-
 Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
-
History beckons for Djokovic and Alcaraz in Australian Open final

-
 Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
-
Epstein offered ex-prince Andrew meeting with Russian woman: files

-
 Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
-
Montreal studio rises from dark basement office to 'Stranger Things'

-
 US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
-
Mertens and Zhang win Australian Open women's doubles title

-
 Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
-
China factory activity loses steam in January

-
 Melania Trump's atypical, divisive doc opens in theatres
Melania Trump's atypical, divisive doc opens in theatres
-
Bad Bunny set for historic one-two punch at Grammys, Super Bowl

-
 Five things to watch for on Grammys night Sunday
Five things to watch for on Grammys night Sunday
-
Venezuelan interim president proposes mass amnesty law

-
 Rose stretches lead at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes cut
Rose stretches lead at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes cut
-
Online foes Trump, Petro set for White House face-to-face

-
 Seattle Seahawks deny plans for post-Super Bowl sale
Seattle Seahawks deny plans for post-Super Bowl sale
-
US Senate passes deal expected to shorten shutdown

-
 'Misrepresent reality': AI-altered shooting image surfaces in US Senate
'Misrepresent reality': AI-altered shooting image surfaces in US Senate
-
Thousands rally in Minneapolis as immigration anger boils

-
 US judge blocks death penalty for alleged health CEO killer Mangione
US judge blocks death penalty for alleged health CEO killer Mangione
-
Lens win to reclaim top spot in Ligue 1 from PSG

-
 Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump Fed pick
Gold, silver prices tumble as investors soothed by Trump Fed pick
-
Ko, Woad share lead at LPGA season opener

-
 US Senate votes on funding deal - but shutdown still imminent
US Senate votes on funding deal - but shutdown still imminent
-
US charges prominent journalist after Minneapolis protest coverage

-
 Trump expects Iran to seek deal to avoid US strikes
Trump expects Iran to seek deal to avoid US strikes
-
US Justice Dept releases documents, images, videos from Epstein files

-
 Guterres warns UN risks 'imminent financial collapse'
Guterres warns UN risks 'imminent financial collapse'
-
NASA delays Moon mission over frigid weather

-
 First competitors settle into Milan's Olympic village
First competitors settle into Milan's Olympic village
-
Fela Kuti: first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award

-
 Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues oil ultimatum
Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues oil ultimatum
-
'Schitt's Creek' star Catherine O'Hara dead at 71

-
 Curran hat-trick seals 11 run DLS win for England over Sri Lanka
Curran hat-trick seals 11 run DLS win for England over Sri Lanka
-
Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues energy ultimatum

-
 France rescues over 6,000 UK-bound Channel migrants in 2025
France rescues over 6,000 UK-bound Channel migrants in 2025
-
Surprise appointment Riera named Frankfurt coach

-
 Maersk to take over Panama Canal port operations from HK firm
Maersk to take over Panama Canal port operations from HK firm
-
US arrests prominent journalist after Minneapolis protest coverage

-
 Analysts say Kevin Warsh a safe choice for US Fed chair
Analysts say Kevin Warsh a safe choice for US Fed chair
-
Trump predicts Iran will seek deal to avoid US strikes

-
 US oil giants say it's early days on potential Venezuela boom
US oil giants say it's early days on potential Venezuela boom
-
Fela Kuti to be first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award

-
 Trump says Iran wants deal, US 'armada' larger than in Venezuela raid
Trump says Iran wants deal, US 'armada' larger than in Venezuela raid
-
US Justice Dept releases new batch of documents, images, videos from Epstein files

-
 Four memorable showdowns between Alcaraz and Djokovic
Four memorable showdowns between Alcaraz and Djokovic
-
Russian figure skating prodigy Valieva set for comeback -- but not at Olympics

-
 Barcelona midfielder Lopez agrees contract extension
Barcelona midfielder Lopez agrees contract extension
-
Djokovic says 'keep writing me off' after beating Sinner in late-nighter


