-
 La Rochelle suffer defeat after shock Atonio retirement
La Rochelle suffer defeat after shock Atonio retirement
-
'It wasn't working': Canada province ends drug decriminalization

-
 Kishan, Arshdeep star as India down New Zealand in T20 finale
Kishan, Arshdeep star as India down New Zealand in T20 finale
-
Moreno bags brace but Villarreal held at Osasuna

-
 Kramaric keeps in-form Hoffenheim rolling in Bundesliga
Kramaric keeps in-form Hoffenheim rolling in Bundesliga
-
'Skimo': Adrenalin-packed sprint to make Olympic debut

-
 Venezuela's 'Helicoide' prison synonymous with torture of dissenters
Venezuela's 'Helicoide' prison synonymous with torture of dissenters
-
Arsenal thrash Leeds to stretch Premier League advantage

-
 Russia's Valieva returns to ice after doping ban
Russia's Valieva returns to ice after doping ban
-
Snow storm barrels into southern US as blast of icy weather widens

-
 Ukraine sees mass power outages from 'technical malfunction'
Ukraine sees mass power outages from 'technical malfunction'
-
Gaza civil defence says Israeli strikes kill 32

-
 Kirsty Coventry set to give clues to her Olympic vision in Milan
Kirsty Coventry set to give clues to her Olympic vision in Milan
-
I'm no angel, Italy's PM says amid church fresco row

-
 Thousands join Danish war vets' silent march after Trump 'insult'
Thousands join Danish war vets' silent march after Trump 'insult'
-
Gaza civil defence says Israeli strikes kill 28

-
 Pakistan spin out Australia in second T20I to take series
Pakistan spin out Australia in second T20I to take series
-
Melbourne champion Rybakina never doubted return to Wimbledon form

-
 Luis Enrique welcomes Ligue 1 challenge from Lens
Luis Enrique welcomes Ligue 1 challenge from Lens
-
Long truck lines at Colombia-Ecuador border as tariffs loom

-
 Ex-prince Andrew dogged again by Epstein scandal
Ex-prince Andrew dogged again by Epstein scandal
-
Separatist attacks in Pakistan kill 21, dozens of militants dead

-
 'Malfunction' cuts power in Ukraine. Here's what we know
'Malfunction' cuts power in Ukraine. Here's what we know
-
Arbeloa backs five Real Madrid stars he 'always' wants playing

-
 Sabalenka 'really upset' at blowing chances in Melbourne final loss
Sabalenka 'really upset' at blowing chances in Melbourne final loss
-
Britain, Japan agree to deepen defence and security cooperation

-
 Rybakina keeps her cool to beat Sabalenka in tense Melbourne final
Rybakina keeps her cool to beat Sabalenka in tense Melbourne final
-
France tightens infant formula rules after toxin scare

-
 Blanc wins final women's race before Winter Olympics
Blanc wins final women's race before Winter Olympics
-
Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's Moscow-born Melbourne champion

-
 Ice-cool Rybakina beats Sabalenka in tense Australian Open final
Ice-cool Rybakina beats Sabalenka in tense Australian Open final
-
Pakistan attacks kill 15, dozens of militants dead: official

-
 Ten security officials, 37 militants killed in SW Pakistan attacks: official
Ten security officials, 37 militants killed in SW Pakistan attacks: official
-
Epstein survivors say abusers 'remain hidden' after latest files release

-
 'Full respect' for Djokovic but Nadal tips Alcaraz for Melbourne title
'Full respect' for Djokovic but Nadal tips Alcaraz for Melbourne title
-
Wollaston goes back-to-back in the Cadel Evans road race

-
 Women in ties return as feminism faces pushback
Women in ties return as feminism faces pushback
-
Ship ahoy! Prague's homeless find safe haven on river boat

-
 Britain's Starmer ends China trip aimed at reset despite Trump warning
Britain's Starmer ends China trip aimed at reset despite Trump warning
-
Carlos Alcaraz: rare tennis talent with shades of Federer

-
 Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
Novak Djokovic: divisive tennis great on brink of history
-
History beckons for Djokovic and Alcaraz in Australian Open final

-
 Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
Harrison, Skupski win Australian Open men's doubles title
-
Epstein offered ex-prince Andrew meeting with Russian woman: files

-
 Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
Jokic scores 31 to propel Nuggets over Clippers in injury return
-
Montreal studio rises from dark basement office to 'Stranger Things'

