-
 Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
-
History beckons for Djokovic and Alcaraz in Australian Open final

-
 Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
-
Epstein offered ex-prince Andrew meeting with Russian woman: files

-
 Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
-
Montreal studio rises from dark basement office to 'Stranger Things'

-
 US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
-
Mertens and Zhang win Australian Open women's doubles title

-
 Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
-
China factory activity loses steam in January

-
 Melania Trump's atypical, divisive doc opens in theatres
Melania Trump's atypical, divisive doc opens in theatres
-
Bad Bunny set for historic one-two punch at Grammys, Super Bowl

-
 Five things to watch for on Grammys night Sunday
Five things to watch for on Grammys night Sunday
-
Venezuelan interim president proposes mass amnesty law

-
 Rose stretches lead at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes cut
Rose stretches lead at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes cut
-
Online foes Trump, Petro set for White House face-to-face

-
 Seattle Seahawks deny plans for post-Super Bowl sale
Seattle Seahawks deny plans for post-Super Bowl sale
-
US Senate passes deal expected to shorten shutdown

-
 'Misrepresent reality': AI-altered shooting image surfaces in US Senate
'Misrepresent reality': AI-altered shooting image surfaces in US Senate
-
Thousands rally in Minneapolis as immigration anger boils

-
 US judge blocks death penalty for alleged health CEO killer Mangione
US judge blocks death penalty for alleged health CEO killer Mangione
-
Lens win to reclaim top spot in Ligue 1 from PSG

-
 Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump Fed pick
Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump Fed pick
-
Ko, Woad share lead at LPGA season opener

-
 US Senate votes on funding deal - but shutdown still imminent
US Senate votes on funding deal - but shutdown still imminent
-
US charges prominent journalist after Minneapolis protest coverage

-
 Trump expects Iran to seek deal to avoid US strikes
Trump expects Iran to seek deal to avoid US strikes
-
US Justice Dept releases documents, images, videos from Epstein files

-
 Guterres warns UN risks 'imminent financial collapse'
Guterres warns UN risks 'imminent financial collapse'
-
NASA delays Moon mission over frigid weather

-
 First competitors settle into Milan's Olympic village
First competitors settle into Milan's Olympic village
-
Fela Kuti: first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award

-
 Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues oil ultimatum
Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues oil ultimatum
-
'Schitt's Creek' star Catherine O'Hara dead at 71

-
 Curran hat-trick seals 11 run DLS win for England over Sri Lanka
Curran hat-trick seals 11 run DLS win for England over Sri Lanka
-
Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues energy ultimatum

-
 France rescues over 6,000 UK-bound Channel migrants in 2025
France rescues over 6,000 UK-bound Channel migrants in 2025
-
Surprise appointment Riera named Frankfurt coach

-
 Maersk to take over Panama Canal port operations from HK firm
Maersk to take over Panama Canal port operations from HK firm
-
US arrests prominent journalist after Minneapolis protest coverage

-
 Analysts say Kevin Warsh a safe choice for US Fed chair
Analysts say Kevin Warsh a safe choice for US Fed chair
-
Trump predicts Iran will seek deal to avoid US strikes

-
 US oil giants say it's early days on potential Venezuela boom
US oil giants say it's early days on potential Venezuela boom
-
Fela Kuti to be first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award

-
 Trump says Iran wants deal, US 'armada' larger than in Venezuela raid
Trump says Iran wants deal, US 'armada' larger than in Venezuela raid
-
US Justice Dept releases new batch of documents, images, videos from Epstein files

-
 Four memorable showdowns between Alcaraz and Djokovic
Four memorable showdowns between Alcaraz and Djokovic
-
Russian figure skating prodigy Valieva set for comeback -- but not at Olympics

-
 Barcelona midfielder Lopez agrees contract extension
Barcelona midfielder Lopez agrees contract extension
-
Djokovic says 'keep writing me off' after beating Sinner in late-nighter


