
-
 Spotify says piracy activists hacked its music catalogue
Spotify says piracy activists hacked its music catalogue
-
Winter Olympics organisers resolve snow problem at ski site

-
 Fuming Denmark summons US ambassador over Greenland envoy
Fuming Denmark summons US ambassador over Greenland envoy
-
UK's street artist Banksy unveils latest mural in London

-
 Rugby players lose order challenge in brain injury claim
Rugby players lose order challenge in brain injury claim
-
UK singer Chris Rea dies at 74, days before Christmas

-
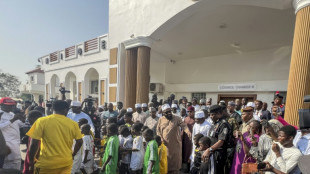 Last of kidnapped Nigerian pupils handed over, government says
Last of kidnapped Nigerian pupils handed over, government says
-
Zambia strike late to hold Mali in AFCON opener

-
 Outcry follows CBS pulling program on prison key to Trump deportations
Outcry follows CBS pulling program on prison key to Trump deportations
-
Sri Lanka cyclone caused $4.1 bn damage: World Bank

-
 Billionaire Ellison offers personal guarantee for son's bid for Warner Bros
Billionaire Ellison offers personal guarantee for son's bid for Warner Bros
-
Tech stocks lead Wall Street higher, gold hits fresh record

-
 Telefonica to shed around 5,500 jobs in Spain
Telefonica to shed around 5,500 jobs in Spain
-
Cambodia says Thailand launches air strikes after ASEAN meet on border clashes

-
 McCullum wants to stay as England coach despite Ashes drubbing
McCullum wants to stay as England coach despite Ashes drubbing
-
EU slams China dairy duties as 'unjustified'

-
 Italy fines Apple nearly 100 mn euros over app privacy feature
Italy fines Apple nearly 100 mn euros over app privacy feature
-
America's Cup switches to two-year cycle

-
 Jesus could start for Arsenal in League Cup, says Arteta
Jesus could start for Arsenal in League Cup, says Arteta
-
EU to probe Czech aid for two nuclear units

-
 Strauss says sacking Stokes and McCullum will not solve England's Ashes woes
Strauss says sacking Stokes and McCullum will not solve England's Ashes woes
-
Clashing Cambodia, Thailand agree to border talks after ASEAN meet

-
 Noel takes narrow lead after Alta Badia slalom first run
Noel takes narrow lead after Alta Badia slalom first run
-
Stocks diverge as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease

-
 Man City players face Christmas weigh-in as Guardiola issues 'fatty' warning
Man City players face Christmas weigh-in as Guardiola issues 'fatty' warning
-
German Christmas markets hit by flood of fake news

-
 Liverpool fear Isak has broken leg: reports
Liverpool fear Isak has broken leg: reports
-
West Indies captain says he 'let the team down' in New Zealand Tests

-
 Thailand says Cambodia agrees to border talks after ASEAN meet
Thailand says Cambodia agrees to border talks after ASEAN meet
-
Alleged Bondi shooters conducted 'tactical' training in countryside, Australian police say

-
 Swiss court to hear landmark climate case against cement giant
Swiss court to hear landmark climate case against cement giant
-
Steelers beat Lions in 'chaos' as three NFL teams book playoffs

-
 Knicks' Brunson scores 47, Bulls edge Hawks epic
Knicks' Brunson scores 47, Bulls edge Hawks epic
-
Global nuclear arms control under pressure in 2026

-
 Five-wicket Duffy prompts West Indies collapse as NZ win series 2-0
Five-wicket Duffy prompts West Indies collapse as NZ win series 2-0
-
Asian markets rally with Wall St as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease

-
 Jailed Malaysian ex-PM Najib loses bid for house arrest
Jailed Malaysian ex-PM Najib loses bid for house arrest
-
Banned film exposes Hong Kong's censorship trend, director says

-
 Duffy, Patel force West Indies collapse as NZ close in on Test series win
Duffy, Patel force West Indies collapse as NZ close in on Test series win
-
Australian state pushes tough gun laws, 'terror symbols' ban after shooting

-
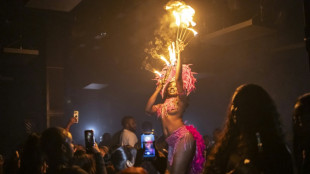 A night out on the town during Nigeria's 'Detty December'
A night out on the town during Nigeria's 'Detty December'
-
US in 'pursuit' of third oil tanker in Caribbean: official

-
 CO2 soon to be buried under North Sea oil platform
CO2 soon to be buried under North Sea oil platform
-
Steelers edge Lions as Bears, 49ers reach playoffs

-
 India's Bollywood counts costs as star fees squeeze profits
India's Bollywood counts costs as star fees squeeze profits
-
McCullum admits errors in Ashes preparations as England look to salvage pride

