-
 Blanc wins final women's race before Winter Olympics
Blanc wins final women's race before Winter Olympics
-
Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's Moscow-born Melbourne champion

-
 Ice-cool Rybakina beats Sabalenka in tense Australian Open final
Ice-cool Rybakina beats Sabalenka in tense Australian Open final
-
Pakistan attacks kill 15, dozens of militants dead: official

-
 Ten security officials, 37 militants killed in SW Pakistan attacks: official
Ten security officials, 37 militants killed in SW Pakistan attacks: official
-
Epstein survivors say abusers 'remain hidden' after latest files release

-
 'Full respect' for Djokovic but Nadal tips Alcaraz for Melbourne title
'Full respect' for Djokovic but Nadal tips Alcaraz for Melbourne title
-
Wollaston goes back-to-back in the Cadel Evans road race

-
 Women in ties return as feminism faces pushback
Women in ties return as feminism faces pushback
-
Ship ahoy! Prague's homeless find safe haven on river boat

-
 Britain's Starmer ends China trip aimed at reset despite Trump warning
Britain's Starmer ends China trip aimed at reset despite Trump warning
-
Carlos Alcaraz: rare tennis talent with shades of Federer

-
 Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
-
History beckons for Djokovic and Alcaraz in Australian Open final

-
 Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
-
Epstein offered ex-prince Andrew meeting with Russian woman: files

-
 Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
-
Montreal studio rises from dark basement office to 'Stranger Things'

-
 US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
-
Mertens and Zhang win Australian Open women's doubles title

-
 Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
-
China factory activity loses steam in January

-
 Melania Trump's atypical, divisive doc opens in theatres
Melania Trump's atypical, divisive doc opens in theatres
-
Bad Bunny set for historic one-two punch at Grammys, Super Bowl

-
 Five things to watch for on Grammys night Sunday
Five things to watch for on Grammys night Sunday
-
Venezuelan interim president proposes mass amnesty law

-
 Rose stretches lead at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes cut
Rose stretches lead at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes cut
-
Online foes Trump, Petro set for White House face-to-face

-
 Seattle Seahawks deny plans for post-Super Bowl sale
Seattle Seahawks deny plans for post-Super Bowl sale
-
US Senate passes deal expected to shorten shutdown

-
 'Misrepresent reality': AI-altered shooting image surfaces in US Senate
'Misrepresent reality': AI-altered shooting image surfaces in US Senate
-
Thousands rally in Minneapolis as immigration anger boils

-
 US judge blocks death penalty for alleged health CEO killer Mangione
US judge blocks death penalty for alleged health CEO killer Mangione
-
Lens win to reclaim top spot in Ligue 1 from PSG

-
 Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump Fed pick
Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump Fed pick
-
Ko, Woad share lead at LPGA season opener

-
 US Senate votes on funding deal - but shutdown still imminent
US Senate votes on funding deal - but shutdown still imminent
-
US charges prominent journalist after Minneapolis protest coverage

-
 Trump expects Iran to seek deal to avoid US strikes
Trump expects Iran to seek deal to avoid US strikes
-
US Justice Dept releases documents, images, videos from Epstein files

-
 Guterres warns UN risks 'imminent financial collapse'
Guterres warns UN risks 'imminent financial collapse'
-
NASA delays Moon mission over frigid weather

-
 First competitors settle into Milan's Olympic village
First competitors settle into Milan's Olympic village
-
Fela Kuti: first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award

-
 Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues oil ultimatum
Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues oil ultimatum
-
'Schitt's Creek' star Catherine O'Hara dead at 71

-
 Curran hat-trick seals 11 run DLS win for England over Sri Lanka
Curran hat-trick seals 11 run DLS win for England over Sri Lanka
-
Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues energy ultimatum

-
 France rescues over 6,000 UK-bound Channel migrants in 2025
France rescues over 6,000 UK-bound Channel migrants in 2025
-
Surprise appointment Riera named Frankfurt coach


