-
 'Schitt's Creek' star Catherine O'Hara dead at 71
'Schitt's Creek' star Catherine O'Hara dead at 71
-
Curran hat-trick seals 11 run DLS win for England over Sri Lanka

-
 Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues energy ultimatum
Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues energy ultimatum
-
France rescues over 6,000 UK-bound Channel migrants in 2025

-
 Surprise appointment Riera named Frankfurt coach
Surprise appointment Riera named Frankfurt coach
-
Maersk to take over Panama Canal port operations from HK firm

-
 US arrests prominent journalist after Minneapolis protest coverage
US arrests prominent journalist after Minneapolis protest coverage
-
Analysts say Kevin Warsh a safe choice for US Fed chair

-
 Trump predicts Iran will seek deal to avoid US strikes
Trump predicts Iran will seek deal to avoid US strikes
-
US oil giants say it's early days on potential Venezuela boom

-
 Fela Kuti to be first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award
Fela Kuti to be first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award
-
Trump says Iran wants deal, US 'armada' larger than in Venezuela raid

-
 US Justice Dept releases new batch of documents, images, videos from Epstein files
US Justice Dept releases new batch of documents, images, videos from Epstein files
-
Four memorable showdowns between Alcaraz and Djokovic

-
 Russian figure skating prodigy Valieva set for comeback -- but not at Olympics
Russian figure skating prodigy Valieva set for comeback -- but not at Olympics
-
Barcelona midfielder Lopez agrees contract extension

-
 Djokovic says 'keep writing me off' after beating Sinner in late-nighter
Djokovic says 'keep writing me off' after beating Sinner in late-nighter
-
US Justice Dept releasing new batch of Epstein files

-
 South Africa and Israel expel envoys in deepening feud
South Africa and Israel expel envoys in deepening feud
-
French eyewear maker in spotlight after presidential showing

-
 Olympic dream 'not over', Vonn says after crash
Olympic dream 'not over', Vonn says after crash
-
Brazil's Lula discharged after cataract surgery

-
 US Senate races to limit shutdown fallout as Trump-backed deal stalls
US Senate races to limit shutdown fallout as Trump-backed deal stalls
-
'He probably would've survived': Iran targeting hospitals in crackdown

-
 Djokovic stuns Sinner to set up Australian Open final with Alcaraz
Djokovic stuns Sinner to set up Australian Open final with Alcaraz
-
Mateta omitted from Palace squad to face Forest

-
 Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump's Fed pick
Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump's Fed pick
-
Trump attorney general orders arrest of ex-CNN anchor covering protests

-
 Djokovic 'pushed to the limit' in stunning late-night Sinner upset
Djokovic 'pushed to the limit' in stunning late-night Sinner upset
-
Tunisia's famed blue-and-white village threatened after record rains

-
 Top EU official voices 'shock' at Minneapolis violence
Top EU official voices 'shock' at Minneapolis violence
-
Kremlin says agreed to halt strikes on Kyiv until Sunday

-
 Carrick calls for calm after flying start to Man Utd reign
Carrick calls for calm after flying start to Man Utd reign
-
Djokovic to meet Alcaraz in Melbourne final after five-set marathon

-
 Italian officials to testify in trial over deadly migrant shipwreck
Italian officials to testify in trial over deadly migrant shipwreck
-
Iran says defence capabilities 'never' up for negotiation

-
 UN appeals for more support for flood-hit Mozambicans
UN appeals for more support for flood-hit Mozambicans
-
Lijnders urges Man City to pile pressure on Arsenal in title race

-
 Fulham sign Man City winger Oscar Bobb
Fulham sign Man City winger Oscar Bobb
-
Strasbourg's Argentine striker Panichelli sets sights on PSG, World Cup

-
 Jesus 'made love': Colombian president irks Christians with steamy claim
Jesus 'made love': Colombian president irks Christians with steamy claim
-
IAEA board meets over Ukraine nuclear safety concerns

-
 Eurozone growth beats 2025 forecasts despite Trump woes
Eurozone growth beats 2025 forecasts despite Trump woes
-
Israel to partially reopen Gaza's Rafah crossing on Sunday