-
 US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
US government shuts down but quick resolution expected
-
Mertens and Zhang win Australian Open women's doubles title

-
 Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
Venezuelan interim president announces mass amnesty push
-
China factory activity loses steam in January


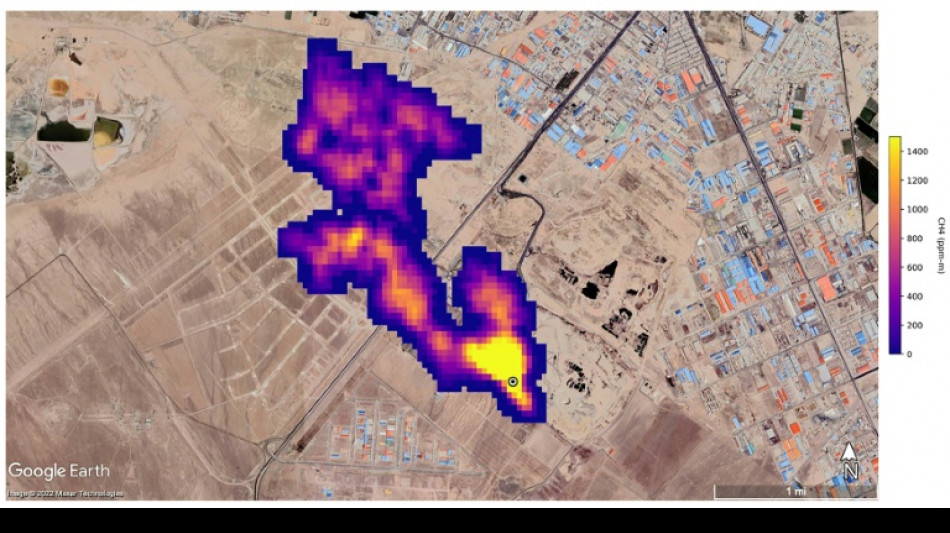
New NASA tool helps detect 'super-emitters' of methane from space
NASA scientists, using a tool designed to study how dust affects climate, have identified more than 50 spots around the world emitting major levels of methane, a development that could help combat the potent greenhouse gas.
"Reining in methane emissions is key to limiting global warming," NASA Administrator Bill Nelson said in a press release on Tuesday.
"This exciting new development will not only help researchers better pinpoint where methane leaks are coming from, but also provide insight on how they can be addressed -- quickly."
NASA said its Earth Surface Mineral Dust Source Investigation (EMIT) is designed to foster understanding of the effects of airborne dust on climate.
But EMIT, which was installed on the International Space Station in July and can focus on areas as small as a soccer field, has also shown the ability to detect the presence of methane.
NASA said more than 50 "super-emitters" of methane gas in Central Asia, the Middle East, and the southwestern United States have been identified so far. Most of them are connected to the fossil-fuel, waste or agriculture sectors.
Kate Calvin, NASA's chief scientist and senior climate advisor, said EMIT's "additional methane-detecting capability offers a remarkable opportunity to measure and monitor greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change."
- 'Exceeds our expectations' -
Methane is responsible for roughly 30 percent of the global rise in temperatures to date.
While far less abundant in the atmosphere than CO2, it is about 28 times more powerful as a greenhouse gas on a century-long timescale. Over a 20-year time frame, it is 80 times more potent.
Methane lingers in the atmosphere for only a decade, compared to hundreds or thousands of years for CO2.
This means a sharp reduction in emissions could shave several tenths of a degree Celsius off of projected global warming by mid-century, helping keep alive the Paris Agreement goal of capping Earth's average temperature increase to 1.5C, according to the UN Environment Programme (UNEP).
"EMIT will potentially find hundreds of super-emitters – some of them previously spotted through air-, space-, or ground-based measurement, and others that were unknown," NASA said.
Andrew Thorpe, a research technologist at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory leading the EMIT methane effort, said some of the methane plumes detected by EMIT are among the largest ever seen.
"What we've found in a just a short time already exceeds our expectations," Thorpe said.
NASA said a methane plume about two miles (3.3 kilometers) long was detected southeast of Carlsbad, New Mexico, in the Permian Basin, one of the largest oilfields in the world.
It said 12 plumes from oil and gas infrastructure were identified in Turkmenistan, east of the Caspian Sea port city of Hazar.
A methane plume at least three miles (4.8 kilometers) long was detected south of Tehran from a major waste-processing complex, NASA said.
D.Johnson--AT