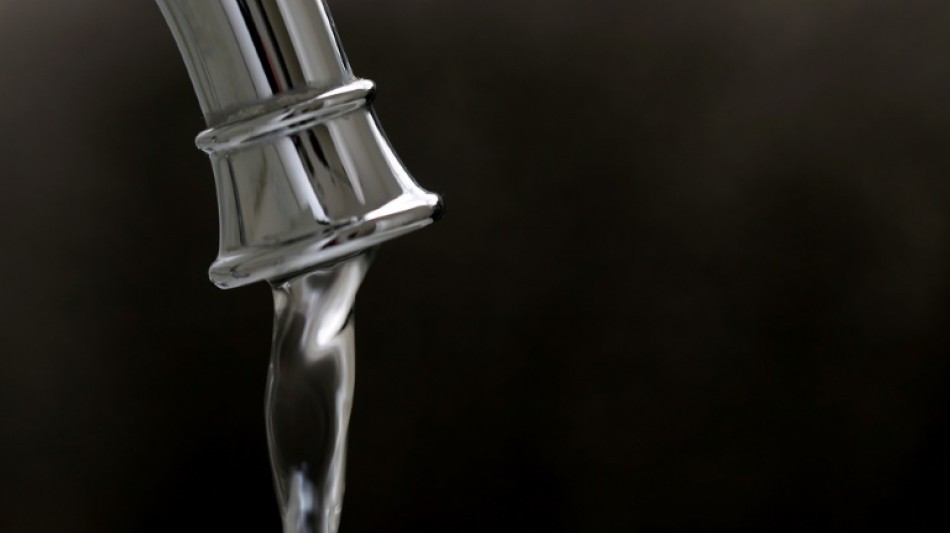
Divisive study finds link between fluoride and childhood IQ loss
A controversial new study out Monday in a US medical journal could reignite debate over fluoride's safety in water, linking higher exposure levels to lower IQ in children.
Published in the prestigious Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) Pediatrics, it has sparked pushback from some scientists who criticize the study's methods, defend the mineral's proven dental benefits, and warn the findings may not directly apply to typical US water fluoridation levels.
Its release comes as President-elect Donald Trump prepares to take office. His health secretary nominee, Robert F. Kennedy Jr., is a vocal critic of fluoridated water, which currently serves over 200 million Americans, or nearly two-thirds of the population.
Researchers from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) reviewed 74 studies on fluoride exposure and children's IQ conducted in 10 countries including Canada, China, and India.
The same scientists helped formulate an official government recommendation in August that there is "moderate confidence" that higher levels of fluoride are linked to lower IQ scores.
Now, the team led by Kyla Taylor told AFP the new analysis found a "statistically significant association" between fluoride exposure and reduced IQ scores.
Specifically, the study estimates that for every 1 milligram per liter increase in urinary fluoride -- a marker of overall exposure -- children's IQ drops by 1.63 points.
- Study limitations-
Fluoride's neurotoxicity at high doses is well known, but the controversy lies in the study's suggestion that exposure below 1.5 milligrams per liter -- currently the World Health Organization's safety limit -- may also affect children's IQ.
Crucially, the paper does not clarify how much lower than 1.5 mg/L could be dangerous, leaving questions about whether the US guideline of 0.7 mg/L needs adjustment.
The authors acknowledged that "there were not enough data to determine if 0.7 mg/L of fluoride exposure in drinking water affected children's IQ."
Steven Levy, a member of the national fluoride committee for the American Dental Association, raised significant concerns about the study's methodology.
He pointed out that 52 of the 74 studies reviewed were rated "low quality" by the authors themselves but were still included in the analysis.
"Almost all of the studies have been done in other settings where there are other contaminants, other things we call confounding factors," he told AFP, citing coal pollution in China as an example.
Levy also questioned the study's use of single-point urine samples instead of 24-hour collections, which provide greater accuracy, as well as the challenges in reliably assessing young children's IQ.
With so many uncertainties, Levy argued in an editorial accompanying the study that current policies "should not be affected by the study findings."
The journal also published an editorial commending the study for its methodological rigor.
- Balancing gains against risks -
On the other side of the debate, the benefits of water fluoridation are well documented.
Introduced in the United States in 1945, it quickly reduced cavities in children and tooth loss in adults, earning recognition from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention as one of the greatest public health achievements of the 20th century.
Fluoride, which also occurs naturally in varying levels, helps restore minerals lost to acid breakdown in teeth, reduces acid production by cavity-causing bacteria, and makes it harder for these bacteria to stick to the teeth.
However, with fluoride toothpastes widely available since the 1960s, some research suggests diminishing returns.
Proponents argue fluoridation reduces socioeconomic disparities in dental care, while critics warn it may pose greater risks of neurological harm to vulnerable communities.
"Evidence on the effects of adjusting levels of fluoride or interrupting community water fluoridation programs is critically needed, especially within the context of the US," Fernando Hugo, Chair of the NYU College of Dentistry, told AFP.
O.Brown--AT