-
 Pets, pedis and peppermints: When the diva is a donkey
Pets, pedis and peppermints: When the diva is a donkey
-
'A den of bandits': Rwanda closes thousands of evangelical churches

-
 Southeast Asia bloc meets to press Thailand, Cambodia on truce
Southeast Asia bloc meets to press Thailand, Cambodia on truce
-
As US battles China on AI, some companies choose Chinese


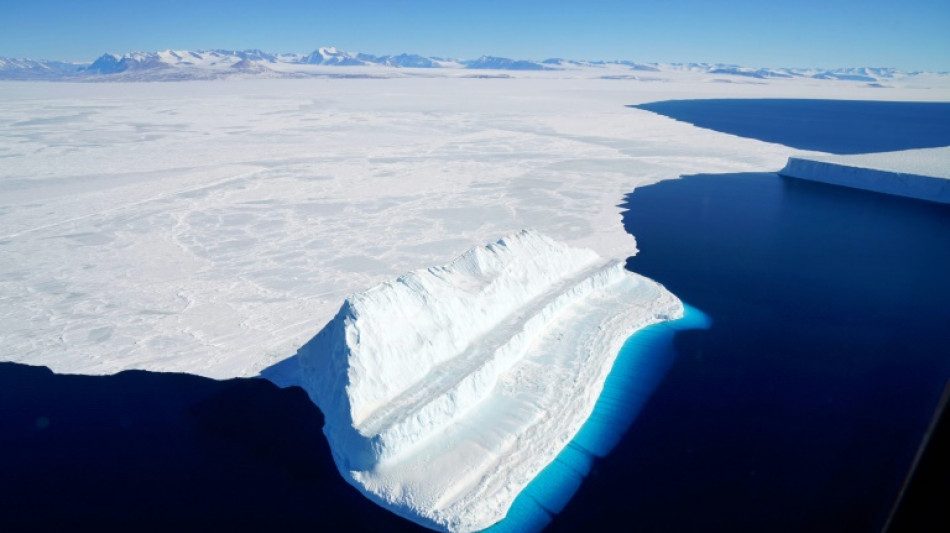
How did life survive 'Snowball Earth'? In ponds, study suggests
Earth has not always been so hospitable to live. During several ice ages, the planet's surface was almost completely frozen over, creating what has been dubbed "Snowball Earth".
Liquid water appears to be the most important ingredient for life on any planet, raising the question: how did anything survive such frosty, brutal times?
A group of scientists said Thursday that they had found an astonishing diversity of micro-organisms in tiny pools of melted ice in Antarctica, suggesting that life could have ridden out Snowball Earth in similar ponds.
During the Cryogenian Period between 635 and 720 million years ago, the average global temperature did not rise above -50 degrees Celsius (-58 Fahrenheit). The climate near the equator at the time resembled modern-day Antarctica.
Yet even in such extreme conditions, life found a way to keep evolving.
Fatima Husain, the lead author of a new study published in Nature Communications, told AFP there was evidence of complex life forms "before and after the Cryogenian in the fossil record".
"There are multiple hypotheses regarding possible places life may have persisted," said Husain, a graduate student at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Perhaps it found shelter in patches of open ocean, or in deep-sea hydrothermal vents, or under vast sheets of ice.
The tiny melted ice pools that dotted the equator were another proposed refuge.
These ponds could have been oases for eukaryotes, complex organisms that eventually evolved into multicellular life forms that would rise to dominate Earth, including humans.
- Could aliens be hiding in ponds? -
Melted ice ponds still exist today in Antarctica, at the edges of ice sheets.
In 2018, members of a New Zealand research team visited the McMurdo ice shelf in east Antarctica, home to several such pools, which are only a few metres wide and less a metre deep.
The bottom of the ponds are lined with a mat of microbes that have accumulated over the years to form slimy layers.
"These mats can be a few centimetres thick, colourful, and they can be very clearly layered," Husain said.
They are made up of single-celled organisms called cyanobacteria that are known to be able to survive extreme conditions.
But the researchers also found signs indicating there were eukaryotes such as algae or microscopic animals.
This suggests there was surprising diversity in the ponds, which appears to have been influenced by the amount of salt each contained.
"No two ponds were alike," Husain said. "We found diverse assemblages of eukaryotes from all the major groups in all the ponds studied."
"They demonstrate that these unique environments are capable of sheltering diverse assemblages of life, even in close proximity," she added.
This could have implications in the search for extraterrestrial life.
"Studies of life within these special environments on Earth can help inform our understanding of potential habitable environments on icy worlds, including icy moons in our Solar System," Husain said.
Saturn's moon Enceladus and Jupiter's Europa are covered in ice, but scientists increasingly suspect they could be home to simple forms of life, and several space missions have been launched to find out more about them.
E.Rodriguez--AT




