-
 Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
-
History beckons for Djokovic and Alcaraz in Australian Open final

-
 Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
-
Epstein offered ex-prince Andrew meeting with Russian woman: files

-
 Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
-
Montreal studio rises from dark basement office to 'Stranger Things'

-
 US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
-
Mertens and Zhang win Australian Open women's doubles title

-
 Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
-
China factory activity loses steam in January

-
 Melania Trump's atypical, divisive doc opens in theatres
Melania Trump's atypical, divisive doc opens in theatres
-
Bad Bunny set for historic one-two punch at Grammys, Super Bowl

-
 Five things to watch for on Grammys night Sunday
Five things to watch for on Grammys night Sunday
-
Venezuelan interim president proposes mass amnesty law

-
 Rose stretches lead at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes cut
Rose stretches lead at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes cut
-
Online foes Trump, Petro set for White House face-to-face

-
 Seattle Seahawks deny plans for post-Super Bowl sale
Seattle Seahawks deny plans for post-Super Bowl sale
-
US Senate passes deal expected to shorten shutdown

-
 'Misrepresent reality': AI-altered shooting image surfaces in US Senate
'Misrepresent reality': AI-altered shooting image surfaces in US Senate
-
Thousands rally in Minneapolis as immigration anger boils

-
 US judge blocks death penalty for alleged health CEO killer Mangione
US judge blocks death penalty for alleged health CEO killer Mangione
-
Lens win to reclaim top spot in Ligue 1 from PSG

-
 Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump Fed pick
Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump Fed pick
-
Ko, Woad share lead at LPGA season opener

-
 US Senate votes on funding deal - but shutdown still imminent
US Senate votes on funding deal - but shutdown still imminent
-
US charges prominent journalist after Minneapolis protest coverage

-
 Trump expects Iran to seek deal to avoid US strikes
Trump expects Iran to seek deal to avoid US strikes
-
US Justice Dept releases documents, images, videos from Epstein files

-
 Guterres warns UN risks 'imminent financial collapse'
Guterres warns UN risks 'imminent financial collapse'
-
NASA delays Moon mission over frigid weather

-
 First competitors settle into Milan's Olympic village
First competitors settle into Milan's Olympic village
-
Fela Kuti: first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award

-
 Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues oil ultimatum
Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues oil ultimatum
-
'Schitt's Creek' star Catherine O'Hara dead at 71

-
 Curran hat-trick seals 11 run DLS win for England over Sri Lanka
Curran hat-trick seals 11 run DLS win for England over Sri Lanka
-
Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues energy ultimatum

-
 France rescues over 6,000 UK-bound Channel migrants in 2025
France rescues over 6,000 UK-bound Channel migrants in 2025
-
Surprise appointment Riera named Frankfurt coach

-
 Maersk to take over Panama Canal port operations from HK firm
Maersk to take over Panama Canal port operations from HK firm
-
US arrests prominent journalist after Minneapolis protest coverage

-
 Analysts say Kevin Warsh a safe choice for US Fed chair
Analysts say Kevin Warsh a safe choice for US Fed chair
-
Trump predicts Iran will seek deal to avoid US strikes

-
 US oil giants say it's early days on potential Venezuela boom
US oil giants say it's early days on potential Venezuela boom
-
Fela Kuti to be first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award

-
 Trump says Iran wants deal, US 'armada' larger than in Venezuela raid
Trump says Iran wants deal, US 'armada' larger than in Venezuela raid
-
US Justice Dept releases new batch of documents, images, videos from Epstein files

-
 Four memorable showdowns between Alcaraz and Djokovic
Four memorable showdowns between Alcaraz and Djokovic
-
Russian figure skating prodigy Valieva set for comeback -- but not at Olympics

-
 Barcelona midfielder Lopez agrees contract extension
Barcelona midfielder Lopez agrees contract extension
-
Djokovic says 'keep writing me off' after beating Sinner in late-nighter