-
 Dutch PM-elect Jetten says not yet time to talk to Putin
Dutch PM-elect Jetten says not yet time to talk to Putin
-
Social media fuels surge in UK men seeking testosterone jabs

-
 Forest face Fenerbahce, Celtic draw Stuttgart in Europa League play-offs
Forest face Fenerbahce, Celtic draw Stuttgart in Europa League play-offs
-
US speed queen Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics

-
 Trump nominates former US Fed official as next central bank chief
Trump nominates former US Fed official as next central bank chief
-
Alcaraz defends controversial timeout after beaten Zverev fumes


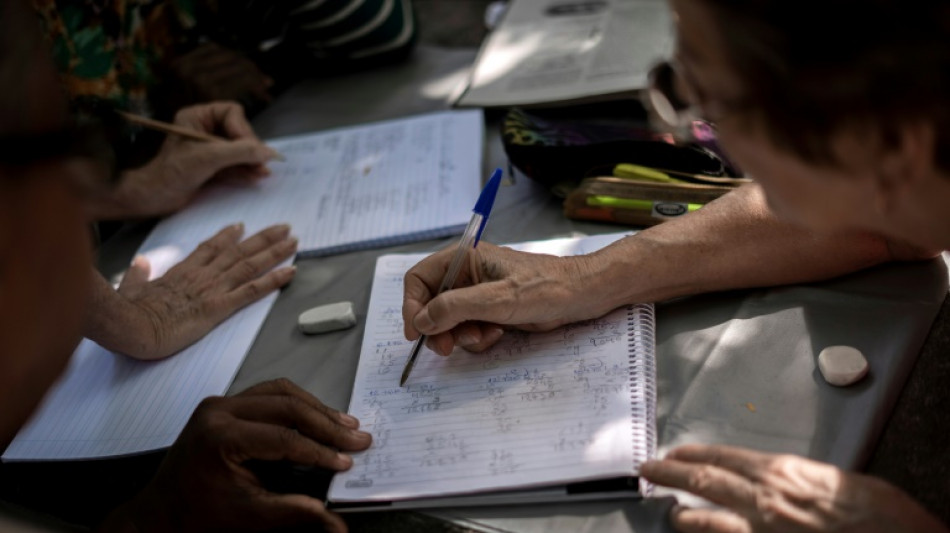
Shock study: Mild electric stimulation boosts math ability
Struggle with math? A gentle jolt to the brain might help.
A new study published Tuesday in PLOS Biology suggests that mild electrical stimulation can boost arithmetic performance -- and offers fresh insight into the brain mechanisms behind mathematical ability, along with a potential way to optimize learning.
The findings could eventually help narrow cognitive gaps and help build a more intellectually equitable society, the authors argue.
"Different people have different brains, and their brains control a lot in their life," said Roi Cohen Kadosh, a neuroscientist at the University of Surrey who led the research.
"We think about the environment -- if you go to the right school, if you have the right teacher -- but it's also our biology."
Cohen Kadosh and colleagues recruited 72 University of Oxford students, scanning their brains to measure connectivity between three key regions.
Participants then tackled math problems that required either calculating answers or recalling memorized solutions.
They found that stronger connections between the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, which governs executive function, and the posterior parietal cortex, involved in memory, predicted better calculation performance.
When the researchers applied a painless form of brain stimulation using electrode-fitted caps -- a technique known as transcranial random noise stimulation -- the low performers saw their scores jump by 25–29 percent.
The team believes the stimulation works by enhancing the excitability of neurons and interacting with GABA, a brain chemical that inhibits excessive activity -- effectively compensating for weak neural connectivity in some participants.
In fact, the stimulation helped underperformers reach or even surpass the scores of peers with naturally stronger brain wiring. But those who already performed well saw no benefit.
"Some people struggle with things, and if we can help their brain to fulfill their potential, we open them a lot of opportunities that otherwise would be closed," said Cohen Kadosh, calling it an "exciting time" for the field of brain stimulation research.
Still, he flagged a key ethical concern: the risk that such technologies could become more available to those with financial means, widening -- rather than closing -- access gaps.
He also urged the public not to try this at home. "Some people struggle with learning, and if our research proves successful beyond the lab, we could help them fulfil their ambitions and unlock opportunities that might otherwise remain out of reach."
H.Thompson--AT