-
 Mertens and Zhang win Australian Open women's doubles title
Mertens and Zhang win Australian Open women's doubles title
-
Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push

-
 China factory activity loses steam in January
China factory activity loses steam in January
-
Melania Trump's atypical, divisive doc opens in theatres

-
 Bad Bunny set for historic one-two punch at Grammys, Super Bowl
Bad Bunny set for historic one-two punch at Grammys, Super Bowl
-
Five things to watch for on Grammys night Sunday

-
 Venezuelan interim president proposes mass amnesty law
Venezuelan interim president proposes mass amnesty law
-
Rose stretches lead at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes cut

-
 Online foes Trump, Petro set for White House face-to-face
Online foes Trump, Petro set for White House face-to-face
-
Seattle Seahawks deny plans for post-Super Bowl sale

-
 US Senate passes deal expected to shorten shutdown
US Senate passes deal expected to shorten shutdown
-
'Misrepresent reality': AI-altered shooting image surfaces in US Senate

-
 Thousands rally in Minneapolis as immigration anger boils
Thousands rally in Minneapolis as immigration anger boils
-
US judge blocks death penalty for alleged health CEO killer Mangione

-
 Lens win to reclaim top spot in Ligue 1 from PSG
Lens win to reclaim top spot in Ligue 1 from PSG
-
Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump Fed pick

-
 Ko, Woad share lead at LPGA season opener
Ko, Woad share lead at LPGA season opener
-
US Senate votes on funding deal - but shutdown still imminent

-
 US charges prominent journalist after Minneapolis protest coverage
US charges prominent journalist after Minneapolis protest coverage
-
Trump expects Iran to seek deal to avoid US strikes

-
 US Justice Dept releases documents, images, videos from Epstein files
US Justice Dept releases documents, images, videos from Epstein files
-
Guterres warns UN risks 'imminent financial collapse'

-
 NASA delays Moon mission over frigid weather
NASA delays Moon mission over frigid weather
-
First competitors settle into Milan's Olympic village

-
 Fela Kuti: first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award
Fela Kuti: first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award
-
Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues oil ultimatum

-
 'Schitt's Creek' star Catherine O'Hara dead at 71
'Schitt's Creek' star Catherine O'Hara dead at 71
-
Curran hat-trick seals 11 run DLS win for England over Sri Lanka

-
 Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues energy ultimatum
Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues energy ultimatum
-
France rescues over 6,000 UK-bound Channel migrants in 2025

-
 Surprise appointment Riera named Frankfurt coach
Surprise appointment Riera named Frankfurt coach
-
Maersk to take over Panama Canal port operations from HK firm

-
 US arrests prominent journalist after Minneapolis protest coverage
US arrests prominent journalist after Minneapolis protest coverage
-
Analysts say Kevin Warsh a safe choice for US Fed chair

-
 Trump predicts Iran will seek deal to avoid US strikes
Trump predicts Iran will seek deal to avoid US strikes
-
US oil giants say it's early days on potential Venezuela boom

-
 Fela Kuti to be first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award
Fela Kuti to be first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award
-
Trump says Iran wants deal, US 'armada' larger than in Venezuela raid

-
 US Justice Dept releases new batch of documents, images, videos from Epstein files
US Justice Dept releases new batch of documents, images, videos from Epstein files
-
Four memorable showdowns between Alcaraz and Djokovic

-
 Russian figure skating prodigy Valieva set for comeback -- but not at Olympics
Russian figure skating prodigy Valieva set for comeback -- but not at Olympics
-
Barcelona midfielder Lopez agrees contract extension

-
 Djokovic says 'keep writing me off' after beating Sinner in late-nighter
Djokovic says 'keep writing me off' after beating Sinner in late-nighter
-
US Justice Dept releasing new batch of Epstein files

-
 South Africa and Israel expel envoys in deepening feud
South Africa and Israel expel envoys in deepening feud
-
French eyewear maker in spotlight after presidential showing

-
 Olympic dream 'not over', Vonn says after crash
Olympic dream 'not over', Vonn says after crash
-
Brazil's Lula discharged after cataract surgery