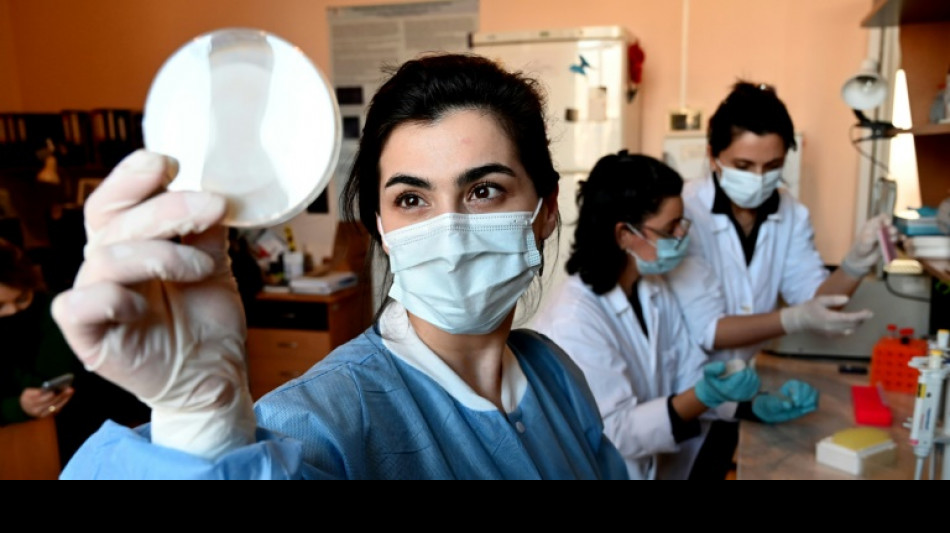
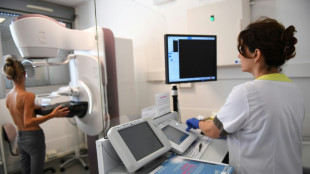
Viruses that could save millions of lives
It may seem strange after a pandemic that has killed millions and turned the world upside down, but viruses could save just as many lives.
In a petri dish in a laboratory in the Georgian capital Tbilisi, a battle is going on between antibiotic resistant bacteria and "friendly" viruses.
This small nation in the Caucasus has pioneered research on a groundbreaking way to tackle the looming nightmare of bacteria becoming resistant to the antibiotics on which the world depends.
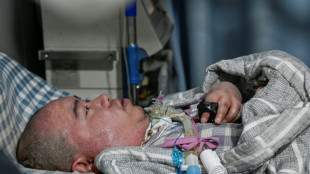
Long overlooked in the West, bacteriophages or bacteria-eating viruses are now being used on some of the most difficult medical cases, including a Belgian woman who developed a life-threatening infection after being injured in the 2016 Brussels airport bombing.
After two years of unsuccessful antibiotic treatment, bacteriophages sent from Tbilisi cured her infection in three months.
"We use those phages that kill harmful bacteria" to cure patients when antibiotics fail, Mzia Kutateladze of the Eliava Institute of Bacteriophages told AFP.
Even a banal infection can "kill a patient because the pathogen has developed resistance to antibiotics," Kutateladze said.
In such cases, phagotherapy "is one of the best alternatives", she added.
Phages have been known about for a century, but were largely forgotten and dismissed after antibiotics revolutionised medicine in the 1930s.
- Stalin's henchman -
It didn't help that the man who did most to develop them, Georgian scientist Giorgi Eliava, was executed in 1937 on the orders of another Georgian, Lavrentiy Beria, Stalin's most notorious henchman and the head of his secret police.
Eliava had worked in the Pasteur Institute in Paris with French-Canadian microbiologist Felix d'Herelle, one of the two men credited with discovering phages, and persuaded Stalin to invite him to Tbilisi in 1934.
But their collaboration was cut short when Beria had Eliava killed, although his motive still remains a mystery.
With the World Health Organization now declaring antimicrobial resistance a global health crisis, phages are making a comeback, especially as they can target bacteria while leaving human cells intact.
A recent study warned that superbugs could kill as many as 10 million people a year when antimicrobial resistance due to overuse of antibiotics reaches a tipping point. That could come within three decades.
- 'Training' viruses -
While phages-based medicines cannot completely replace antibiotics, researchers say they have major pluses in being cheap, not having side-effects nor damaging organs or gut flora.
"We produce six standard phages that are of wide spectrum and can heal multiple infectious diseases," said Eliava Institute physician Lia Nadareishvili.
In some 10 to 15 percent of patients, however, standard phages don't work and "we have to find ones capable of killing the particular bacterial strain," she added.
Tailored phages to target rare infections can be selected from the institute's massive collection -- the world's richest -- or be found in sewage or polluted water or soil, Kutateladze said.
The institute can even "train" phages so that "they can kill more and more different harmful bacteria."
"It is a cheap and easily accessible therapy," she added.
- Last-resort treatment -
A 34-year-old American mechanical engineer suffering from a chronic bacterial disease for six years told AFP he "already felt improvement" after two weeks at the Tbilisi institute.
"I've tried every possible treatment in the United States," said Andrew, who would only give his first name.
He is one of the hundreds of patients from around the globe who arrive in Georgia every year for last-resort treatment, said Nadareishvili.
With the traditional antimicrobial armoury depleting rapidly, more clinical studies are needed so that phagotherapy can be more widely approved, Kutateladze argued.
In 2019, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) authorised a clinical study on the use of bacteriophages to cure secondary infections in Covid patients.
Beyond medicine, phages are already being used to stop food going off, and they "can be used in agriculture to protect crops and animals from harmful bacteria," Kutateladze said.
The institute has already conducted research on bacteria targeting cotton and rice.
Bacteriophages also have potential to counter biological weapons and combat bioterrorism, with Canadian researchers publishing a 2017 study on using them to counter an anthrax attack on crowded public places.
Ch.Campbell--AT