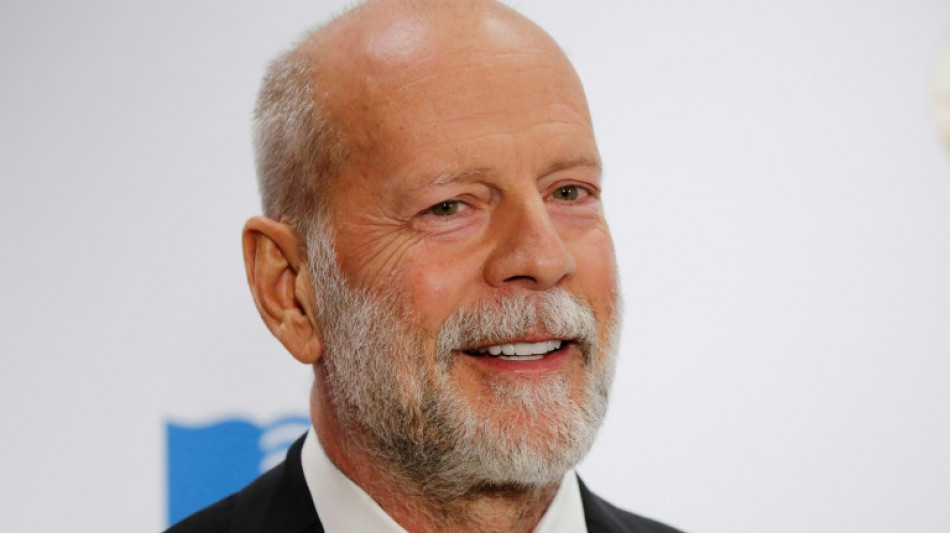
What is aphasia? Here's what you need to know
The news that film star Bruce Willis has retired from acting due to aphasia has shone a spotlight on the poorly understood communication disorder.
Here's what you should know.
- What is aphasia? -
"Aphasia just means that someone has a problem with language that they weren't born with," Hugo Botha, a neurologist at Mayo Clinic in Minnesota explained.
The most common cause is stroke or head injury -- and experts stress that while it can affect the production and comprehension of both speech and written words, it normally doesn't impact intelligence.
It affects some two million Americans, according to the National Aphasia Association, making it more common than Parkinson's Disease, cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy.
A 2016 survey carried out by the same group found that fewer than nine percent of people knew what was.
While it's normally caused by a specific one-time event such as stroke, "there are other possibilities, such as from a neurodegenerative disease," explained Brenda Rapp, a cognition scientist at Johns Hopkins University.
In such cases the damage is progressive and therapy focuses on preventing further loss of function.
Willis' family did not share the cause of his diagnosis in their statement.
- What are the different forms? -
The brain system governing language is a "very complex machine" that involves selecting the right words, moving the mouth appropriately to vocalize them, and on the other end hearing and decoding their meaning, said Rapp.
Everyone occasionally struggles to find the right word, "but you could imagine in aphasia, this happens a lot," she added.
Doctors sometimes split aphasia into broad clinical categories which correlate to where in the brain injury occurred.
In expressive aphasia, people "usually understand fairly well but have trouble getting words out," said speech pathologist Brooke Hatfield, of the American Speech Language Hearing Association (ASHA).
A person with this type of aphasia might use simple sentences like "want food" to be understood.
In receptive aphasia "the words come easily, but they might not be the right words. And it's difficult for that person to understand what they're hearing," added Hatfield.
- Speech therapy -
The good news, says Hatfield, is "everybody has a chance to get better" over the long term.
"There are people who had their stroke 30 years ago, who still work at their language and communication and they still make gains."
The brain is extremely plastic, and speech therapy can engage other parts of it to "bypass the roadblocks" of the damaged areas, and forge new connections, said Rapp.
Such therapy also trains people to talk around the subject if they get stuck on a specific word.
Family members can also develop strategies to make themselves better understood: "Things like shorter sentences, and making sure that you're talking to the person in full view instead of the other room, and minimizing background noise," said Botha.
Some people do well with assistive devices because their ability to write isn't affected in the same way.
Over the horizon, there are experimental treatments that combine electrical stimulation of the brain with speech therapy that have shown promise in recovering function, said Rapp.
- Bottom line -
All the experts emphasized patience. Aphasia can be frustrating and isolating, because "our relationships with others depend so much on being able to talk to them and communicate with them," said Rapp, leading to a person or their caregivers withdrawing.
"It's similar to all of a sudden waking up in a country where you don't speak the language," said Hatfield, rather a change in underlying cognitive abilities.
F.Wilson--AT