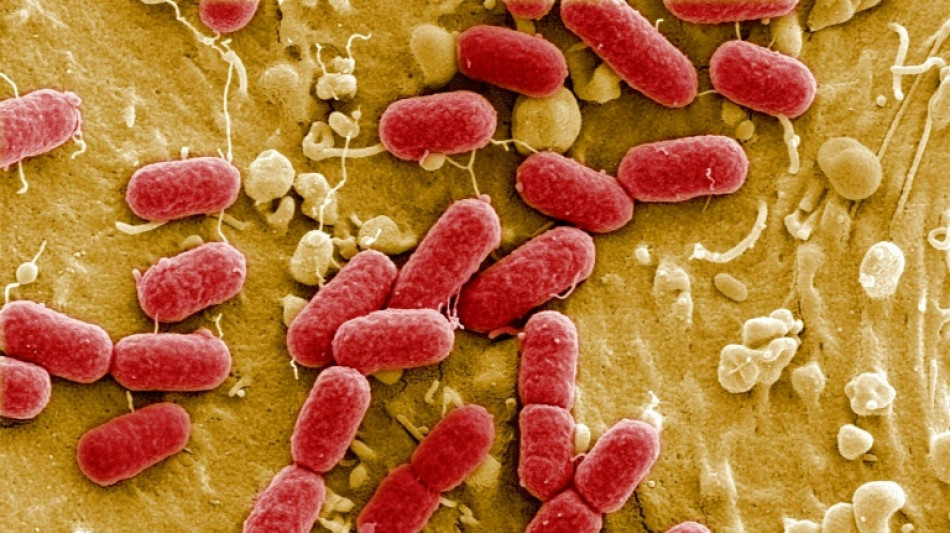
Harmful pollution boosting superbug 'silent pandemic'
Containing and cleaning up environmental pollution, especially in waterways, is crucial to controlling increasingly bullet-proof superbugs which could kill tens of millions by mid-century, a new UN report said Tuesday.
Superbugs -- strains of bacteria resistant to antibiotics -- are estimated to have killed 1.27 million people in 2019, and the World Health Organization says antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the top global health threats on the near-term horizon.
Up to 10 million deaths could occur every year by 2050 because of AMR, the UN says.
The disinfectants, antiseptics and antibiotics that can help microbes become stronger are everywhere, from toothpaste and shampoo to cow's milk and wastewater.
A new report Tuesday said pollution is a key driver in the "development, transmission and spread" of AMR, calling for urgent action to clean up the environment.
"With increasing pollution and lack of management of sources of pollution, combined with AMR in clinical and hospital settings and agriculture, risks are increasing," said the report from the UN Environment Programme.
Antimicrobial resistance is a natural phenomenon, but the overuse and misuse of antibiotics in humans, animals and plants has made the problem worse.
This means antibiotics may no longer work to fight the very infections they were designed to treat.
The UN report Tuesday said that pollution in the environment from key economic sectors has exacerbated the problem, namely from the pharmaceutical and chemical manufacturing sectors, along with agriculture and health care.
Herbicides to control weeds on farms may also increase AMR, while heavy metals are also contributing to the problem.
Once antimicrobials enter the environment they seep into the food chain -- they've been found in fish and cattle -- and loop back into factories making everyday toiletries, for example.
- 'Silent pandemic' -
Antimicrobial resistant genes are in waterways across the globe, from the Ganges River in India to the Cache la Poudre River in the US state of Colorado, the UN study found.
"This is a real issue, because rivers are often the source of our drinking water," Jonathan Cox, senior lecturer in microbiology at Britain's Aston University, told AFP.
"It's already the silent pandemic," warned Cox, who is not linked to the UN study. "It is becoming the next pandemic without us really recognising it."
Prevention is key, the UN said.
"Fuelled by population growth, urbanisation and growing demand for food and healthcare, we can expect an increase in the use of antimicrobials and in pollutant releases into the environment," it said.
The UN urged governments and international groups to address "key pollution sources", including sewage, city waste, healthcare delivery, pharmaceutical manufacturing and intensive crop sectors.
Cox said solutions need to be global, since AMR is so pervasive.
One answer is to focus on clinical approaches, such as improving rapid testing for infections so that antibiotics are not incorrectly prescribed.
Another is improving wastewater management to remove antimicrobials. But such processes are complicated and costly.
"The technology is out there, it just isn't being employed because governments don't care so much about the environment as they do about the bottom line," Cox said.
M.King--AT




