worldwide.
If successful, the technology called in-vitro gametogenesis (IVG) would allow older women or women who lack eggs for other reasons to genetically reproduce, Paula Amato, the co-author of a new study announcing the achievement, told AFP.
"It also would allow same-sex couples to have a child genetically related to both partners," said Amato, a researcher at the Oregon Health & Science University in the United States.
Scientists have been making significant advances in this field in recent years, with Japanese researchers announcing in July they had created mice with two biological fathers.
But the new study, published in the journal Nature Communications, marks a major advance by using DNA from humans, rather than mice.
The scientists first removed the nucleus from normal skin cells and transferred them into a donor egg which had its nucleus removed. This technique, called somatic cell nuclear transfer, was used to clone Dolly the sheep in 1996.
However a problem still had to be overcome: skin cells have 46 chromosomes, but eggs have 23.
The scientists managed to remove these extra chromosomes using a process they are calling "mitomeiosis", which mimics how cells normally divide.
They created 82 developing eggs called oocytes, which were then fertilised by sperm via in vitro fertilisation (IVF).
After six days, less than nine percent of the embryos developed to the point that they could hypothetically be transferred to the uterus for a standard IVF process.
However the embryos displayed a range of abnormalities, and the experiment was ended.
While the nine-percent rate was low, the researchers noted that during natural reproduction only around a third of embryos make it to the IVF-ready "blastocyst" stage.
Amato estimated the technology was at least a decade away from becoming widely available.
"The biggest hurdle is trying to achieve genetically normal eggs with the correct number and complement of chromosomes," she said.
- Breakthrough -
Ying Cheong, a reproductive medicine researcher at the UK's University of Southampton, hailed the "exciting" breakthrough.
"For the first time, scientists have shown that DNA from ordinary body cells can be placed into an egg, activated, and made to halve its chromosomes, mimicking the special steps that normally create eggs and sperm," she said.
"While this is still very early laboratory work, in the future it could transform how we understand infertility and miscarriage, and perhaps one day open the door to creating egg- or sperm-like cells for those who have no other options."
Other researchers trying to create eggs in the lab are using a different technique. It involves reprogramming skin cells into what are called induced pluripotent stem cells -- which have the potential to develop into any cell in the body -- then turning those into eggs.
"It's too early to tell which method will be more successful," Amato said. "Either way, we are still many years away."
The researchers followed existing US ethical guidelines regulating the use of embryos, the study said.
Ch.Campbell--AT