-
 Venezuelan activist ends '1,675 days' of suffering in prison
Venezuelan activist ends '1,675 days' of suffering in prison
-
Real Madrid scrape win over Rayo, Athletic claim derby draw

-
 PSG beat Strasbourg after Hakimi red to retake top spot in Ligue 1
PSG beat Strasbourg after Hakimi red to retake top spot in Ligue 1
-
NFL Cardinals hire Rams' assistant LaFleur as head coach

-
 Arsenal scoop $2m prize for winning FIFA Women's Champions Cup
Arsenal scoop $2m prize for winning FIFA Women's Champions Cup
-
Atletico agree deal to sign Lookman from Atalanta

-
 Real Madrid's Bellingham set for month out with hamstring injury
Real Madrid's Bellingham set for month out with hamstring injury
-
Man City won't surrender in title race: Guardiola

-
 Korda captures weather-shortened LPGA season opener
Korda captures weather-shortened LPGA season opener
-
Czechs rally to back president locking horns with government

-
 Prominent Venezuelan activist released after over four years in jail
Prominent Venezuelan activist released after over four years in jail
-
Emery riled by 'unfair' VAR call as Villa's title hopes fade

-
 Guirassy double helps Dortmund move six points behind Bayern
Guirassy double helps Dortmund move six points behind Bayern
-
Nigeria's president pays tribute to Fela Kuti after Grammys Award

-
 Inter eight clear after win at Cremonese marred by fans' flare flinging
Inter eight clear after win at Cremonese marred by fans' flare flinging
-
England underline World Cup
credentials with series win over Sri Lanka

-
 Guirassy brace helps Dortmund move six behind Bayern
Guirassy brace helps Dortmund move six behind Bayern
-
Man City held by Solanke stunner, Sesko delivers 'best feeling' for Man Utd

-
 'Send Help' debuts atop N.America box office
'Send Help' debuts atop N.America box office
-
Ukraine war talks delayed to Wednesday, says Zelensky

-
 Iguanas fall from trees in Florida as icy weather bites southern US
Iguanas fall from trees in Florida as icy weather bites southern US
-
Carrick revels in 'best feeling' after Man Utd leave it late

-
 Olympic chiefs admit 'still work to do' on main ice hockey venue
Olympic chiefs admit 'still work to do' on main ice hockey venue
-
Pope says Winter Olympics 'rekindle hope' for world peace

-
 Last-gasp Demirovic strike sends Stuttgart fourth
Last-gasp Demirovic strike sends Stuttgart fourth
-
Sesko strikes to rescue Man Utd, Villa beaten by Brentford

-
 'At least 200' feared dead in DR Congo landslide: government
'At least 200' feared dead in DR Congo landslide: government
-
Coventry says 'sad' about ICE, Wasserman 'distractions' before Olympics

-
 In-form Lyon make it 10 wins in a row
In-form Lyon make it 10 wins in a row
-
Man Utd strike late as Carrick extends perfect start in Fulham thriller

-
 Van der Poel romps to record eighth cyclo-cross world title
Van der Poel romps to record eighth cyclo-cross world title
-
Mbappe penalty earns Real Madrid late win over nine-man Rayo

-
 Resurgent Pakistan seal T20 sweep of Australia
Resurgent Pakistan seal T20 sweep of Australia
-
Fiji top sevens standings after comeback win in Singapore

-
 Alcaraz sweeps past Djokovic to win 'dream' Australian Open
Alcaraz sweeps past Djokovic to win 'dream' Australian Open
-
Death toll from Swiss New Year bar fire rises to 41

-
 Alcaraz says Nadal inspired him to 'special' Australian Open title
Alcaraz says Nadal inspired him to 'special' Australian Open title
-
Pakistan seeks out perpetrators after deadly separatist attacks

-
 Ukraine war talks delayed to Wednesday, Zelensky says
Ukraine war talks delayed to Wednesday, Zelensky says
-
Djokovic says 'been a great ride' after Melbourne final loss

-
 Von Allmen storms to downhill win in final Olympic tune-up
Von Allmen storms to downhill win in final Olympic tune-up
-
Carlos Alcaraz: tennis history-maker with shades of Federer

-
 Alcaraz sweeps past Djokovic to win maiden Australian Open title
Alcaraz sweeps past Djokovic to win maiden Australian Open title
-
Israel says partially reopening Gaza's Rafah crossing

-
 French IT giant Capgemini to sell US subsidiary after row over ICE links
French IT giant Capgemini to sell US subsidiary after row over ICE links
-
Iran's Khamenei likens protests to 'coup', warns of regional war

-
 New Epstein accuser claims sexual encounter with ex-prince Andrew: report
New Epstein accuser claims sexual encounter with ex-prince Andrew: report
-
Italy's extrovert Olympic icon Alberto Tomba insists he is 'shy guy'

-
 Chloe Kim goes for unprecedented snowboard halfpipe Olympic treble
Chloe Kim goes for unprecedented snowboard halfpipe Olympic treble
-
Pakistan combing for perpetrators after deadly separatist attacks