-
 US Senate races to limit shutdown fallout as Trump-backed deal stalls
US Senate races to limit shutdown fallout as Trump-backed deal stalls
-
'He probably would've survived': Iran targeting hospitals in crackdown


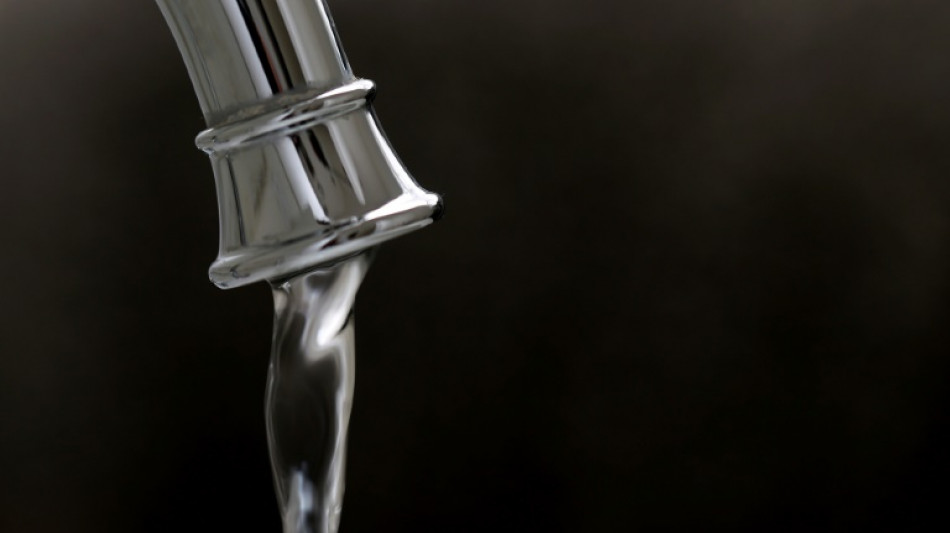
Utah becomes first US state to ban fluoride in drinking water
The western US state of Utah has become the first to prohibit fluoridation of its public drinking water, part of a growing movement reexamining the decades-old public health practice.
New US Health Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. has long been a vocal critic of fluoridated water, which currently reaches an estimated 200 million Americans -- about two-thirds of the population.
Utah's ban, signed into law by Governor Spencer Cox on Thursday, is set to take effect on May 7. Legislatures in other Republican-led states including North Dakota, Tennessee, and Montana, are considering similar measures.
Opposition is not limited to red states. Liberal-leaning cities such as Portland, Oregon, and the City and County of Honolulu, Hawaii, have also banned fluoridation.
Fluoride was first introduced to US water systems in 1945, dramatically reducing childhood cavities and adult tooth loss. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention hails it as one of the top public health achievements of the 20th century.
But controversy has grown around its potential neurotoxic effects. Last year, the Department of Health and Human Services under former president Joe Biden concluded with "moderate confidence" that higher levels of fluoride are linked to lower IQ scores.
This January, a paper in the prestigious journal JAMA Pediatrics, authored by the same government scientists, found a "statistically significant association" between fluoride exposure and reduced IQ. However, it left open key questions about what dosage levels may be harmful.
The World Health Organization's safety threshold stands at 1.5 milligrams per liter -- about double the US guideline of 0.7 mg/L -- and the study said there was insufficient data to determine whether that limit should be revised.
Ending fluoridation is generally opposed by the dental and public health communities. Critics of the recent study argue it failed to adequately control for confounding variables and environmental factors.
Fluoride occurs naturally in varying concentrations and strengthens teeth in several ways: by restoring minerals lost to acid, reducing acid production by cavity-causing bacteria, and making it harder for those bacteria to adhere to enamel.
Proponents argue fluoridation reduces socioeconomic disparities in dental care.
But with fluoride toothpastes widely available since the 1960s, some research suggests diminishing returns.
A recent Canadian study found that ending fluoridation increased dental caries, while an Irish study reported a decline in severe caries in both fluoridated and non-fluoridated areas.
Fluoridation policies also vary widely by country, with many, including Germany and France eschewing the practice altogether.
F.Wilson--AT