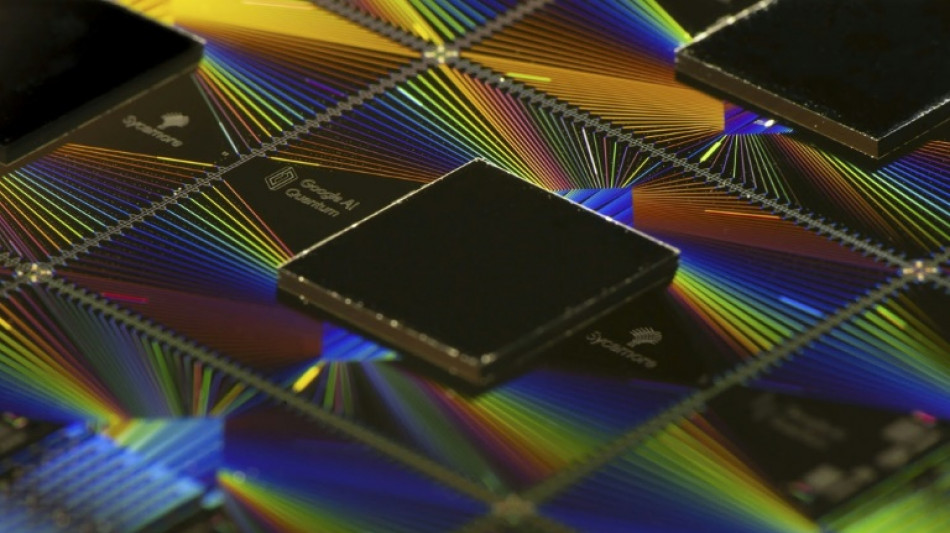
Observing quantum weirdness in our world: Nobel physics explained
The Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to three scientists on Tuesday for discovering that a bizarre barrier-defying phenomenon in the quantum realm could be observed on an electrical circuit in our classical world.
The discovery, which involved an effect called quantum tunnelling, laid the foundations for technology now being used by Google and IBM aiming to build the quantum computers of the future.
Here is what you need to know about the Nobel-winning work by John Clarke of the UK, Frenchman Michel Devoret and American John Martinis.
- What is the quantum world? -
In the classical or "macroscopic" world -- which includes everything you can see around you -- everything behaves according to the trustworthy rules of traditional physics.
But when things get extremely small, to around the scale of an atom, these laws no longer apply. That is when quantum mechanics takes over.
Just one oddity of the quantum world is called superposition, in which a particle can exist in multiple locations at once -- until it is observed, at least.
However scientists have struggled to directly observe quantum mechanics in this "microscopic" world -- which somewhat confusingly cannot be seen through a microscope.
- What is quantum tunnelling? -
Quantum tunnelling is a strange effect that physicists first theorised almost a century ago.
Imagine a man trying to climb a mountain, Eleanor Crane, a quantum physicist at King's College London, told AFP.
In the classical world, if the climber is too tired he will not make it to the other side.
But if a particle is weak in the quantum world, there is still a "a probability of finding it on the other side of the mountain," Crane said.
Because the particle is in superposition, it could have been on both sides of the mountain simultaneously. But if you then, for example, took a picture of the particle, it would then have to pick a side.
- What did the Nobel-winners do? -
In the mid-1980s, Clarke, Devoret and Martinis built a very small -- but not quantum-level -- electrical circuit.
They set it up with two superconductors, which are cooled to almost the lowest possible temperature so they have no electrical resistance.
They then separated the two superconductors with a thin layer of material.
This would break a normal electrical circuit, but thanks to quantum tunnelling, some electrons could appear on the other side.
- Why is that important? -
French physicist Alain Aspect, a 2022 physics Nobel laureate, told AFP that an outstanding question in the field had been whether an object in our macroscopic world could "behave in a quantum way".
By illustrating quantum effects on this "somewhat large object -- though not large on our scale", the new Nobel laureates answered that question with a resounding yes, Aspect said.
Scientists could now observe this quantum effect using a normal microscope, offering a new view of this weird world.
- What about quantum computing? -
The discovery's biggest technological legacy may be that it laid the groundwork for the development of superconducting quantum bits.
While classical computers have bits that work in ones and zeros, quantum bits, or qubits, can exist in two states at once.
This gives them massive potential to spark a range of breakthrough -- though they have yet to fully live up to the hype.
Crane estimated that quantum computers could be powerful enough to "change the course of society" in the next five to 10 years.
The new Nobel laureates "set the foundation for a lot of technology that many companies are investing millions of dollars in right now to try to realise large-scale quantum computers that can actually solve certain types of problems much faster than our classical alternatives," physicist Gregory Quiroz at Johns Hopkins University told AFP.
However there are several other leading techniques in the race to build to build a quantum computer, including neutral atoms and ion traps.
The Nobel-winning work also contributed to "extremely sensitive methods of measuring electromagnetic fields and magnetic fields that rely on these kinds of circuits," Aspect added.
R.Garcia--AT



